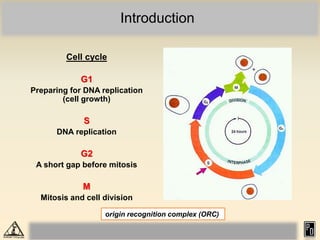
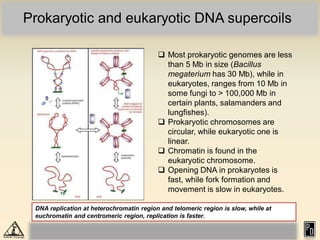
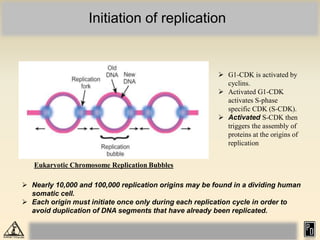
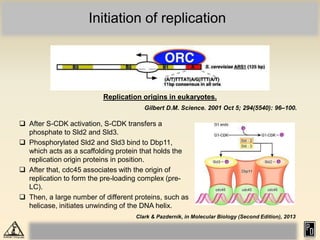
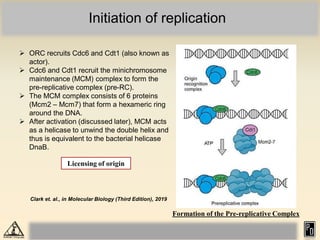
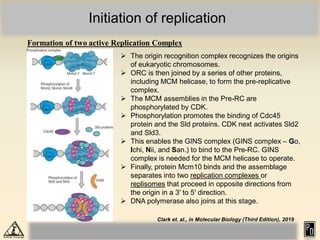
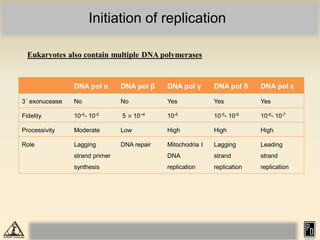
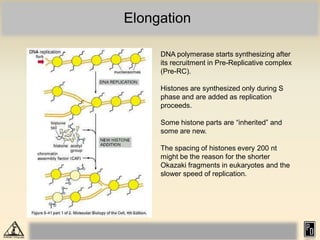
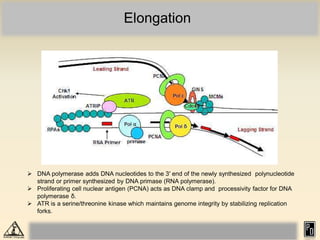
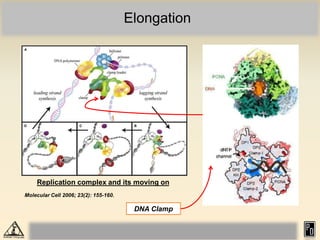
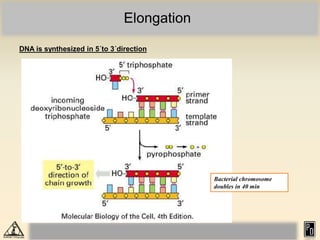
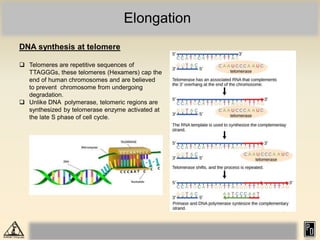
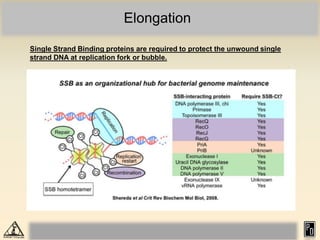
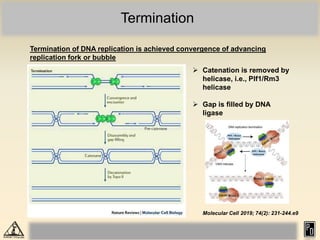
DNA replication in eukaryotes is more complex than prokaryotes due to eukaryotic DNA being condensed into nucleosomes. Replication occurs during S phase of the cell cycle and is bidirectional. The process involves unwinding of DNA and formation of a pre-replication complex, including ORC and MCM proteins. This licenses the origin for replication initiation. Elongation then occurs via DNA polymerases synthesizing new DNA strands in 5' to 3' direction. Termination occurs when replication forks converge and the newly synthesized DNA is ligated.