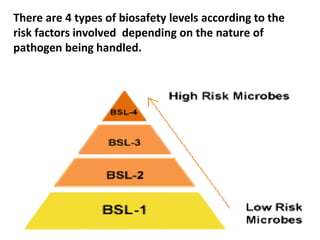
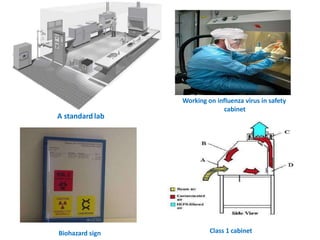
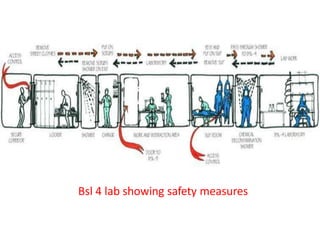
This document outlines the four biosafety levels (BSL 1-4) according to the risk posed by pathogens. BSL1 is for low risk agents and requires basic precautions like gloves and disinfection. BSL2 is for agents that cause human disease but effective treatment exists; it requires biosafety cabinets, restricted access, and medical evaluation for accidents. BSL3 is for indigenous or exotic agents that may cause serious disease; it has enhanced containment like vertical laminar hoods, strict access control, and decontamination of wastes. BSL4 is the highest level, for dangerous exotic agents with no treatment, and requires a completely sealed cabinet, positive pressure personnel suits, showers, and specialized waste