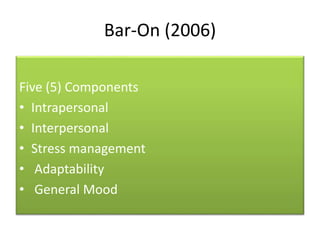
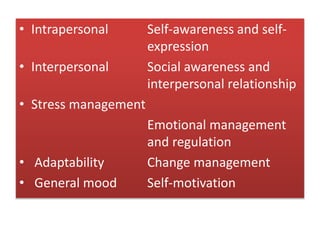
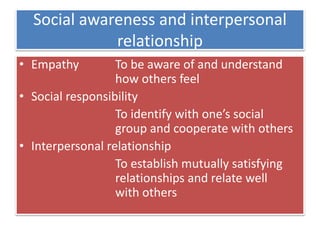
This document discusses the history and development of the concept of emotional intelligence. It traces emotional intelligence from early concepts of social intelligence in the 1920s to current models that define emotional intelligence as having four main domains: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. Another model identifies five components of emotional-social intelligence: intrapersonal skills, interpersonal skills, stress management, adaptability, and general mood. The document provides details on the specific competencies within each domain and component.