Enzymes and body organization
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•1,149 views
1) Enzymes are proteins that catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions in the body. They do this by binding to substrate molecules and facilitating their transformation into product molecules. 2) The body is organized into a hierarchy of levels from smallest to largest: cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Cells work together to form tissues, tissues work together to form organs, and organs work together to form organ systems. 3) Enzyme activity can be destroyed by extreme heat, changes in pH, or inhibitor molecules that bind to the active site and prevent substrate binding. Without enzymes, important reactions like digestion could not occur fast enough.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Mr Exham IGCSE - Cell Differentiation and Organisation

Mr Exham IGCSE - Cell Differentiation and Organisation
2012 topic 4.3 intermolecular forces and physical properties

2012 topic 4.3 intermolecular forces and physical properties
Similar to Enzymes and body organization
Similar to Enzymes and body organization (20)
Biology unit 7 organ systems living organization notes

Biology unit 7 organ systems living organization notes
More from Rosio DeLeon
More from Rosio DeLeon (20)
AP bio ch. 46 & 47 reproduction and development for 4 /2 /18

AP bio ch. 46 & 47 reproduction and development for 4 /2 /18
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
FAIRSpectra - Towards a common data file format for SIMS images

FAIRSpectra - Towards a common data file format for SIMS images
ESR_factors_affect-clinic significance-Pathysiology.pptx

ESR_factors_affect-clinic significance-Pathysiology.pptx
Predicting property prices with machine learning algorithms.pdf

Predicting property prices with machine learning algorithms.pdf
insect taxonomy importance systematics and classification

insect taxonomy importance systematics and classification
erythropoiesis-I_mechanism& clinical significance.pptx

erythropoiesis-I_mechanism& clinical significance.pptx
Circulatory system_ Laplace law. Ohms law.reynaults law,baro-chemo-receptors-...

Circulatory system_ Laplace law. Ohms law.reynaults law,baro-chemo-receptors-...
GLOBAL AND LOCAL SCENARIO OF FOOD AND NUTRITION.pptx

GLOBAL AND LOCAL SCENARIO OF FOOD AND NUTRITION.pptx
Cancer cell metabolism: special Reference to Lactate Pathway

Cancer cell metabolism: special Reference to Lactate Pathway
Earliest Galaxies in the JADES Origins Field: Luminosity Function and Cosmic ...

Earliest Galaxies in the JADES Origins Field: Luminosity Function and Cosmic ...
word2vec, node2vec, graph2vec, X2vec: Towards a Theory of Vector Embeddings o...

word2vec, node2vec, graph2vec, X2vec: Towards a Theory of Vector Embeddings o...
Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx

Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...
platelets- lifespan -Clot retraction-disorders.pptx

platelets- lifespan -Clot retraction-disorders.pptx
Enzymes and body organization
- 1. Enzymes and Body Organization
- 2. Did you know…? • Every box of Jello says “Do NOT add fresh or frozen pineapple.” Why is that?
- 3. What is the function (job) of proteins? • Proteins have many different jobs, such as: 1) Help cells move (example: help muscle fibers contract) 2) Help cells grow 3) Repair (heal) injuries to cells or to the body 4) Structure (example: building blocks for skin and bone) 5) Transport (carry) molecules (example: hemoglobin is a protein in blood cells that carries oxygen) 6) Catalyze “speed up” reactions
- 4. What are enzymes? • Proteins that catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions in the body • Enzymes are important because, without them, important reactions, like digesting our food, wouldn’t happen fast enough. What is a substrate? • The molecule that an enzyme binds to.
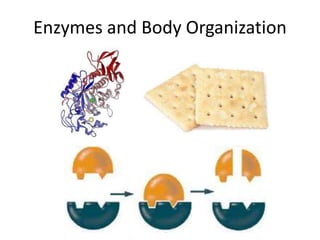
- 5. What is an active site? • The part of the enzyme that binds to the substrate. • The substrate HAS TO fit into the active site, like a key fits in a lock, or else the enzyme won’t work. • This is called the “lock and key” model.
- 6. Processing Piece: • Look at the diagram. See if you can label the enzyme, the active site, and the substrate.
- 7. How do enzyme-catalyzed reactions work? 1) Substrate binds to the enzyme’s active site. 2) The enzyme catalyzes (speeds up) a chemical reaction that makes the substrate change shape; the substrate changes into the products. 3) When the reaction is done, the enzyme releases the products. The enzyme stays the same, ready to catalyze another reaction.
- 8. Processing Piece: • Illustrate the 3 steps of an enzyme catalyzed reaction. • Label the substrate, enzyme, and active site.
- 9. How does enzyme concentration affect reaction rate? • As enzyme concentration (the amount of enzyme) increases, the reaction rate (how fast the reaction happens) increases.
- 10. What is one example of an enzyme? • Amylase is an enzyme in your saliva that breaks down starch (a long polymer chain of carbohydrates) into glucose (small monomers of carbohydrates).
- 11. Processing Piece: 1) Why are enzymes important? (What do they do for our bodies?) 2) What do you think would happen if we didn’t have enzymes like amylase?
- 12. What 3 things can destroy enzymes? 1) Extreme heat (boiling temperatures) 2) pH change (like adding an acid or a base) 3) Molecules called “inhibitors” that bind to an enzyme. All three of these things change an enzyme’s shape, so that it can no longer bind to the substrate.
- 13. How is the body organized? • Cells tissues organs organ systems • Cells working together = a tissue • Tissues working together = an organ – Examples: Stomach, lungs, heart • Organs working together = a system – Examples: Respiratory system, circulatory system • Systems working together = whole body
- 14. Processing Piece: • Illustrate each level of organization in the body.
- 15. Processing Piece: • Identify each of the following examples as cells, tissues, organs, or organ systems. 1. A layer of muscle cells inside your stomach 2. Lungs (many tissues working together) 3. A cell in your stomach that secretes acid 4. Heart, veins, arteries, capillaries and blood cells all working together to move blood around your body 5. A layer of fatty cells in your skin that work together to keep you warm 6. Heart (many tissues working together to pump blood)
- 16. Exit Ticket 1. Draw a picture illustrating the 3 steps of an enzyme- catalyzed reaction. - In your drawing, label the enzyme, substrate, and active site. 2. The enzymes in fresh pineapple dissolve Jello, but the enzymes in canned pineapple don’t. Why is this? 3. What are the 4 levels of organization in the body, from smallest to largest?
