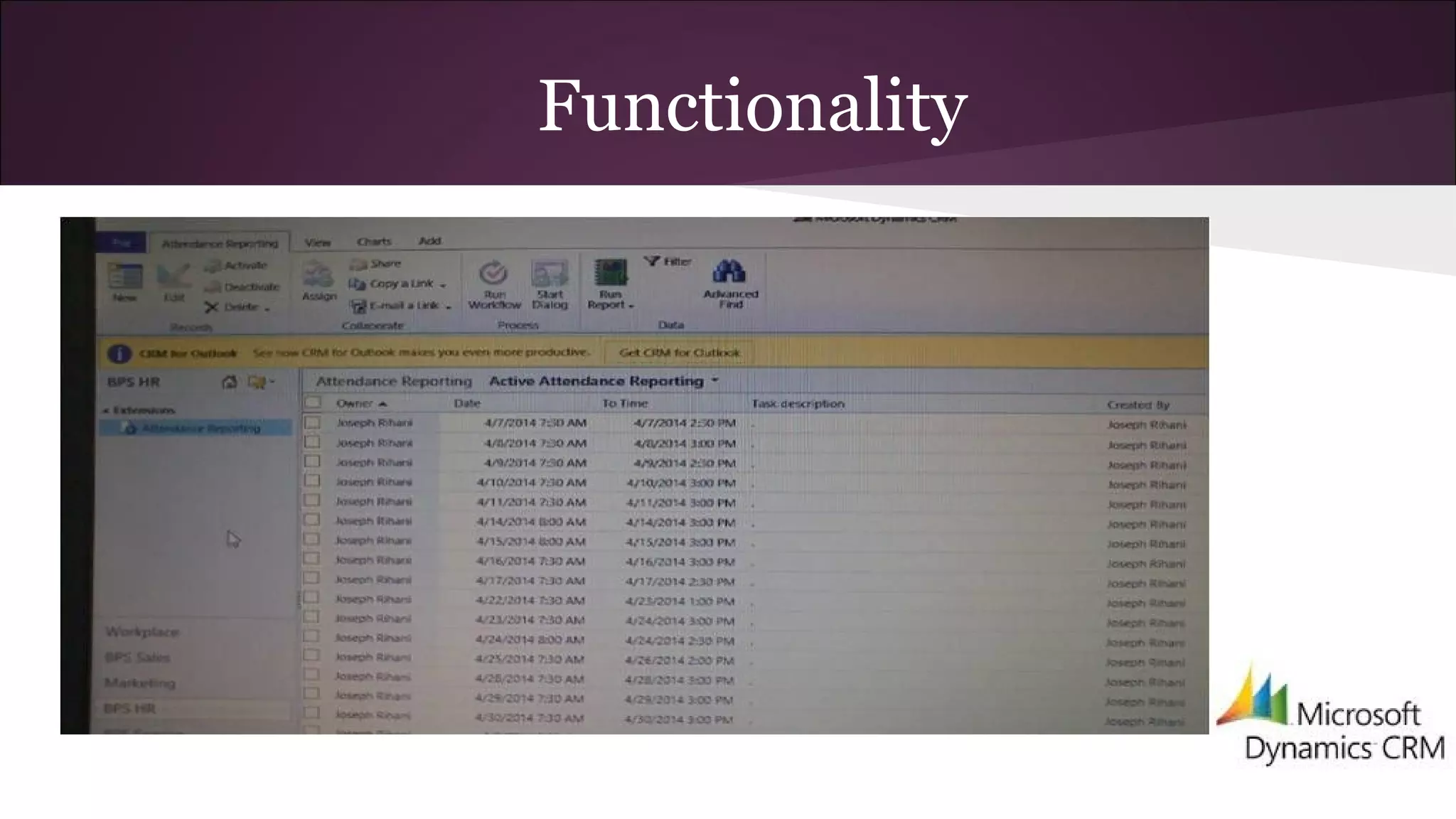
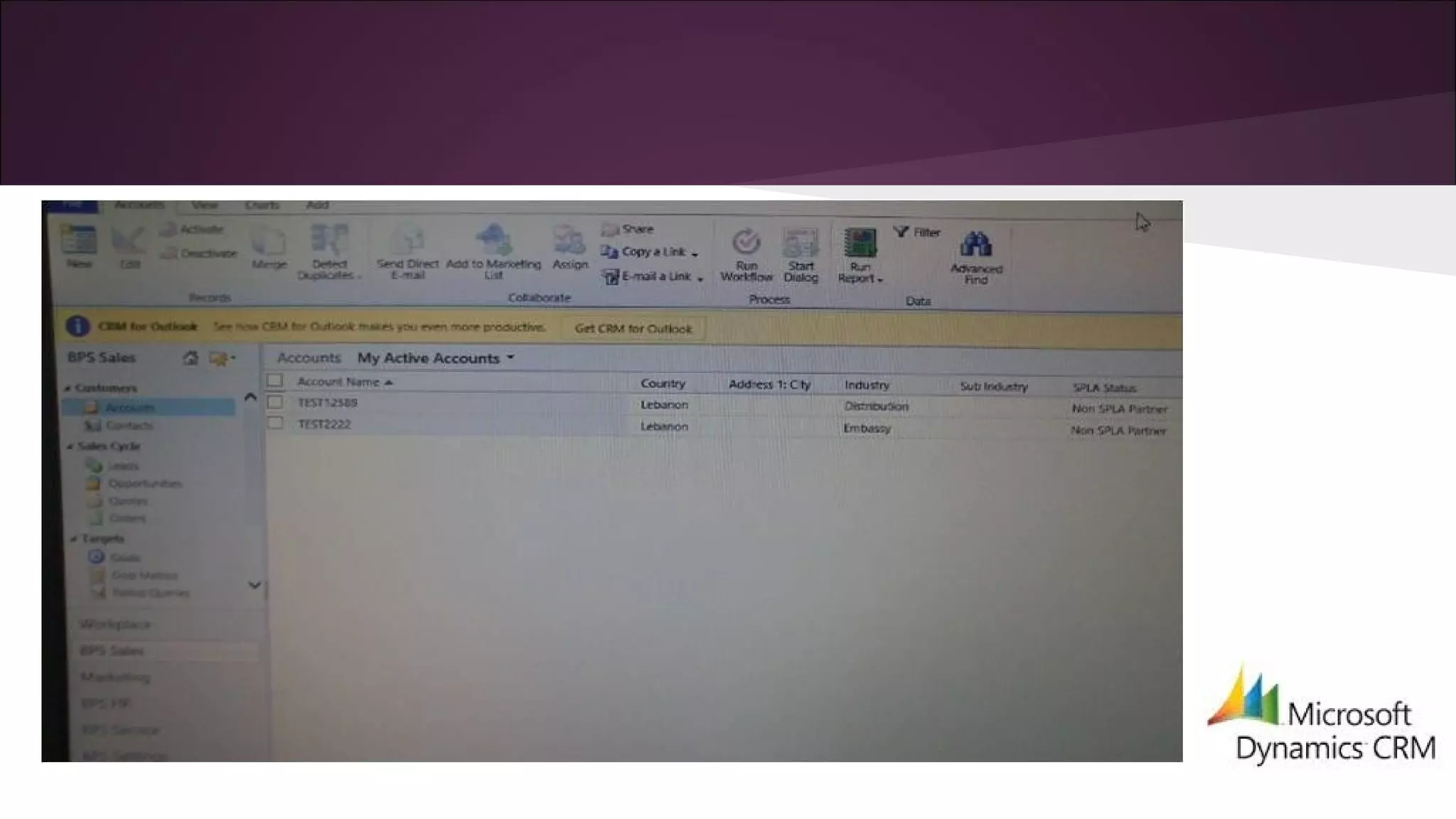
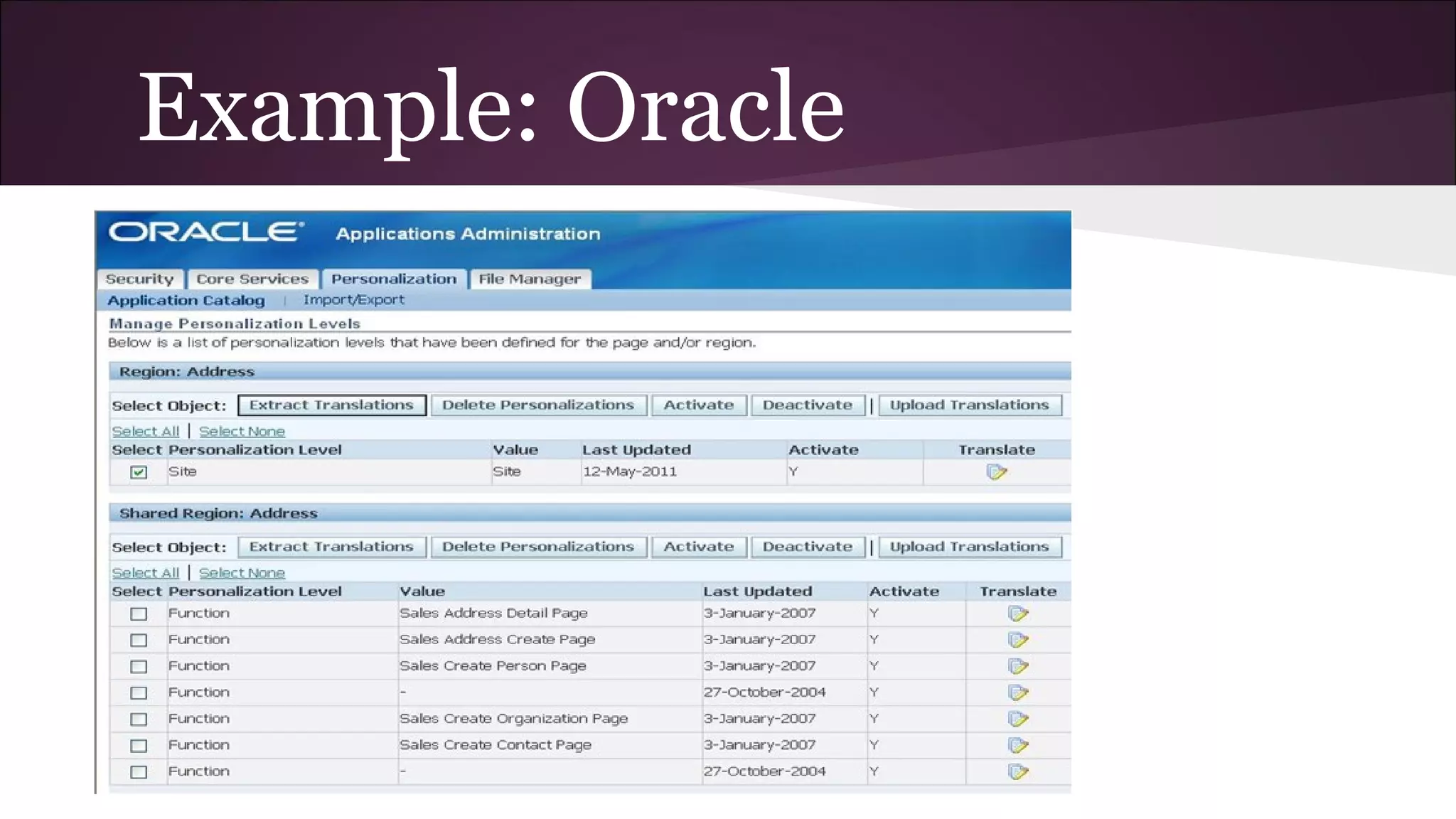
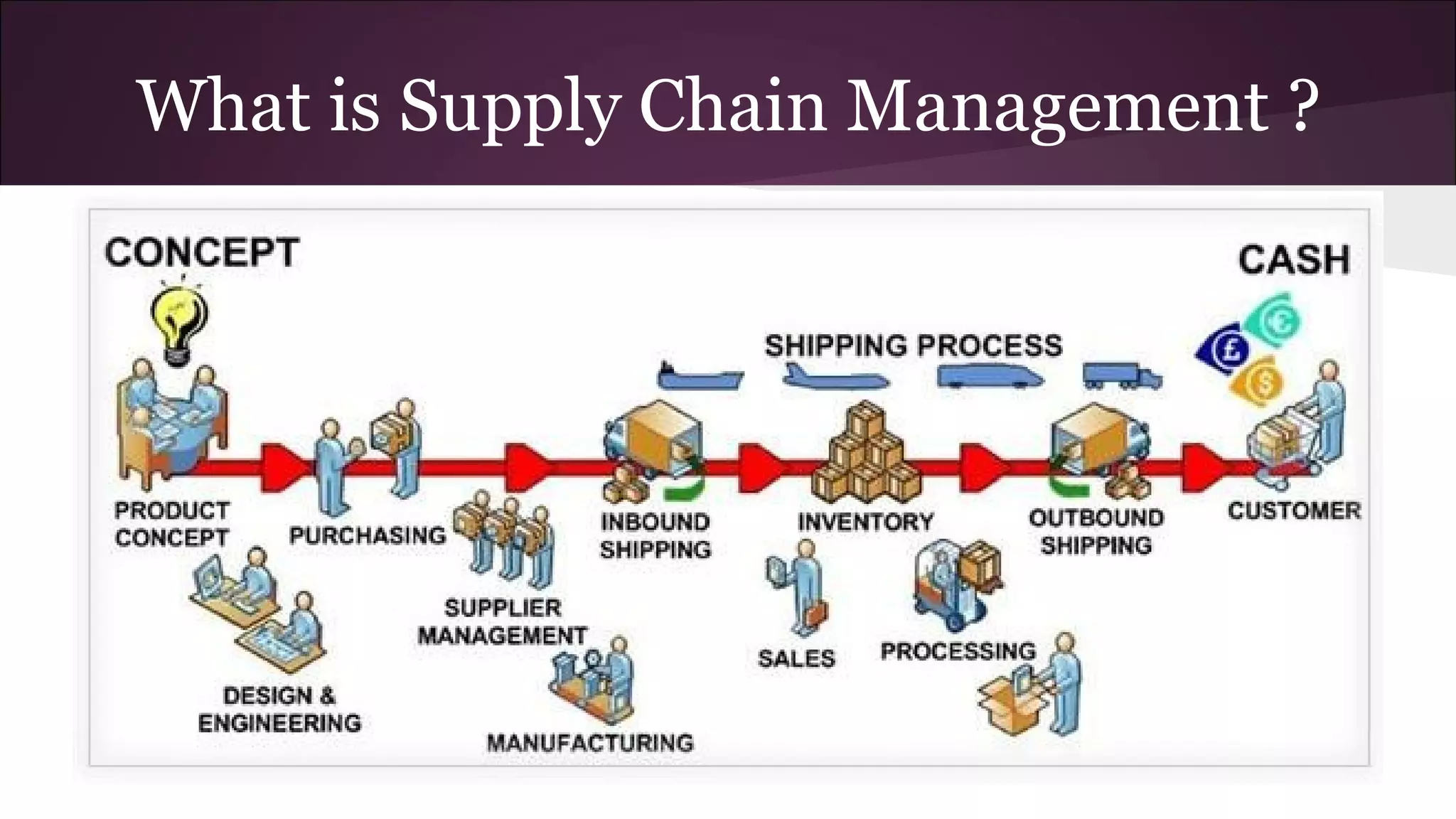
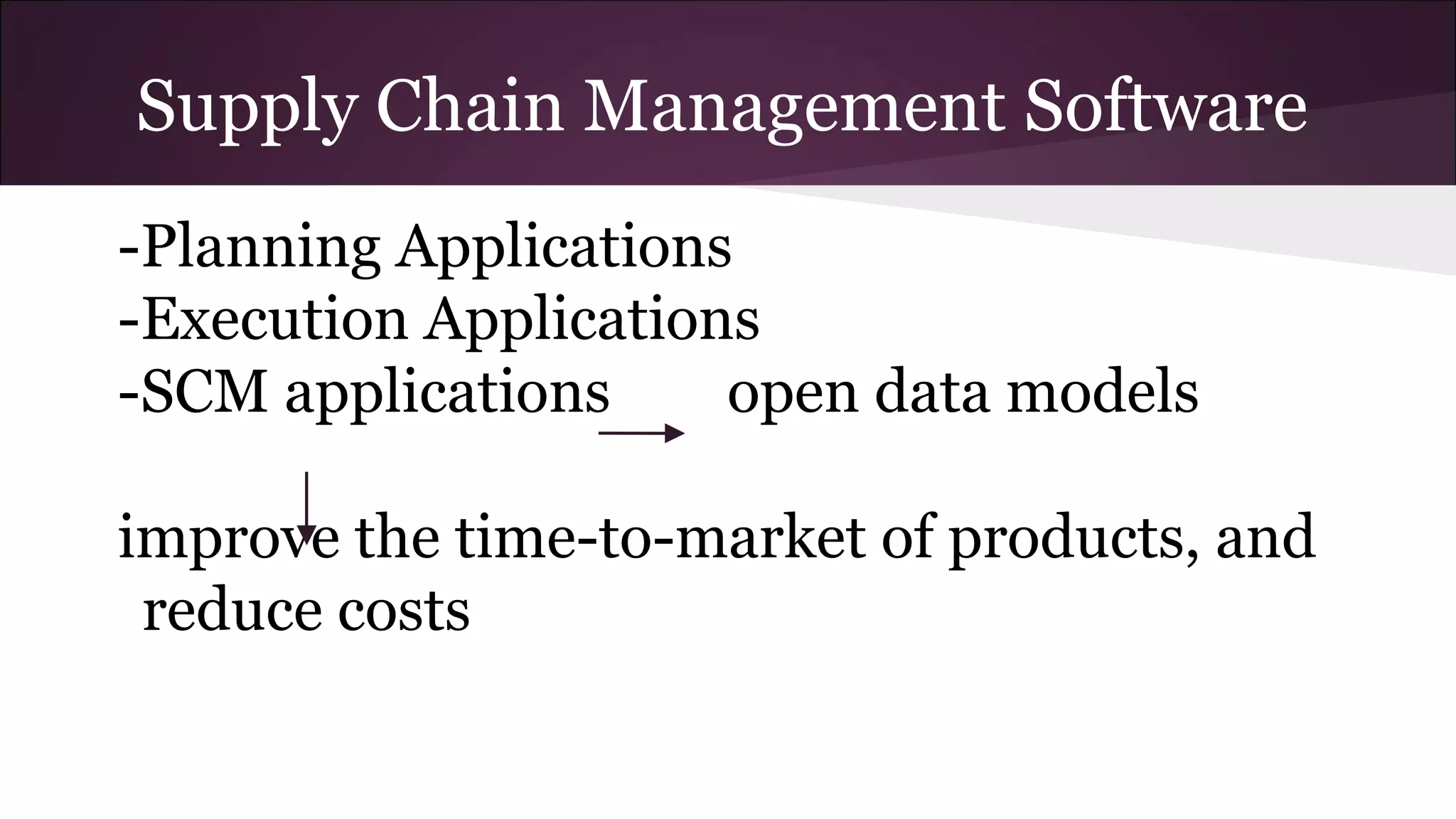
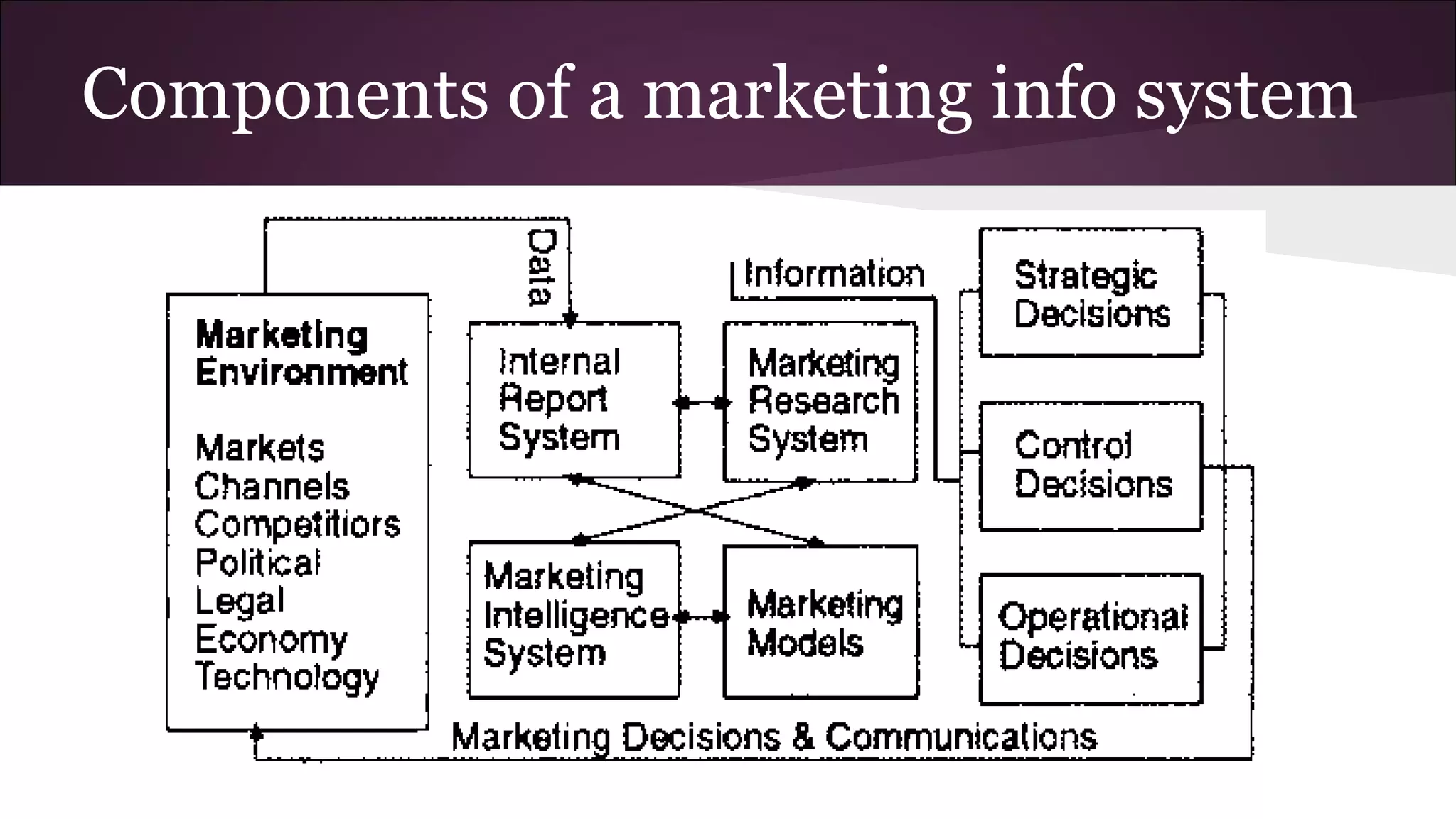
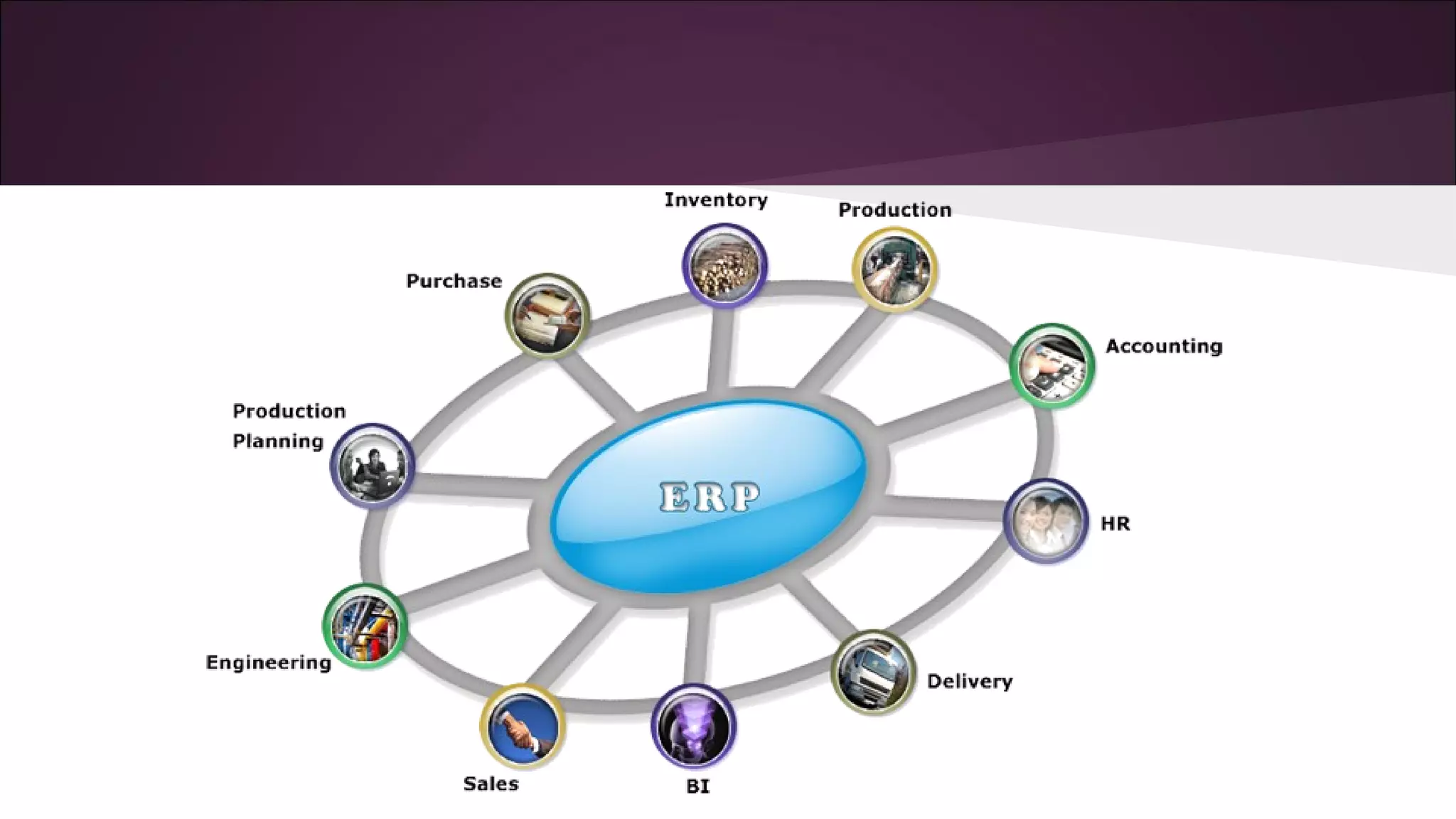
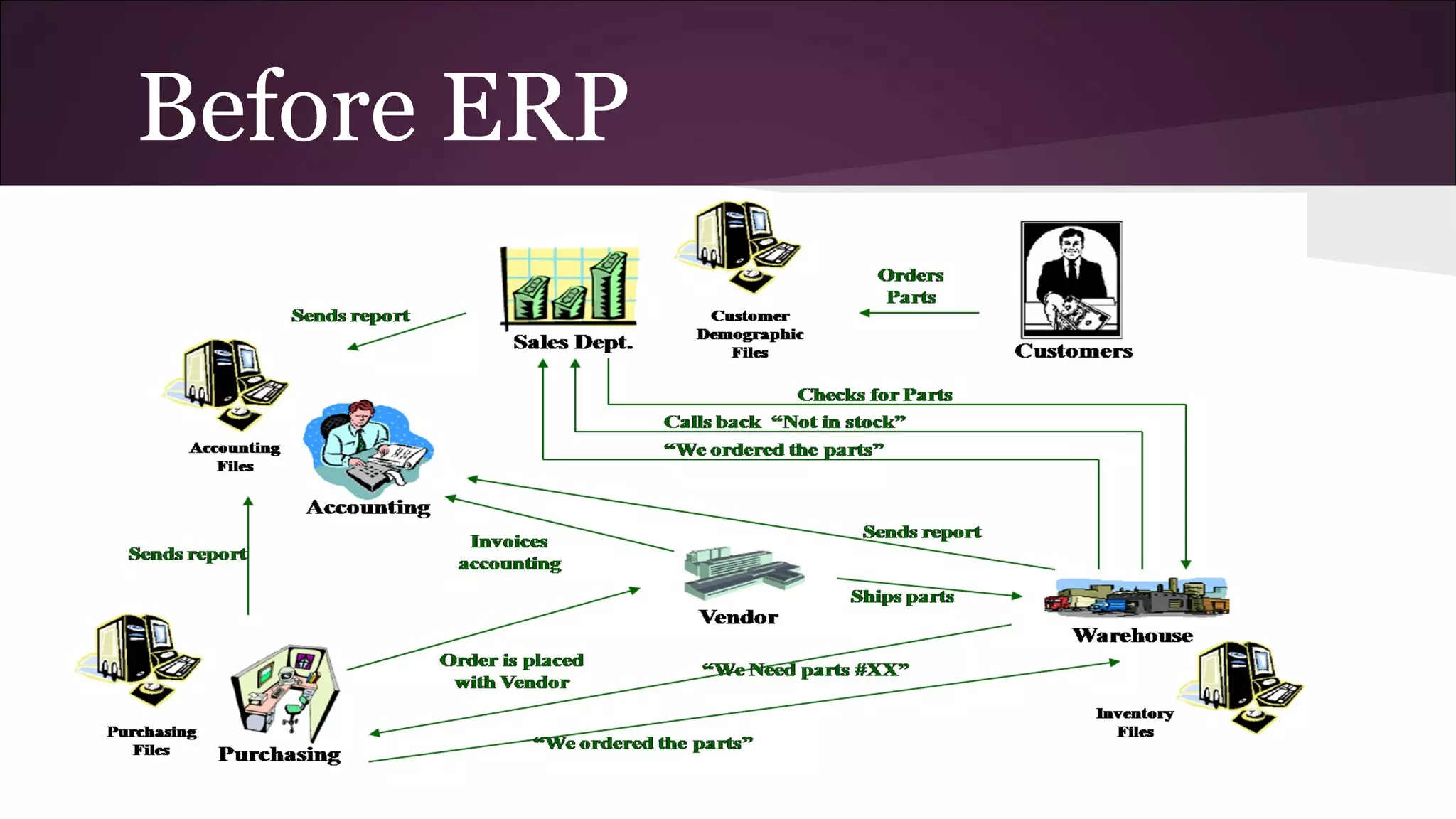
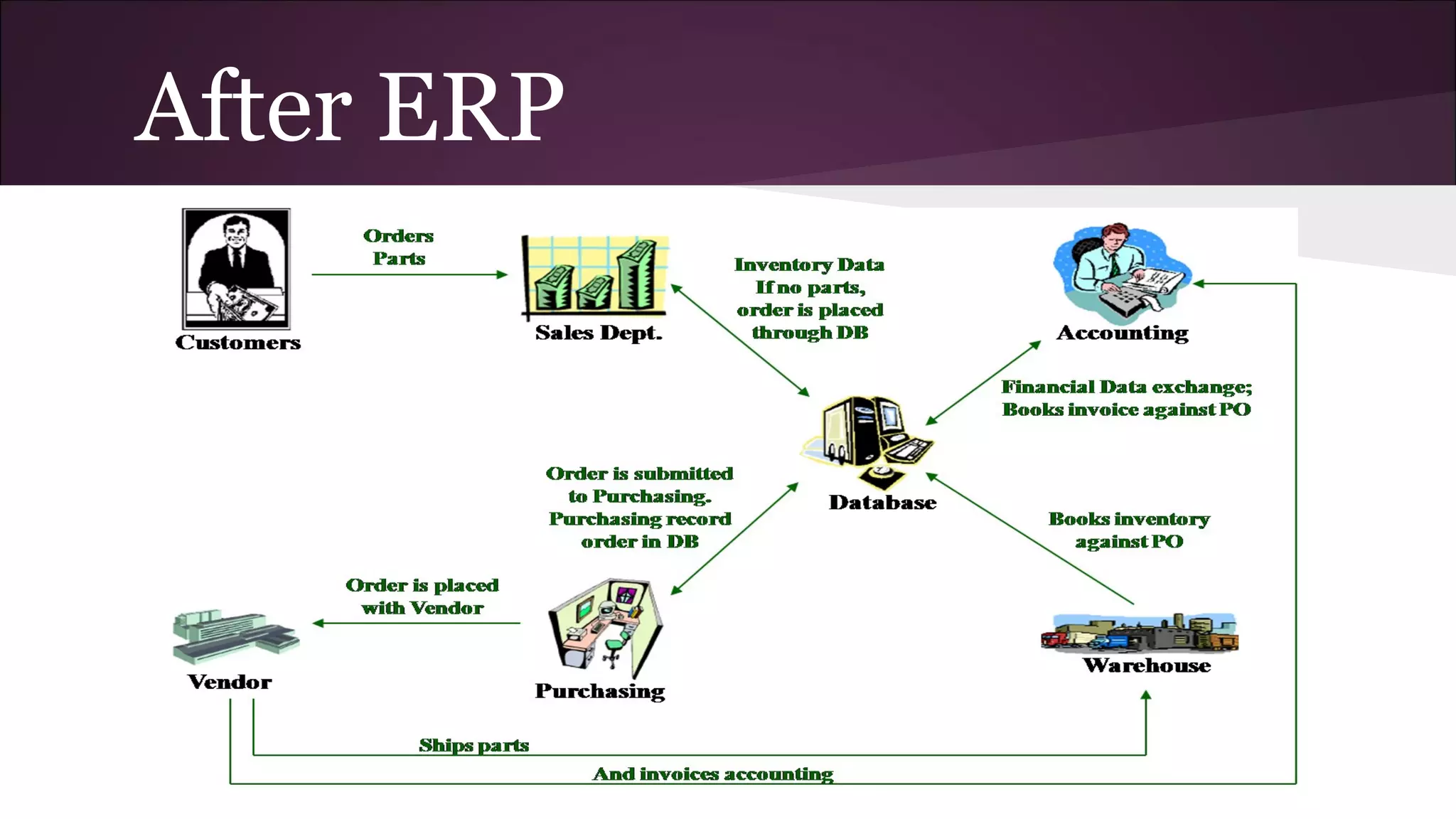
This document discusses various business information systems including CRM, HRMS, SCM, MIS, and ERP. It provides overviews and definitions of each system. CRM involves identifying and enhancing relationships with customers. HRMS handles payroll, time and attendance, performance reviews, and other human resource functions using software. SCM manages supply chains from production to distribution. MIS provides organized marketing information and includes internal reporting, research, intelligence, and models. ERP integrates databases across departments into a single system for coordinated resource management.