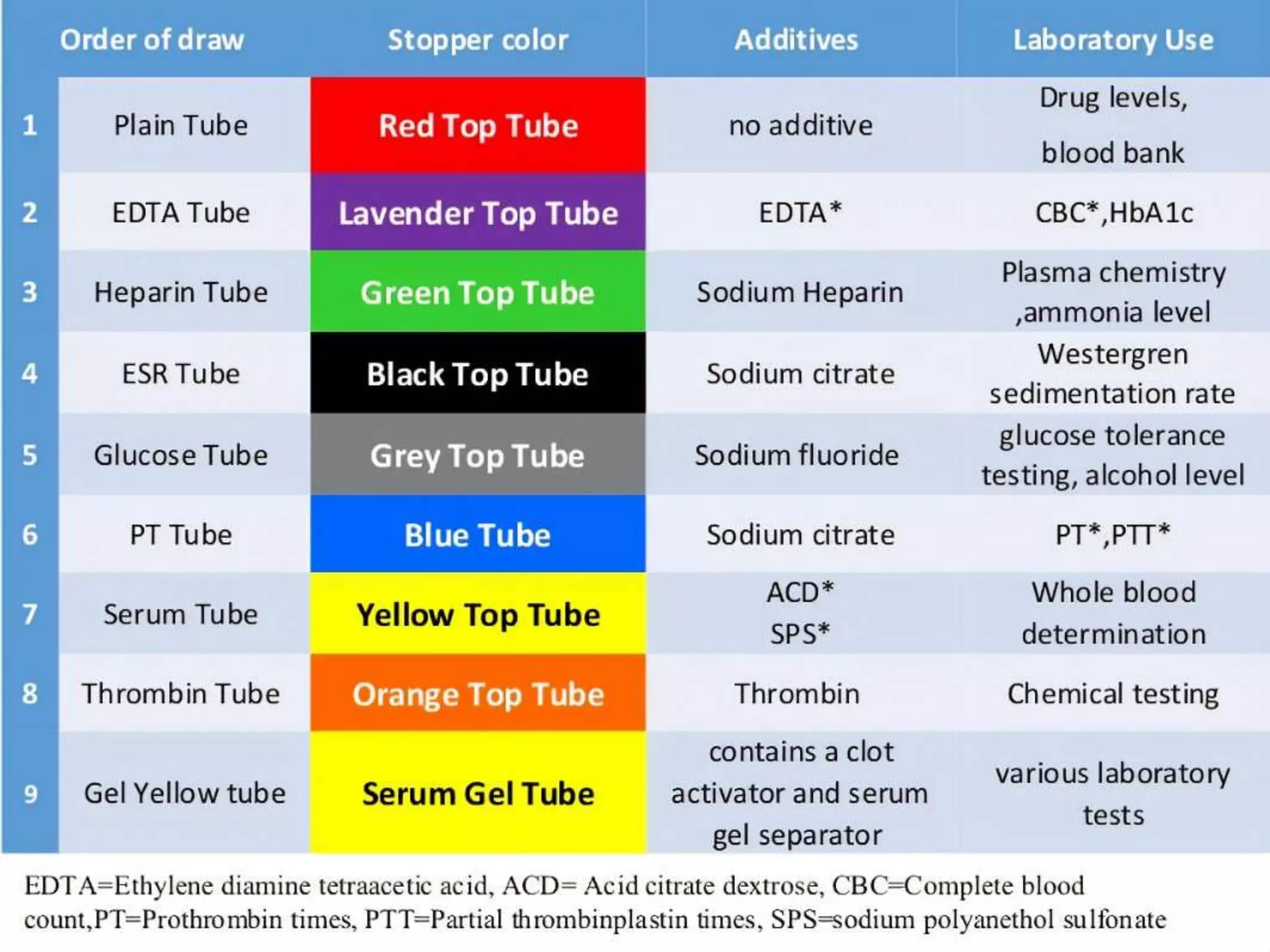
This document discusses the common types of blood collection test tubes used in hospitals. It explains that red top tubes contain silica clot activators and are used for serum tests like cholesterol and liver enzymes. Purple top tubes contain anticoagulants and are used for blood and fluid cultures. Blue top tubes contain sodium citrate to prevent clotting and are used for coagulation tests. Green top tubes contain heparin and are used for chemistry tests. Lavender top tubes contain EDTA and are used for hematology tests. Gray top tubes contain sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate to prevent glucose breakdown and are used for chemistry tests like glucose. The document stresses that the proper test tube must be chosen according to the diagnostic