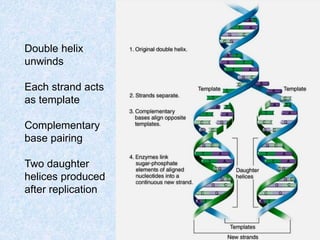
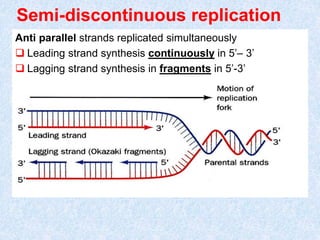
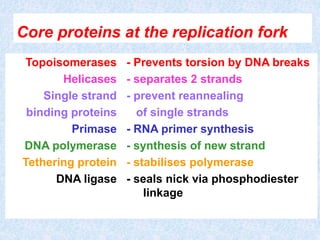
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. It involves unwinding the DNA double helix and using each strand as a template to synthesize a new complementary strand. Replication is semi-conservative, meaning each new DNA molecule contains one old and one new strand. It initiates at origins of replication and proceeds bidirectionally. The leading strand is synthesized continuously while the lagging strand is synthesized in fragments. Core replication proteins include helicases, primase, DNA polymerase, topoisomerases, and ligase.