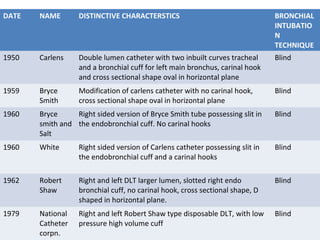
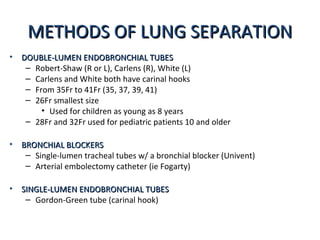
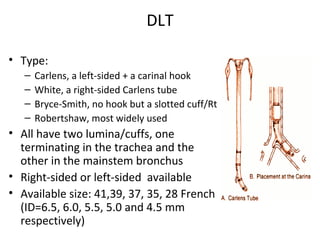
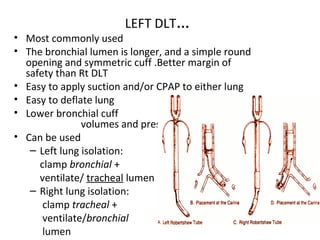
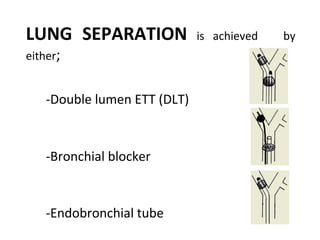
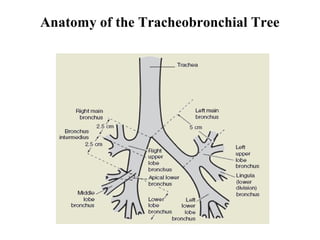
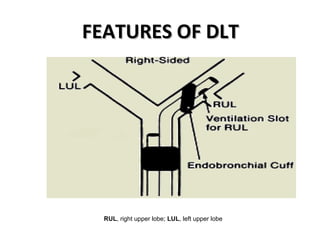
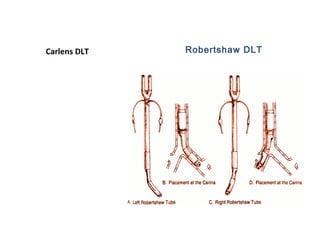
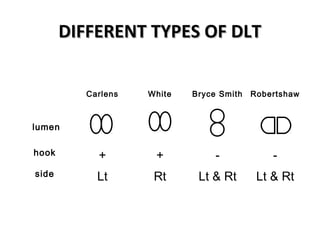
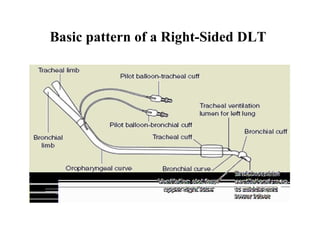
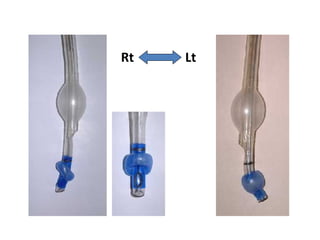
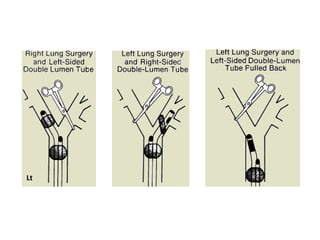
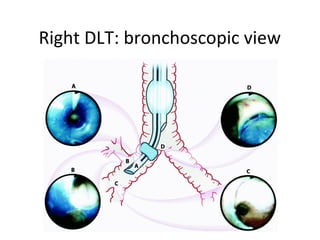
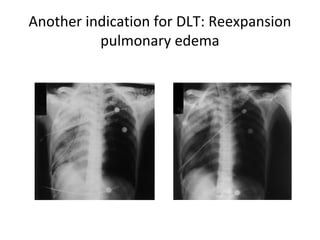
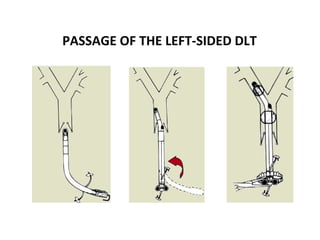
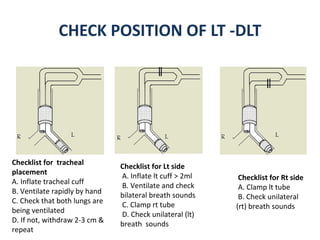
Double lumen tubes were developed in the 1950s-60s to enable lung isolation during thoracic surgery. The Carlens and Bryce-Smith tubes were some of the earliest designs, featuring curves and cuffs to isolate the left or right mainstem bronchus. Modern tubes like the Robertshaw are widely used and come in varying sizes from 26-41 French. Placement requires careful advancement and confirmation via auscultation, cuff inflation, and bronchoscopy to avoid malposition and injury. Double lumen tubes allow selective ventilation and treatment of each lung but require replacement with a single tube after surgery.












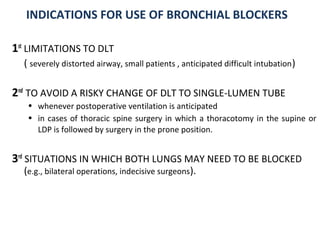
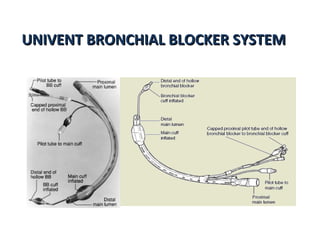
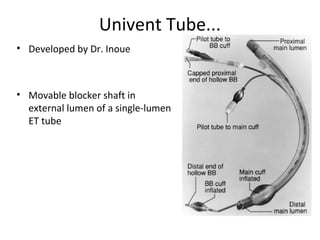
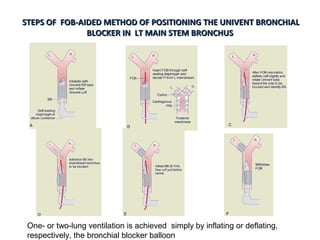
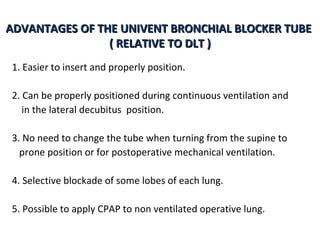
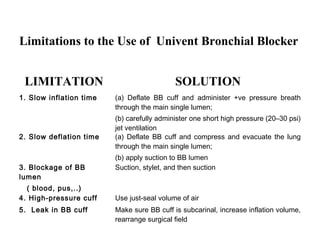
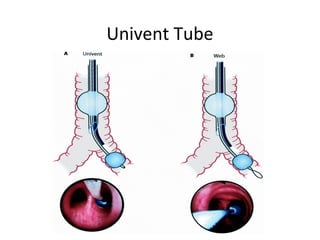
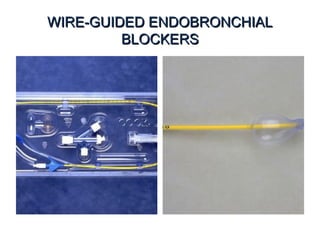
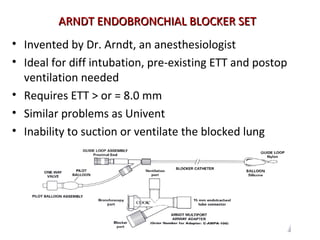


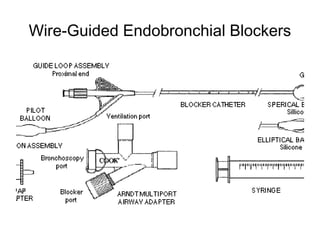
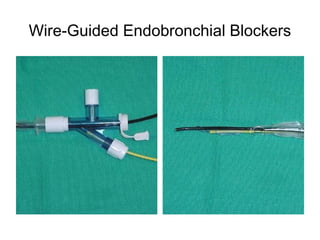
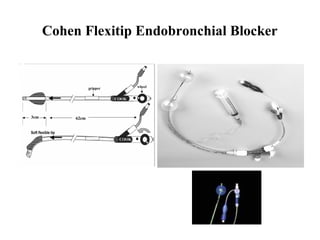
![Arndt endobronchial blocker
[Wire guided Endobronchial Blocker (WEB)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dltppt-170510190115/85/Double-Lumen-Endobronchial-Tubes-ppt-58-320.jpg)