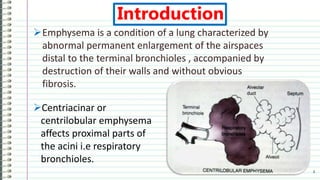
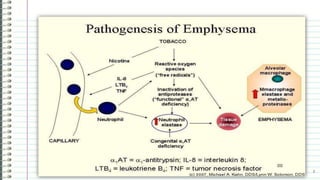
Emphysema is a condition characterized by abnormal permanent enlargement of the airspaces in the lungs. It can be caused by an imbalance between proteases that break down lung tissue and antiproteases that inhibit them, allowing proteases like elastase to dominate and destroy alveolar walls. Alternatively, it may be due to an imbalance between oxidants from cigarette smoke and antioxidants in the lungs, as smoke depletes antioxidants, increases oxidative stress, and damages lung tissue. The document goes on to provide more details on the protease-antiprotease and oxidant-antioxidant pathways of emphysema development.