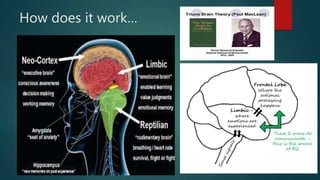
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize and manage emotions in ourselves and in our relationships. There are three main models of emotional intelligence: ability, mixed, and trait. The ability model focuses on accurately perceiving, using, understanding, and managing emotions. The mixed model developed by Daniel Goleman emphasizes emotional and social competencies important for leadership. Research has found emotional intelligence correlates with important work outcomes like job performance, decision-making, creativity, and leadership effectiveness. Assessing and developing emotional intelligence can benefit organizations in areas such as selection, motivation, negotiation, and customer service.


![What is Emotional Intelligence???
Emotional Intelligence refers to the capacity for recognizing our
own feelings and those of others, for motivating ourselves, and for
managing emotions well within ourselves and in our relationships.
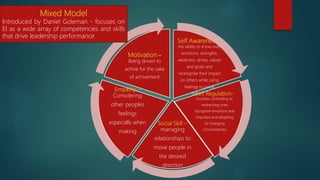
[Daniel Goleman, Mixed Model Theory]
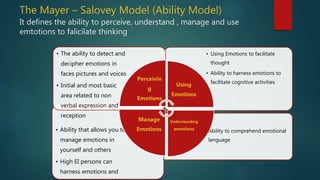
Emotional Intelligence consists of ones ability to perceive emotions,
to access and generate emotions so as to assist thought, to
understand emotions and emotional knowledge, and to reflectively
regulate emotions so as to promote emotional and intellectual
growth [Mayer and Salovey 1997, Ability Model Theory]
Bar-On et aI., (2000) view emotional intelligence as a non-cognitive
intelligence and defines the concept as an array of emotional,
personal, and social abilities and skills that influence an individual’s
ability to cope effectively with environmental demands and
pressures.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emotionalintelligence-200621075600/85/Emotional-intelligence-3-320.jpg)

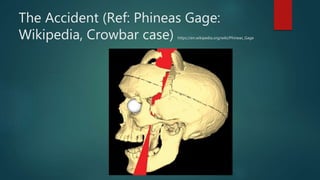
![Evolution of Emotional Intelligence
Thorndike (1920) was the first one to use the term “ Social
Intelligence” and define it as the ability to understand ,men
and women, manage them, boys and girls to act wisely in
human relations.Mc Clelland (1973) A researcher with Harvard offered his view that
conventional concept of Intelligent Quotient ( IQ) simply couldnot predict how
will people perform in the whole workplace.
Howard Gardner (1984) a Harvard Psychologist proposed model of multiple
intelligence where he listed 7 types of Intelligence.
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theory_of_multiple_intelligences]
A comprehensive theory was proposed in 1990 by two psychologists Peter
Salovey and John Mayer . These two defined EI in terms of being able to
monitor and requlate one’s own and others feelings and to use feelings to
guide thought and action.
It was Daniel Goleman( 1995) who fine tuned the theory and popularized the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emotionalintelligence-200621075600/85/Emotional-intelligence-5-320.jpg)


![EQ Vs IQ
Changes little after teen
years
Academic intelligence
Coginitive capacities,
strategy, long term
capacity
Can be largely
learned through
life and
experiences
EI grows as years,
called as Maturity.
More plasticity
associated
Tactical(
Immediate
functioning)
Emotional Intelligence is the reflection of one's "common sense" and ability to get along in the world (Bar-On, 1997).
[https://dyuthi.cusat.ac.in/xmlui/bitstream/handle/purl/2681/Dyuthi-T0733.pdf?sequence=1], INTELLIGENT USE OF EMOTIONS IN PERSONAL SELLING: A STUDY INTO THE EFFECT
OF EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE ON THE PERFORMANCE OF SALES EXECUTIVES – Study by Dr Zakkariya K A.
Personal
Competency of an
Individual. Qualify
him for a job, but
does not
guarantee
success.
EI relates to
understating of oneself
and others and there by
coping up to diverse
situations and obtaining
success](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emotionalintelligence-200621075600/85/Emotional-intelligence-10-320.jpg)






![Applications of EI in Organizational
Behavior
Selection ( Recruitment & Hiring)
Employers are currently using EI to hire people, especially in jobs that demand
high degree of Interaction.
Employers find that a person hired wrong is a cost to the company ( Cost of Hire,
Training etc – equal to a years pay)
Eg: Exxon Mobil uses competency testing involved in numerical reasoning tests
P & G uses success drivers Assessment and the P&G Reasoning tests
NDA has their own psychometric tests
Pilot PABT tests
Background Reference Checks
[ An Article in the journal by MIT college of Management by Mr Pranav Jyoti 2015,
states that their study has proved that EI has a huge role in the HR processes
specific to Hiring]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emotionalintelligence-200621075600/85/Emotional-intelligence-21-320.jpg)












![References
Working with Emotional Intelligence – Daniel Goleman
Emotional Intelligence Coachin – Neals, Spence, Liz Wilson
Organizational Behavior – Robbins and Judge
Organizational Behavior – Luthans
Increase Your emotional Intelligence, Geetu Bharwaney
Ted Talks by Jason Bridge and Tavis Bradberry ( Author of EI 2.0)
Research papers on Emotional Intelligence.
https://dyuthi.cusat.ac.in/xmlui/bitstream/handle/purl/2681/Dyuthi-
T0733.pdf?sequence=1], INTELLIGENT USE OF EMOTIONS IN PERSONAL
SELLING: A STUDY INTO THE EFFECT OF EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE ON
THE PERFORMANCE OF SALES EXECUTIVES – Study by Dr Zakkariya K A.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emotionalintelligence-200621075600/85/Emotional-intelligence-34-320.jpg)
