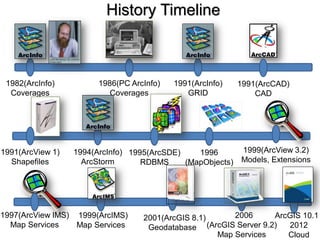
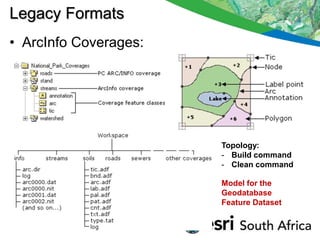
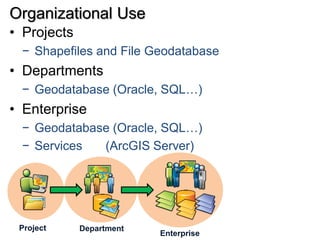
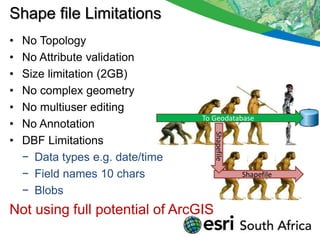
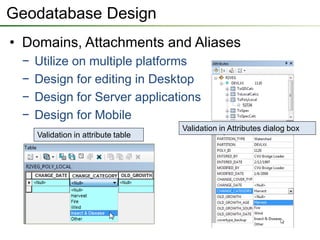
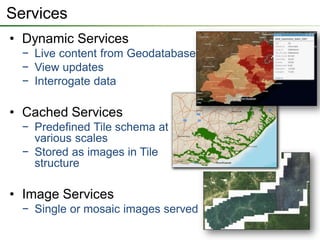
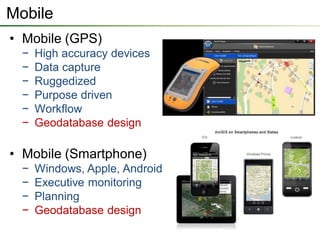
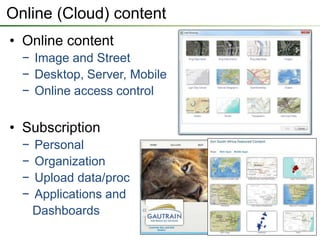
The seminar outlines the evolution of ESRI data formats, covering legacy formats like ArcInfo and shapefiles, current formats such as geodatabases, and future trends in data handling and service delivery. The discussion emphasizes the advantages and limitations of various formats, including the enhancements offered by geodatabases for multi-user editing and spatial data management. Additionally, it highlights the impact of mobile and cloud technologies on data access and usage in organizational and societal contexts.