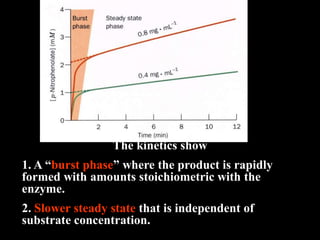
This document discusses enzyme kinetics and catalytic mechanisms. It provides details on:
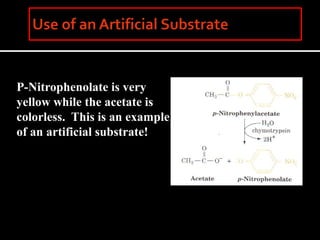
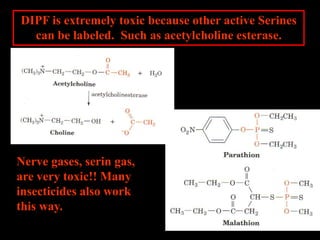
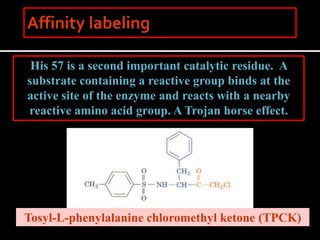
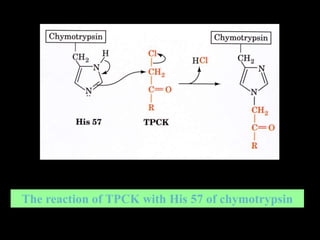
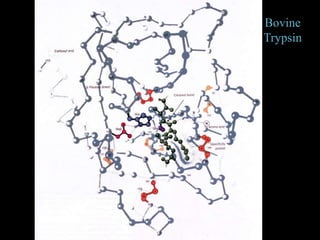
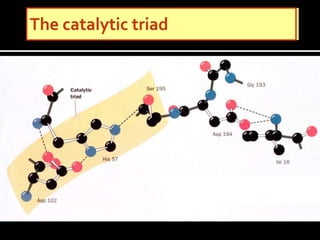
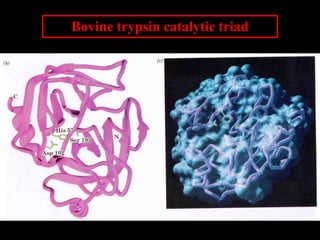
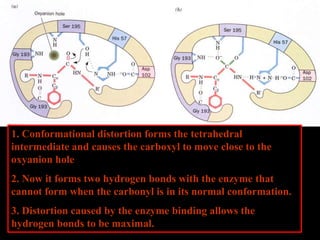
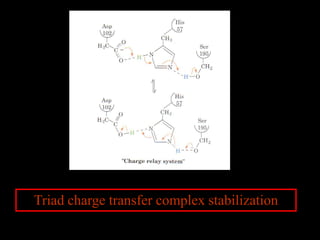
1. The catalytic triad of serine proteases (Ser195, His57, Asp102) and how inhibitors like DIPF can label the active site serine, disabling the enzyme.
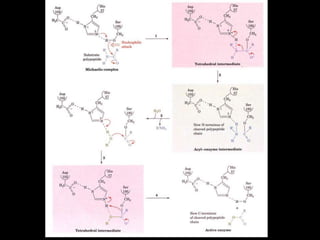
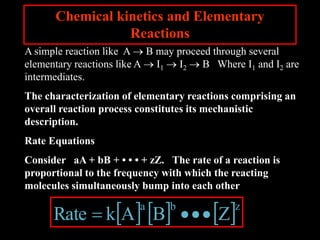
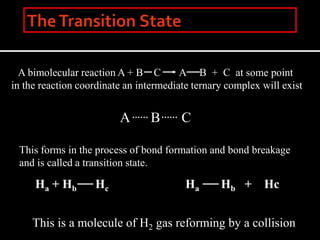
2. The kinetic steps of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, including substrate binding, formation of a tetrahedral intermediate, and release of products.
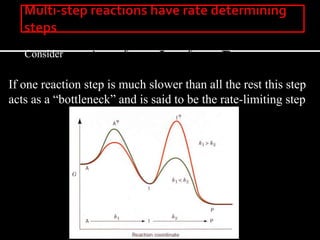
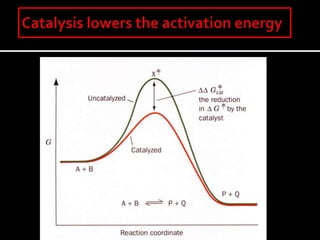
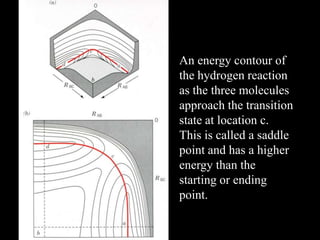
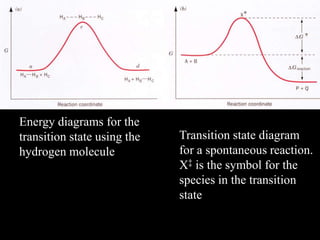
3. How transition state theory is used to explain the kinetic barrier for reactions, and how enzymes lower this activation energy to greatly increase reaction rates.
4. How reaction rates depend on parameters like temperature, activation energy, and catalysts through equations derived from Arrhenius kinetics








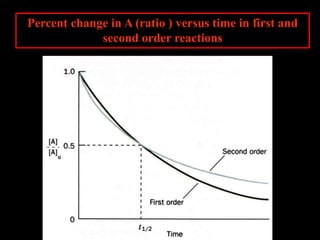

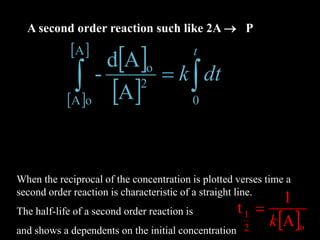
![However, the natural log of the concentration is
directly proportional to the time.
- for a first order reaction-
The rate constant for the
first order reaction has
units of s-1 or min-1 since
velocity = molar/sec
and v = k[A] : k = v/[A]
Gather your data and plot
ln[A] vs time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekineticsandcatalysis-140330114232-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-kinetics-and-catalysis-24-320.jpg)


![ Xk'BAk
dt
Pd
QPBA
For the reaction
‡ Where [X] is the
concentration of the
transition state species
BA
X
K
‡
‡
GRTlnK- D
‡ ‡
DG‡ is the Gibbs free energy of the activated
complex.
k' = rate constant for the decom-
position of the activated complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekineticsandcatalysis-140330114232-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-kinetics-and-catalysis-31-320.jpg)