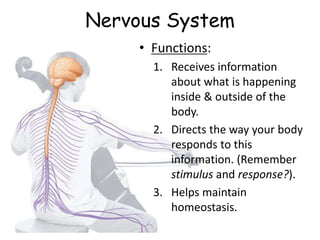
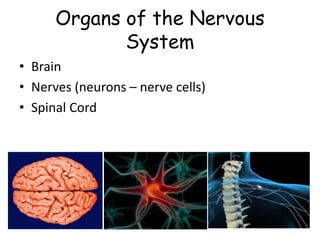
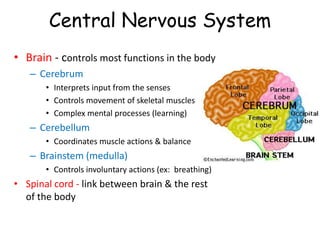
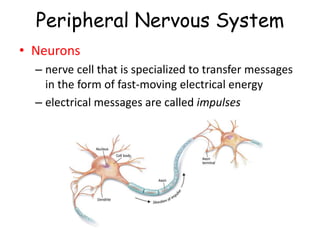
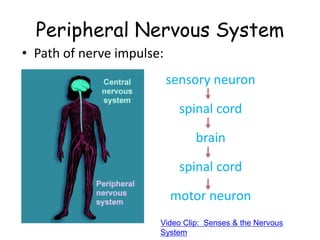
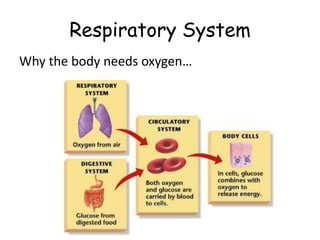
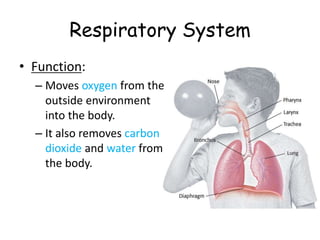
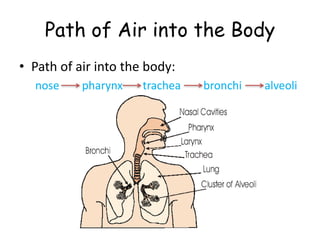
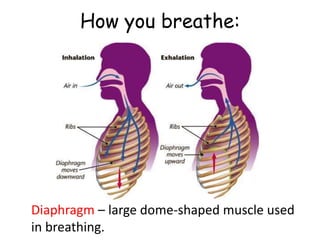
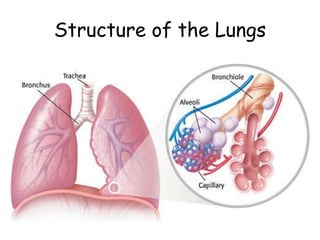
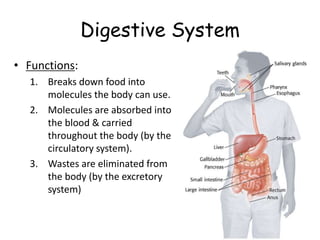
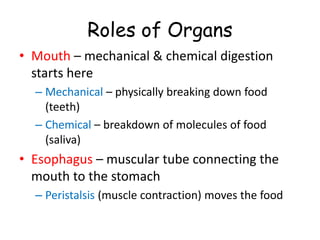
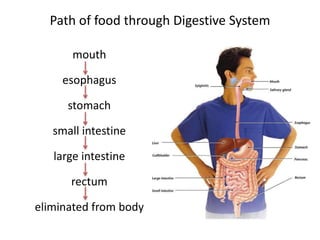
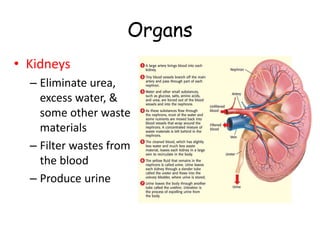
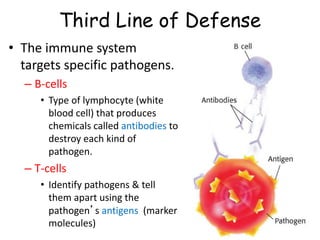
The document provides information about several key human body systems, including:
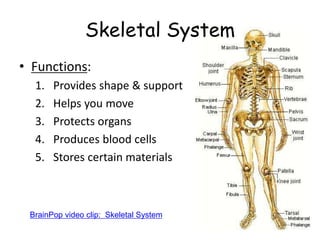
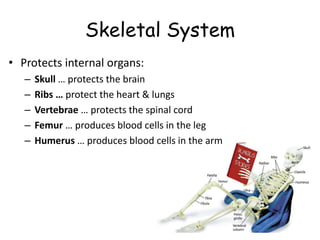
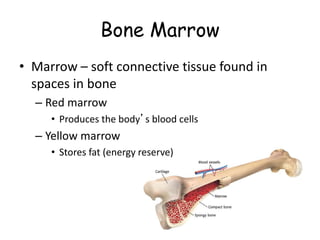
1. The skeletal system, which provides structure, shape, and protection for organs. It works with the muscular system to allow movement as muscles contract and bones lever against each other at joints.
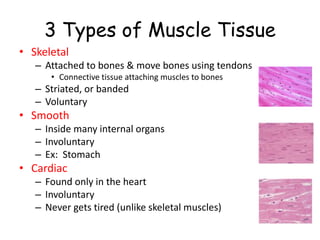
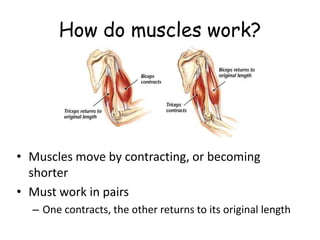
2. The muscular system contains three types of muscle tissue that allow both voluntary and involuntary movement. Muscles work in pairs to contract and relax in order to move bones at joints.
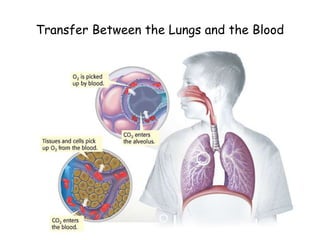
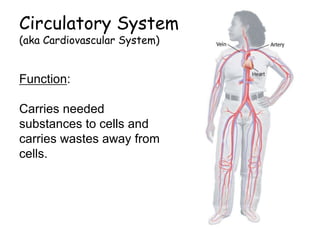
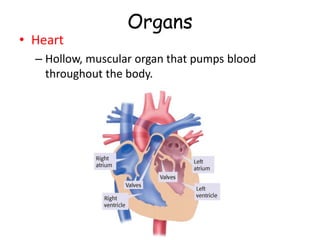
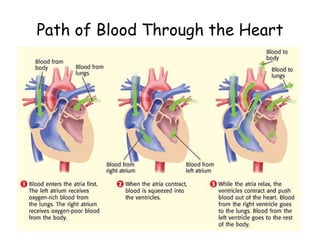
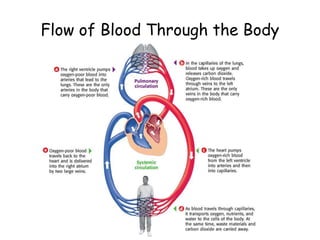
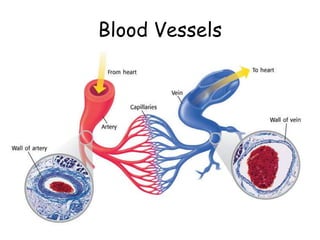
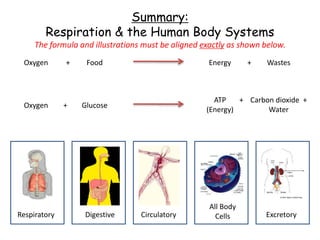
3. The circulatory system carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other materials throughout the body via the blood and returns carbon dioxide and wastes to the lungs and kidneys. It works with all body systems to support cellular respiration and homeostasis.