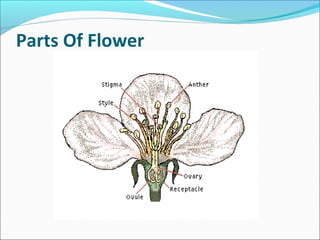
This document describes the structure and development of the anther and pollen grain. It contains the following key points:
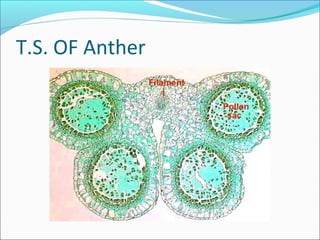
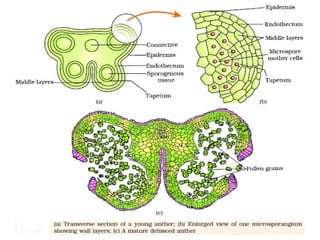
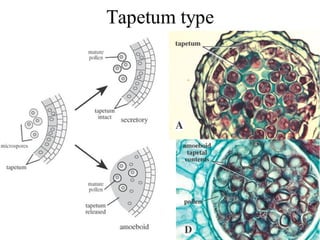
1. The anther has four microsporangia surrounded by four layers - epidermis, endothecium, middle layers, and tapetum. The tapetum nourishes developing pollen grains.
2. Microsporogenesis occurs as microspore mother cells in the sporogenous tissue undergo meiosis to form microspore tetrads.
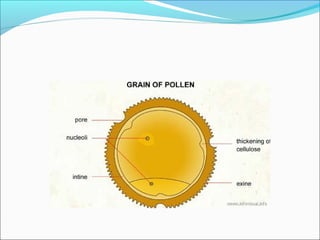
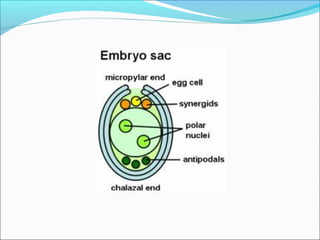
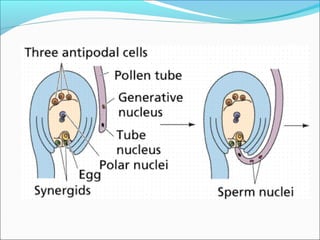
3. Mature pollen grains contain a vegetative cell and generative cell. The generative cell can divide to form two sperm cells ready for fertilization.