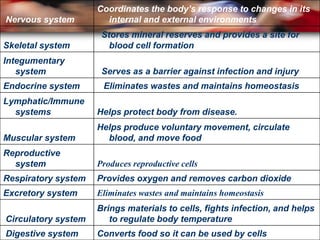
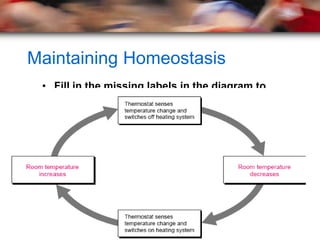
The document provides information about the major human body systems and how they work to maintain homeostasis. It discusses the levels of organization from cells to organ systems. The main organ systems described are the nervous, skeletal, integumentary, endocrine, lymphatic/immune, muscular, reproductive, respiratory, excretory, circulatory, and digestive systems. It also explains how feedback inhibition allows the hypothalamus to regulate body temperature and maintain homeostasis.