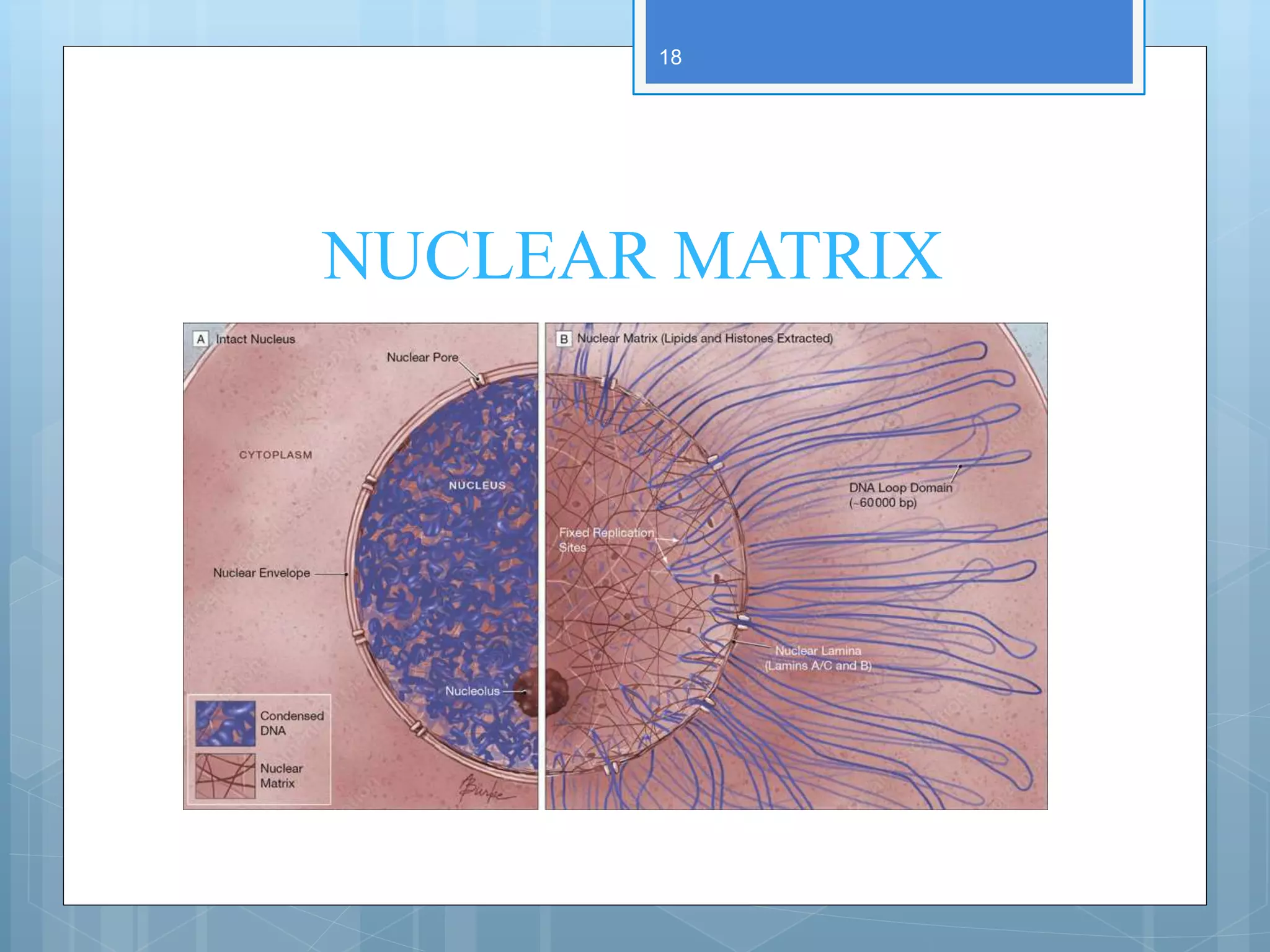
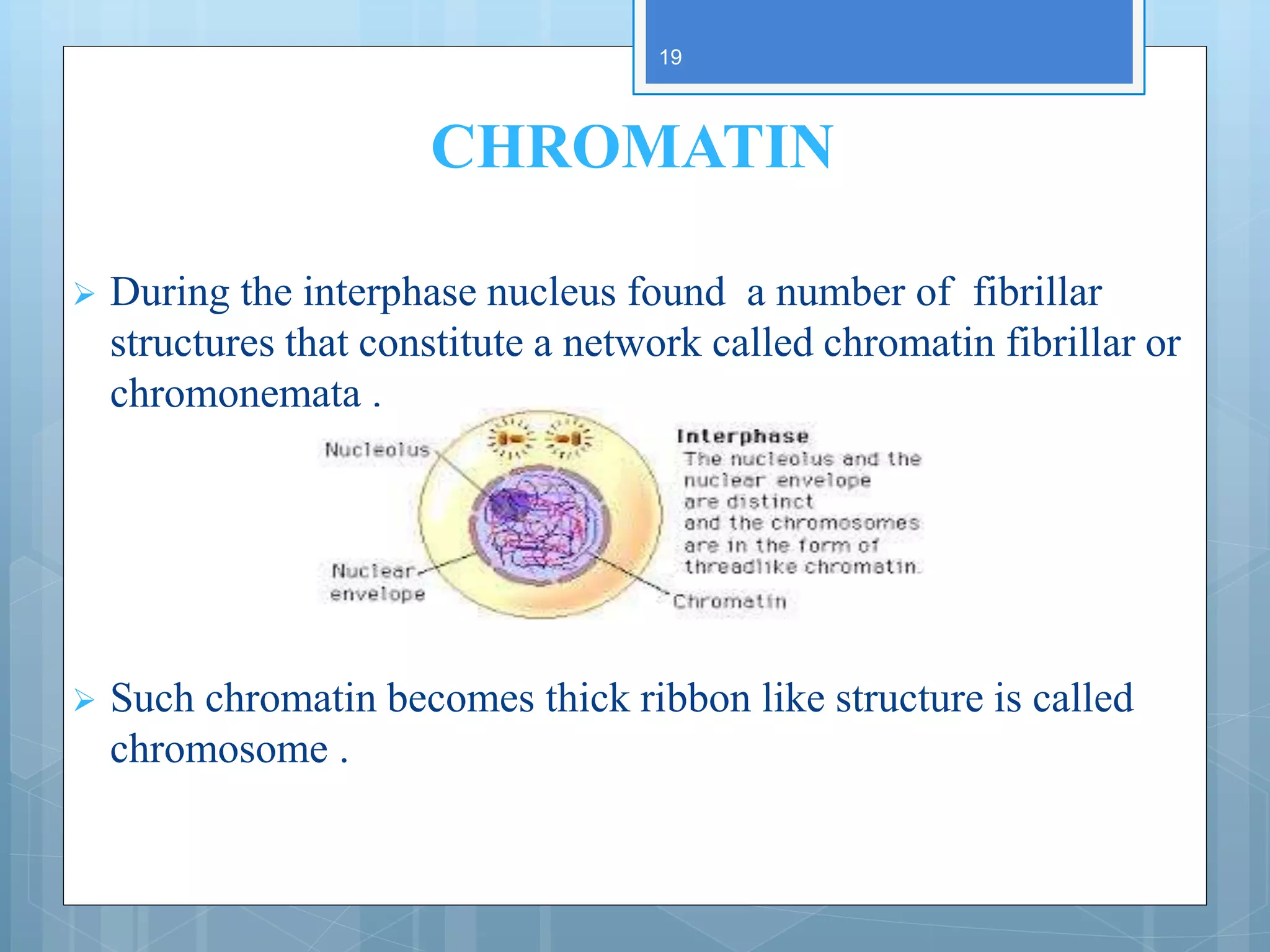
The document provides information about the nucleus and its components. It discusses that the nucleus is a prominent organelle found in eukaryotic cells that controls cellular activity. It describes the various structures of the nucleus including the nuclear envelope, nucleolus, chromatin, and nuclear pores. The nuclear envelope forms the boundary of the nucleus and contains nuclear pores that regulate transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Chromatin and the nucleolus are also described along with their roles in packaging DNA and synthesizing RNA, respectively.