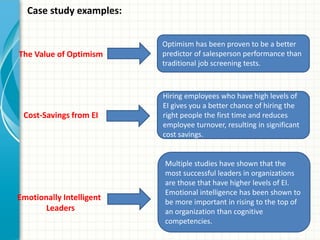
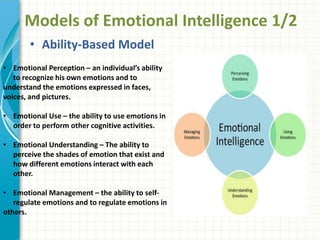
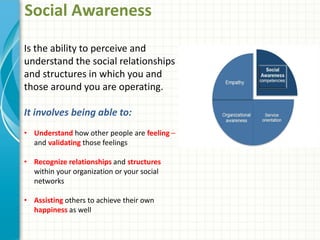
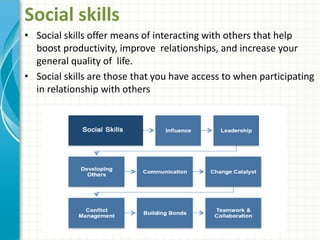
Emotional intelligence involves being aware of one's own emotions and the emotions of others, managing emotions effectively in oneself and others, and using this awareness to guide thinking and behavior. High emotional intelligence is important for success in the workplace as it allows one to understand how emotions impact work and relationships. Models of emotional intelligence include ability-based, trait-based, and mixed models assessing skills like self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and social skills. Developing emotional intelligence competencies such as empathy, influence, and developing others can help improve productivity, relationships, and quality of life.