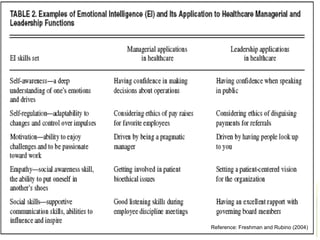
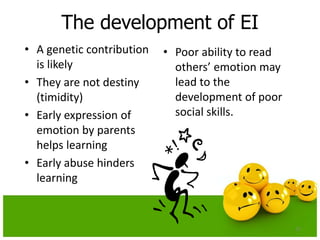
The document provides an introduction to emotional intelligence (EI) over the course of a 2 hour seminar. It defines EI and explains why it is important, covering both the physiological and psychological aspects. It discusses the development of EI and ways it can be assessed. The seminar aims to introduce the basic concepts of EI, explain how physiological factors influence behavior, and involve guest speakers and exercises.