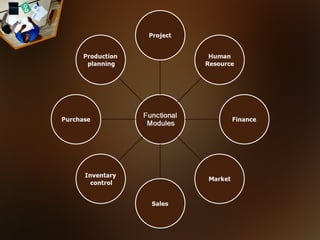
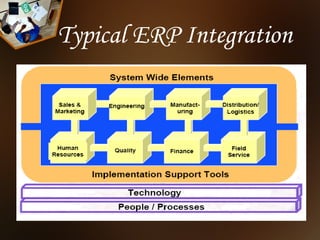
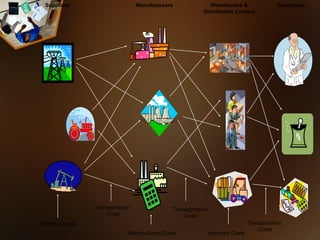
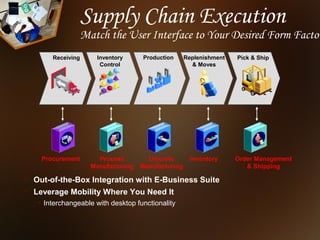
ERP systems integrate various business modules and processes through a common database. Key ERP modules include production planning, purchasing, inventory control, sales, marketing, finance, and human resources. ERP aims to optimize business operations by allowing different departments to share information and collaborate more efficiently.