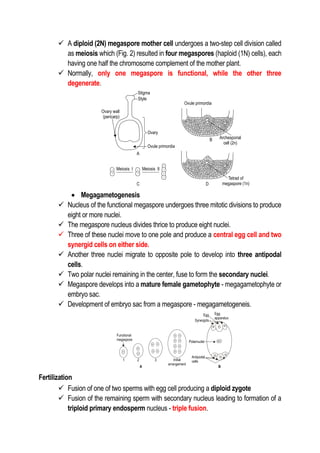
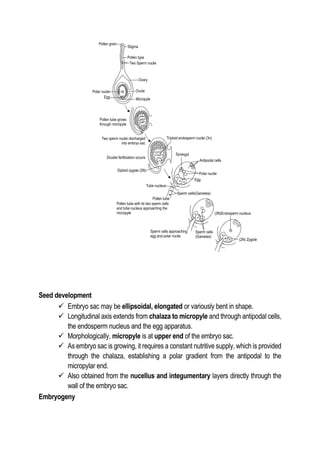
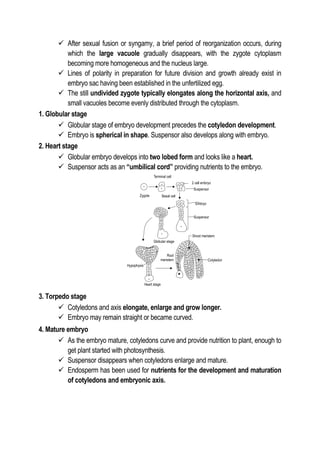
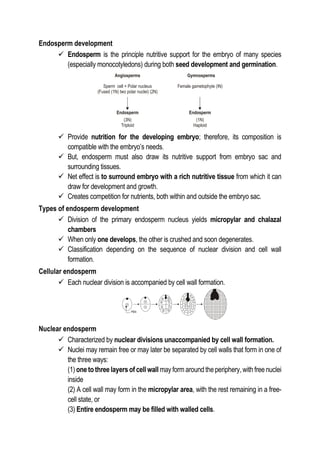
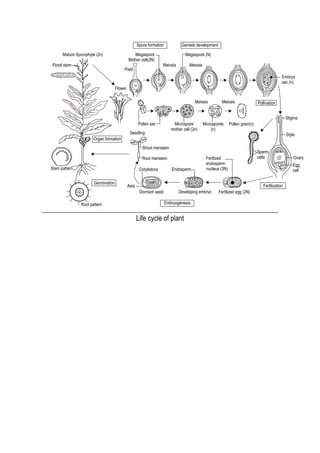
This document discusses the processes of reproduction in crop plants, focusing on both sexual and asexual reproduction. Key stages such as sporogenesis, gametogenesis, fertilization, and seed development are explained in detail, highlighting the roles of various structures like the ovule, integuments, and endosperm. The document also covers embryogeny and different forms of endosperm development, emphasizing their significance in plant growth and reproduction.