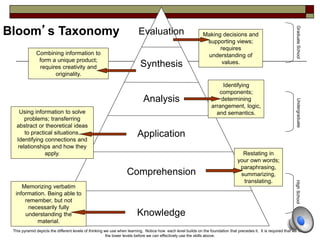
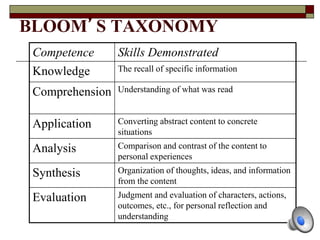
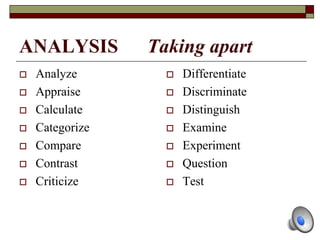
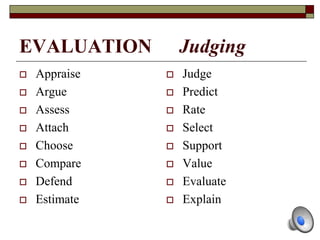
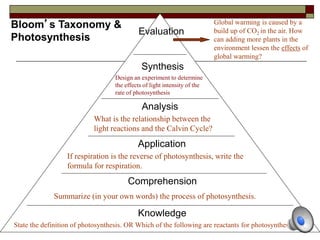
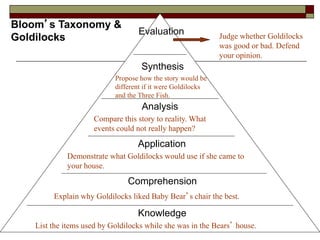
The document provides information about Bloom's Taxonomy, which categorizes different levels of thinking and learning. It presents the six levels from lowest to highest order: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation. For each level, it gives examples of related cognitive processes and thinking skills as well as sample verbs that could be used to frame learning objectives or assessment questions targeting that level. It also provides examples applying Bloom's Taxonomy to analyze thinking levels required by tasks and questions related to common stories.