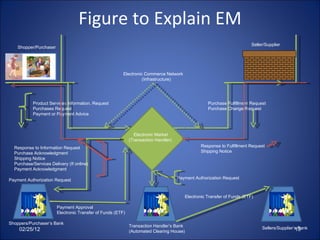
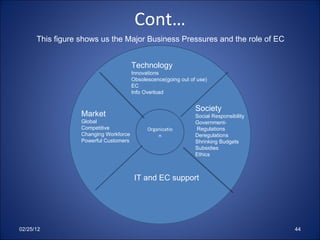
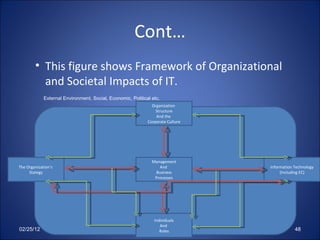
This document provides an overview of electronic commerce (EC), including definitions, applications, classifications, and the interdisciplinary nature of the field. EC is defined as the process of buying and selling or exchanging products, services, and information via computer networks and the internet. It discusses different types of EC like business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), and consumer-to-consumer (C2C). The document also outlines the benefits and limitations of EC.