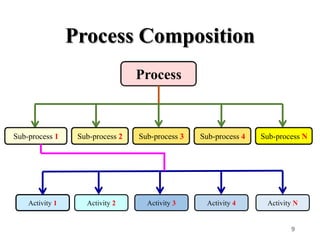
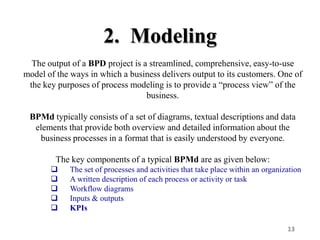
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach aimed at enhancing an organization's workflow to be effective, efficient, and responsive to change, focusing on reducing errors and linking processes to corporate strategies. Key components include Business Process Models (BPMDs), software tools for process mapping, and methodologies such as Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) for ongoing improvements. Benefits of BPM include improved process quality, operational efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and better resource optimization.