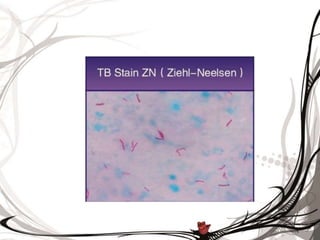
A sputum culture test identifies bacteria and fungi affecting the lungs, with specific organisms listed for both gram-positive and gram-negative categories. The document outlines collection, examination procedures, and staining techniques needed for accurate diagnosis, emphasizing the importance of timely sample delivery to the laboratory. Additionally, methods for reducing commensal organisms and culturing techniques on various agar types are described to ensure pure cultures of respiratory pathogens.