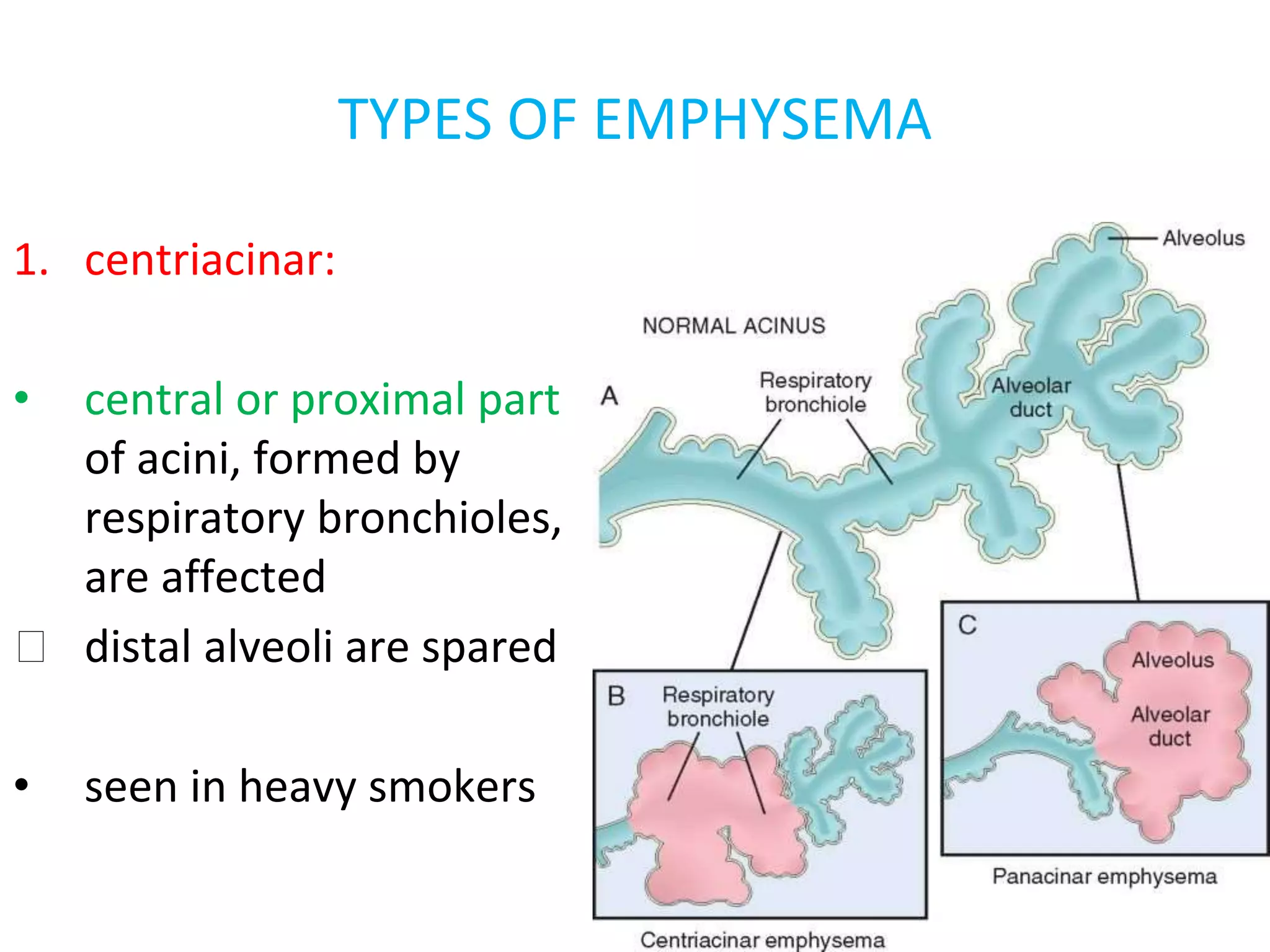
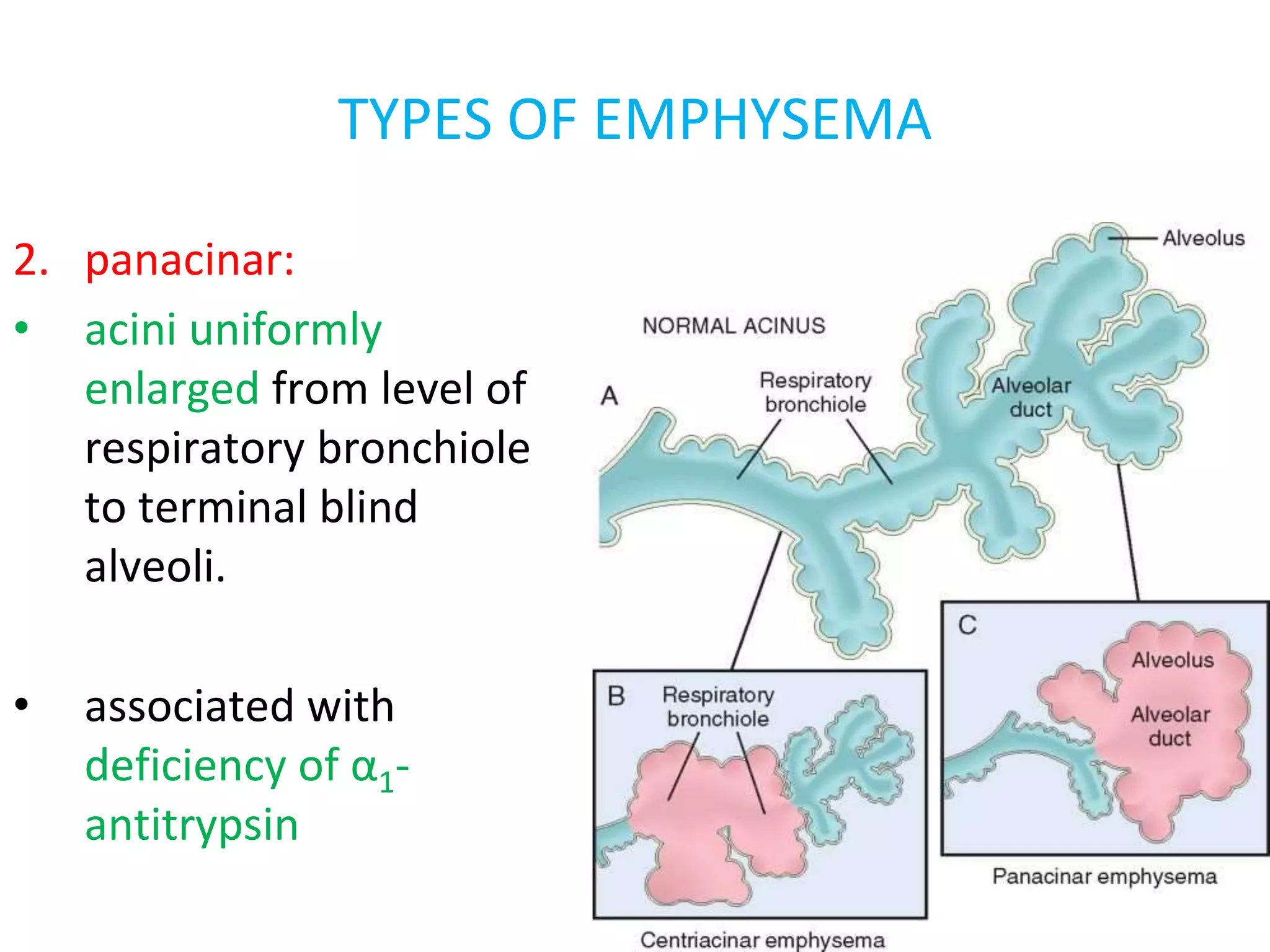
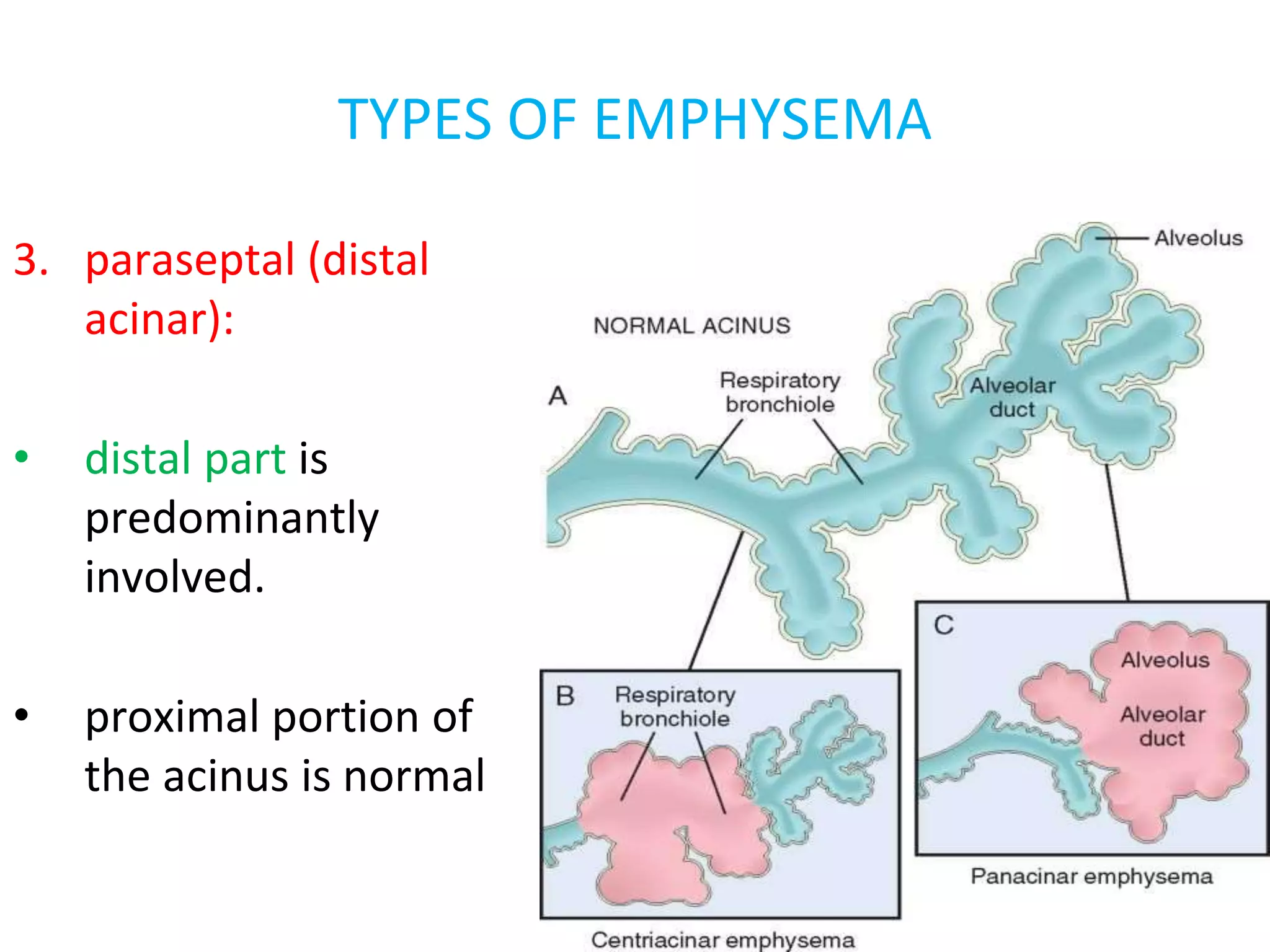
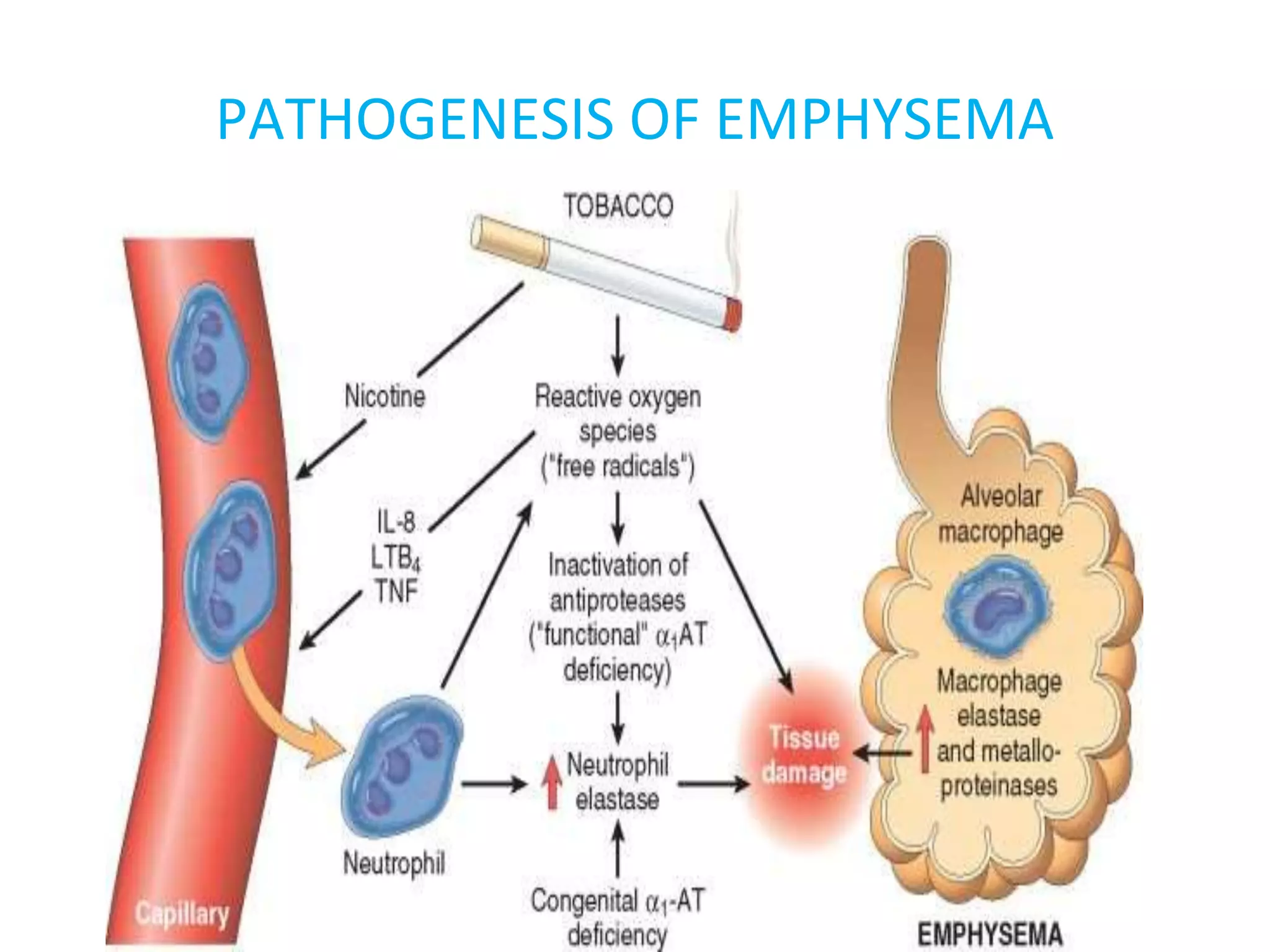
Emphysema is a condition characterized by irreversible enlargement of the airspaces in the lungs. There are four main types: centriacinar, panacinar, paraseptal, and irregular. Emphysema develops due to an imbalance between proteases like elastase and antiproteases like alpha-1 antitrypsin, as well as an imbalance between oxidants from cigarette smoke and antioxidants in the lungs. This protease-antiprotease and oxidant-antioxidant imbalance leads to lung tissue damage and the development of emphysema. Symptoms include progressive dyspnea, cough, and weight loss.