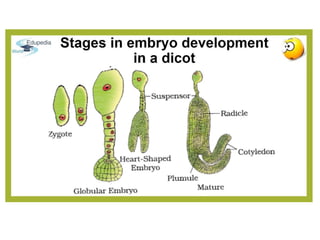
Double fertilization is a complex mechanism in flowering plants, involving the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote and a triploid endosperm. The two processes, syngamy and triple fusion, lead to the development of an embryo and endosperm, which provide nutrition to the developing seed. Following fertilization, the ovary transforms into a fruit, and the ovule develops into a seed, encompassing changes in structure and composition.