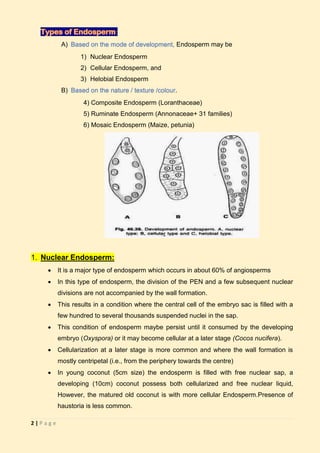
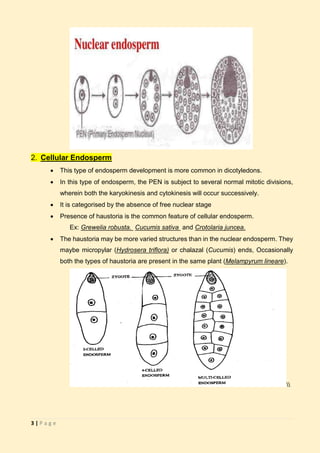
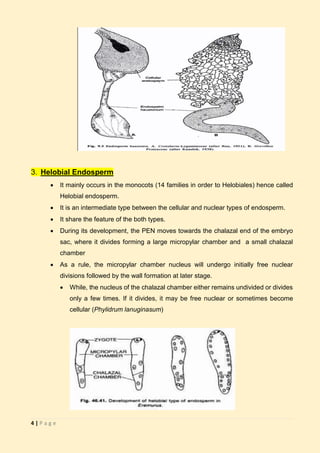
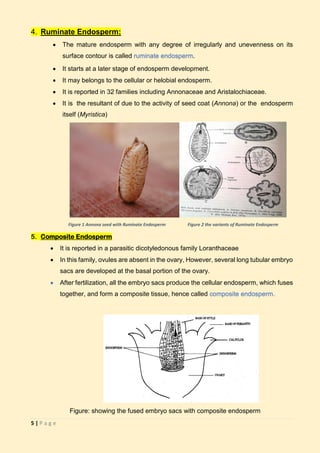
The document discusses endosperm, a vital plant tissue in fertilized seeds that provides nutrients to developing embryos and seedlings. It outlines various types of endosperm development, including nuclear, cellular, and helobial types, along with specific characteristics and examples. Additionally, it highlights functions, variations, and unique cases like ruminate and mosaic endosperm in different plant families.