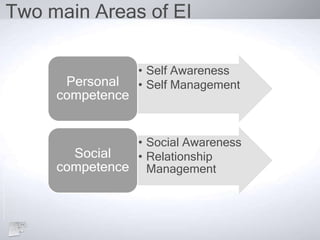
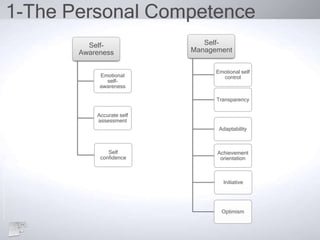
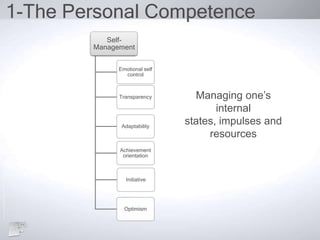
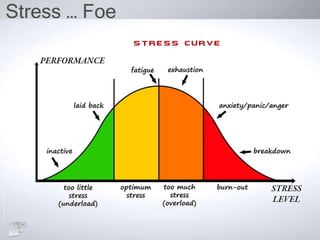
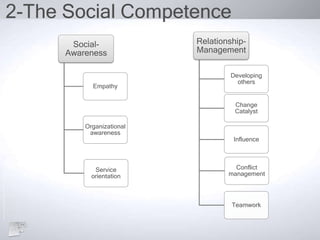
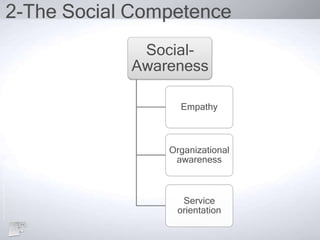
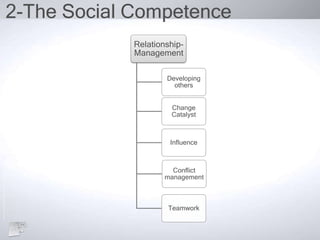
The document outlines the concept of emotional intelligence (EI), focusing on personal and social competencies essential for effective emotional management. It details dimensions of self-awareness and self-management, as well as social awareness and relationship management, emphasizing the importance of these skills in organizational performance and personal well-being. Additionally, it suggests strategies for developing emotional intelligence and reflects on the significance of managing emotions effectively.