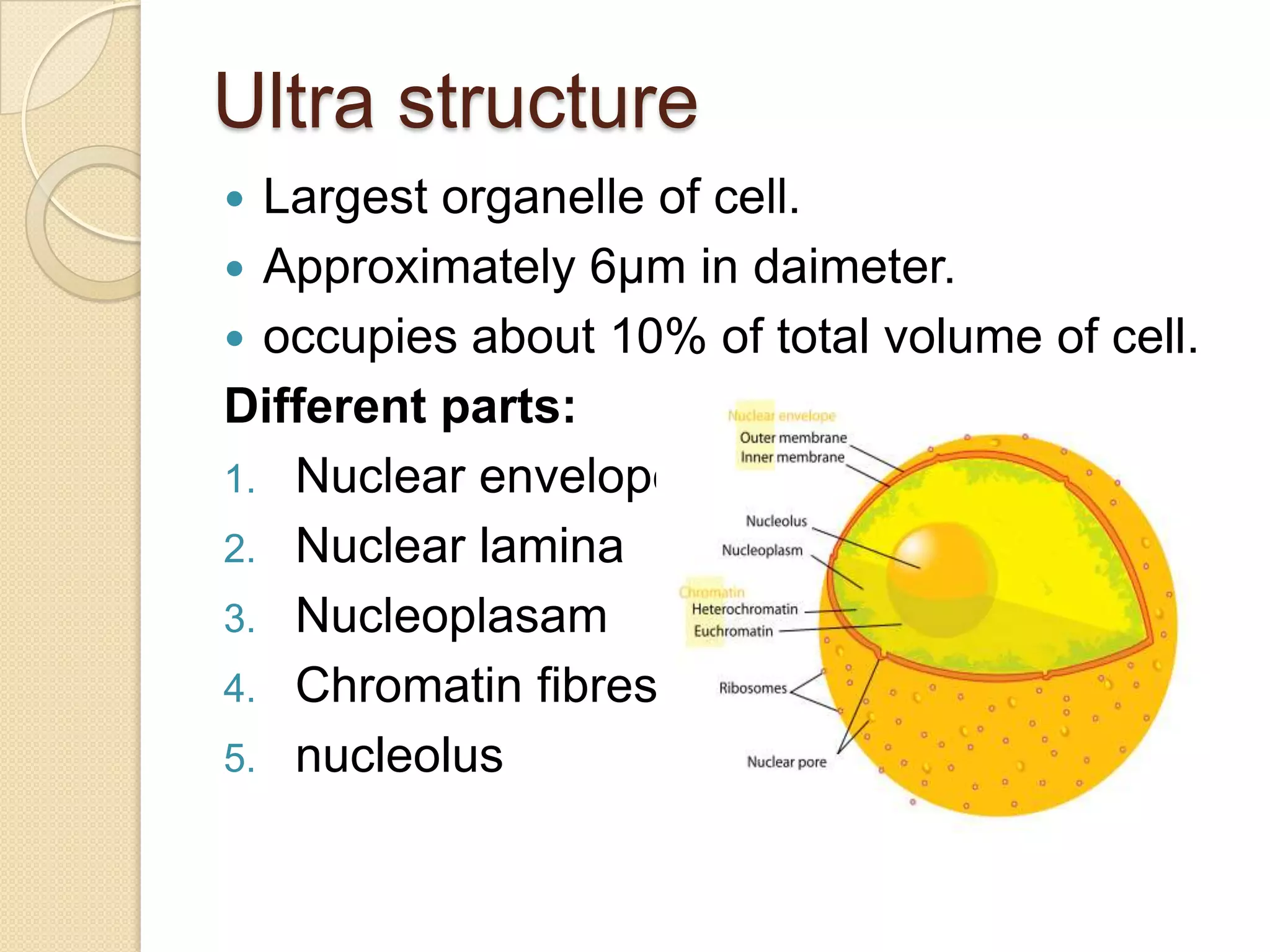
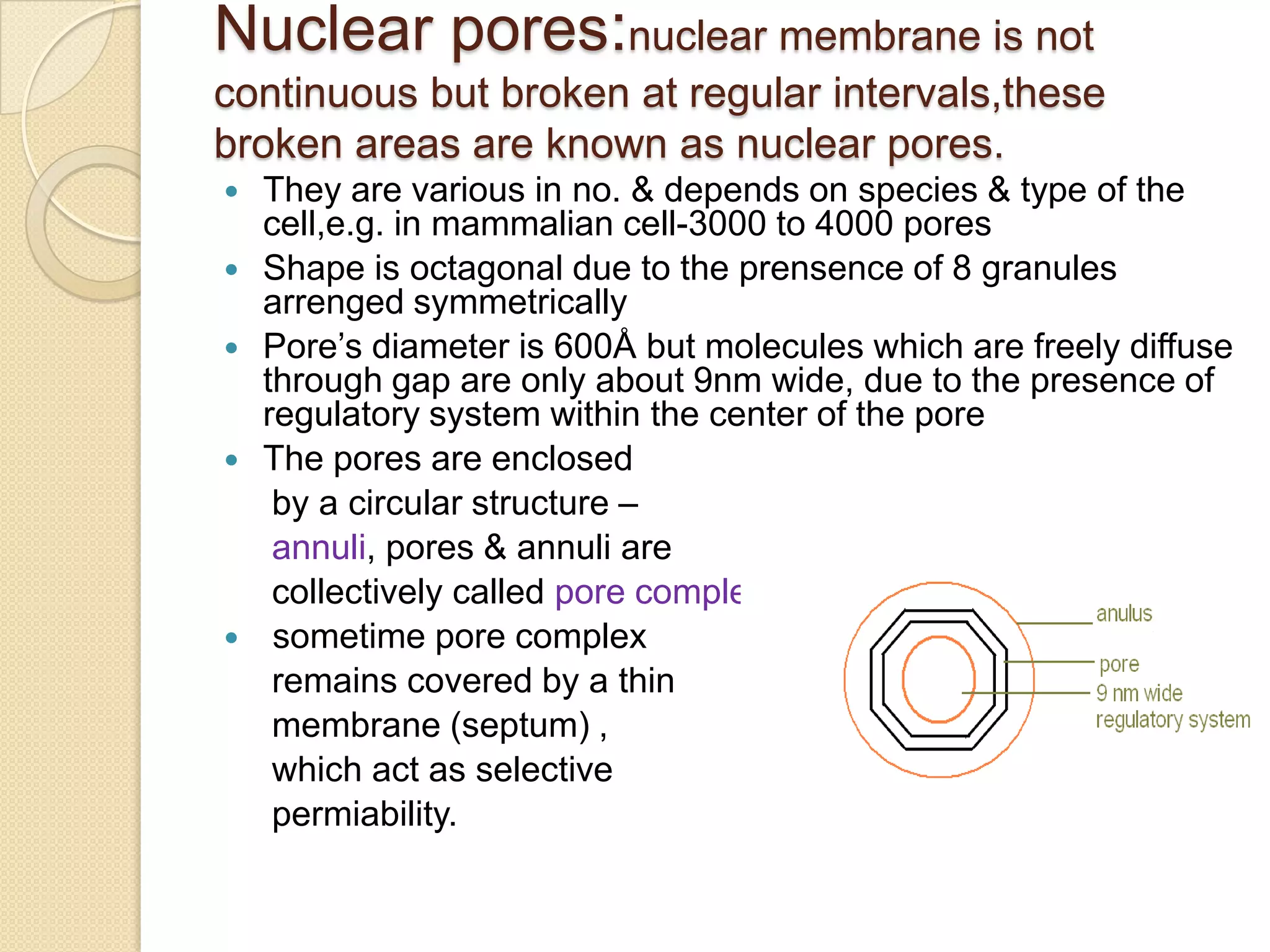
The nucleus is the control center of the cell that contains DNA and controls its metabolic and hereditary activities. It is enclosed by a double nuclear membrane with nuclear pores that regulate transport. Inside the nucleus is nucleoplasm containing chromatin fibers that coil to form chromosomes during cell division. The nucleolus forms within the nucleus and is responsible for synthesizing ribosomes. The nucleus varies in shape, size, and number depending on the cell but is typically a single, spherical organelle located in the cell's center.
![HISTORY1831:Robert Brown [while he was studing orchid’s outer layer,he observed an opaque area which he called Nucleus] 1838:Mittehias Schleiden [proposed that the nucleus plays a role in generating cells,introduced name Cytoblast(cell builder)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleus-100810141247-phpapp01/75/Nucleus-3-2048.jpg)