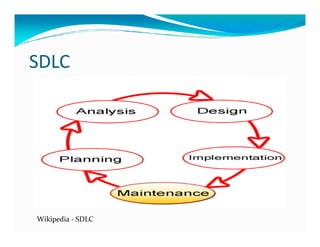
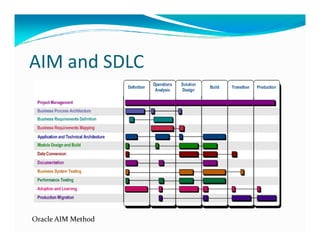
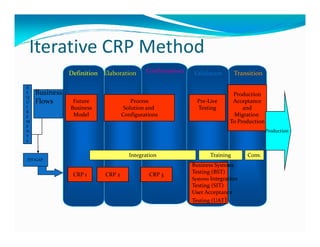
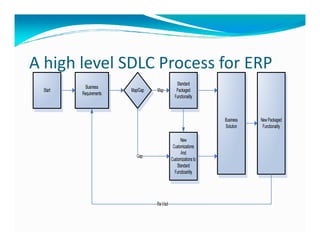
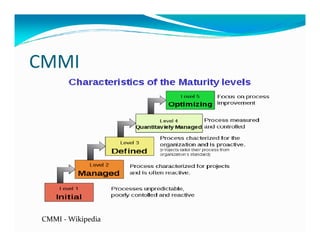
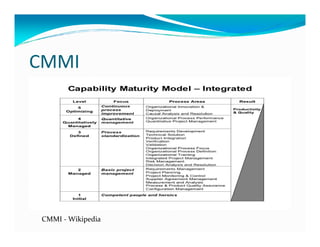
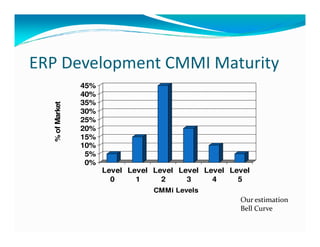
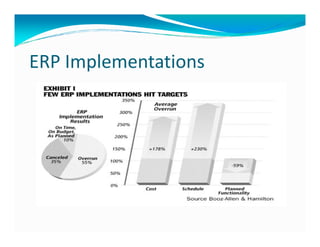
The document discusses the role of ERP managers and the challenges they face in the context of software development life cycles (SDLC) and capability maturity model integration (CMMI). It emphasizes the importance of adopting an iterative CRP approach to ERP implementations to avoid cost overruns and improve operational maintenance efficiency. Additionally, it outlines the complexities of ERP systems and stresses the need for understanding these complexities to successfully manage and implement ERP solutions.