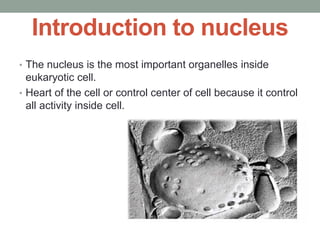
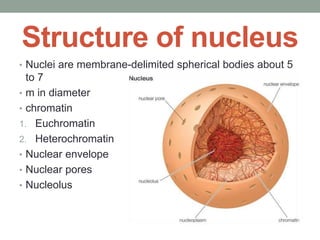
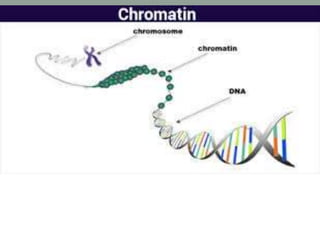
The document provides an overview of the eukaryotic nucleus, highlighting its importance as the control center of the cell, its discovery by Robert Brown in 1831, and its key structural components including chromatin, the nuclear envelope, nuclear pores, and the nucleolus. Chromatin exists in forms such as euchromatin and heterochromatin, while the nuclear envelope is characterized by its dual membranes and association with the endoplasmic reticulum. The nucleolus, vital for ribosome synthesis, is a non-membrane-bound organelle that forms around the nucleolar organizer after cell division.