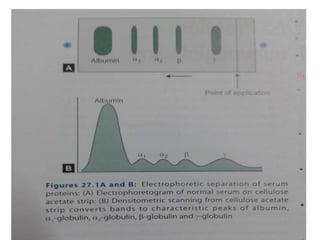
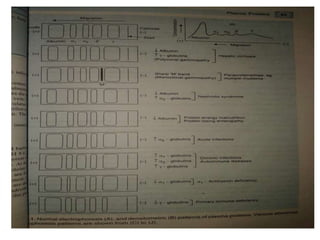
This document discusses electrophoresis, which is the movement of charged particles in an electric field. It separates molecules based on their charge and size. Key factors that affect migration rate are listed. The main requirements for electrophoresis are an electrophoresis tank, electrodes, power supply, buffer, and specimens like serum or plasma. Common electrophoresis techniques described include zone electrophoresis using paper or gel, isoelectric focusing, immuno electrophoresis, and SDS-PAGE which separates based on size. Clinical applications involve using electrophoresis to analyze conditions like liver disease or infections.