This document discusses epidural anesthesia. Some key points:
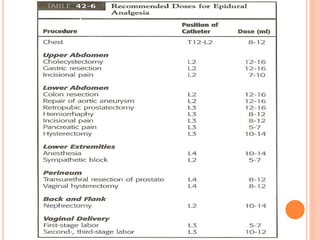
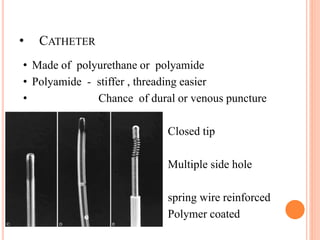
- Epidural anesthesia allows for placement of a continuous catheter, which is useful for cases of unpredictable duration, prolonged postoperative analgesia, chronic pain control, and obstetric analgesia/anesthesia.
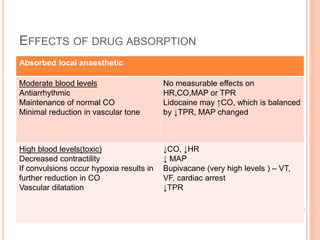
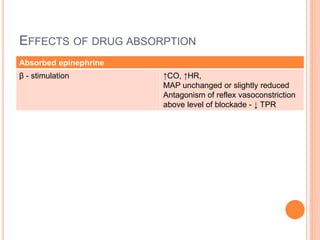
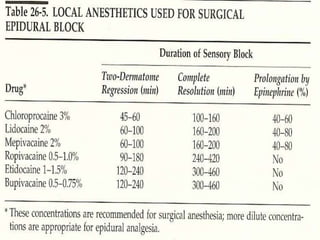
- Local anesthetics injected into the epidural space spread horizontally to nearby dermatomes and vertically in a preferentially cephalad direction.
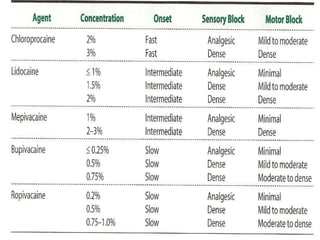
- Factors affecting the level and spread of an epidural block include injection site, dose, volume, concentration, position, age, and speed of injection. Increasing dose and volume increases spread, while concentration mostly affects density.
- Onset is usually within 5 minutes, and peak