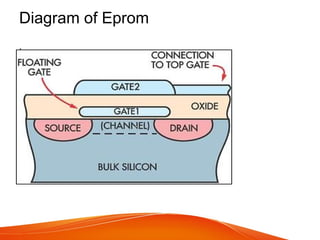
This document defines and compares different types of programmable read-only memory (PROM), including EPROM. It states that EPROM can be erased and reprogrammed using ultraviolet light, as UV exposure causes the stored charge on the floating gate to dissipate, erasing the entire memory at once. The document provides details on the structure, working, erasing process, and disadvantages of EPROM compared to other types of PROM like ROM, PROM, and EEPROM.