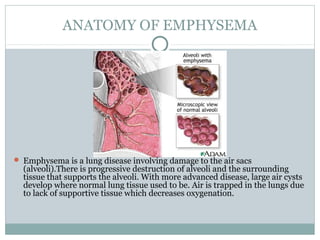
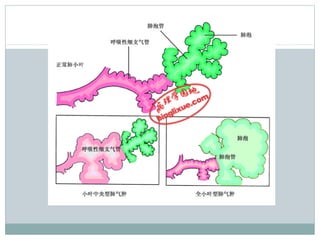
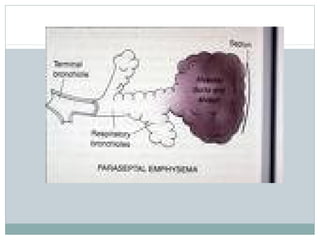
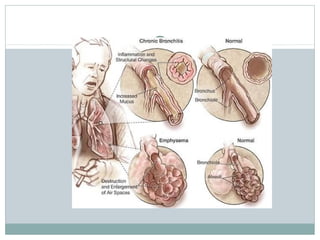
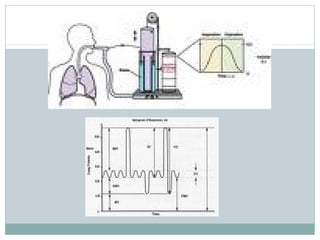
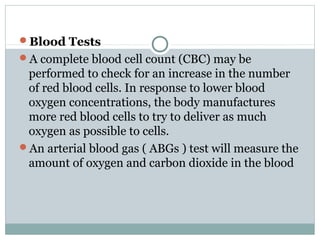
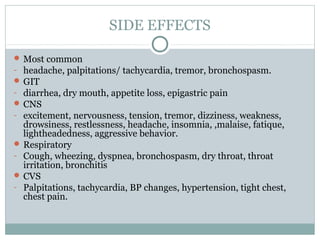
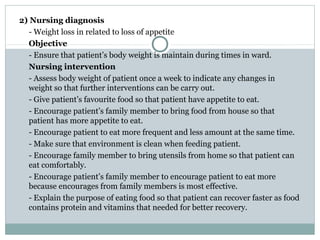
Emphysema is a lung disease where the air sacs (alveoli) are progressively destroyed, resulting in fewer and larger air spaces. The main causes are smoking and genetic conditions. In emphysema, elastic fibers and alveolar walls are broken down due to an imbalance between proteases from inflammatory cells and their inhibitors like alpha-1 antitrypsin. Symptoms include shortness of breath, cough, and fatigue. Diagnosis involves pulmonary function tests, chest imaging, and blood tests. Treatment focuses on bronchodilators, supplemental oxygen, and reducing risk factors.