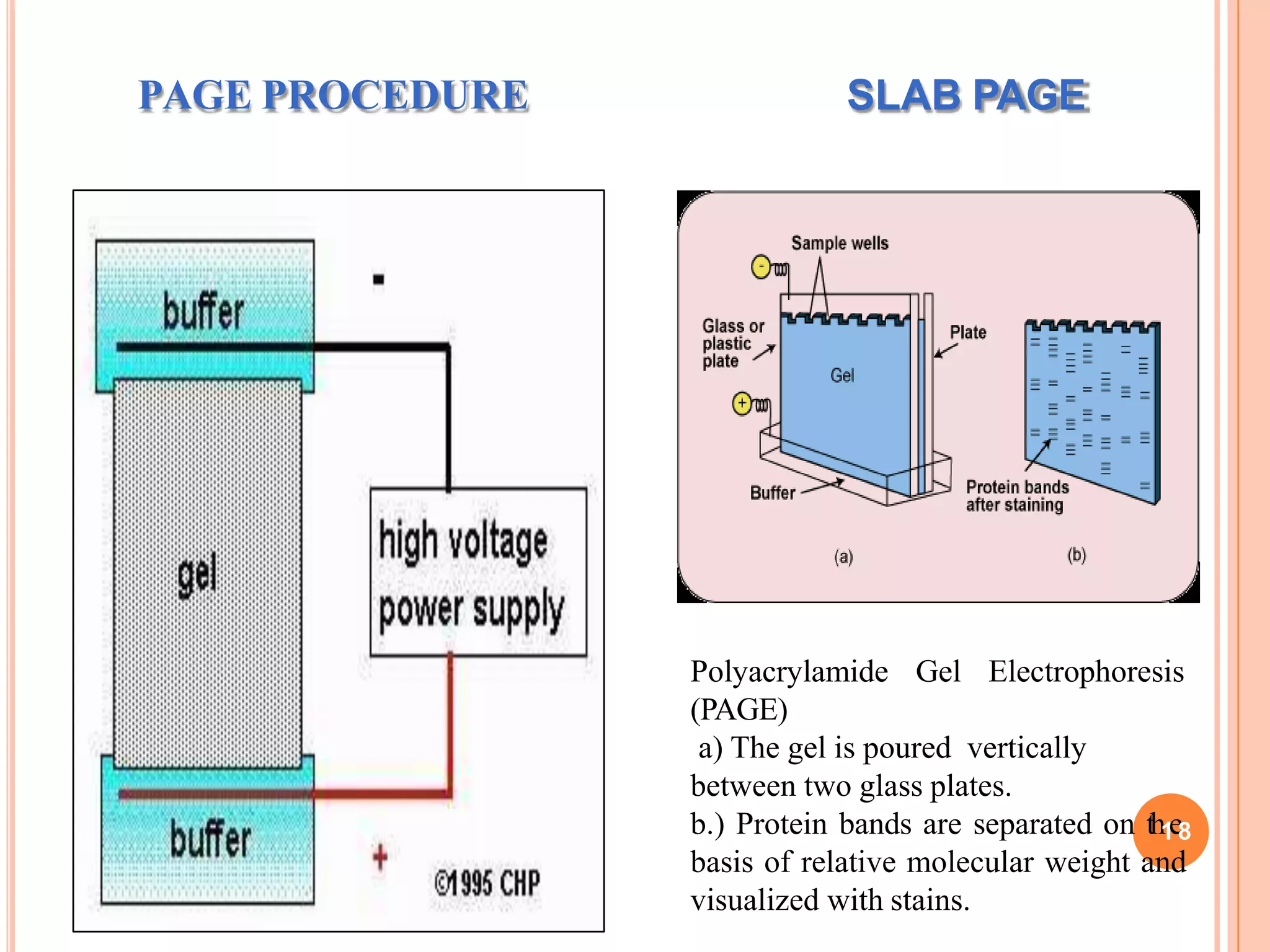
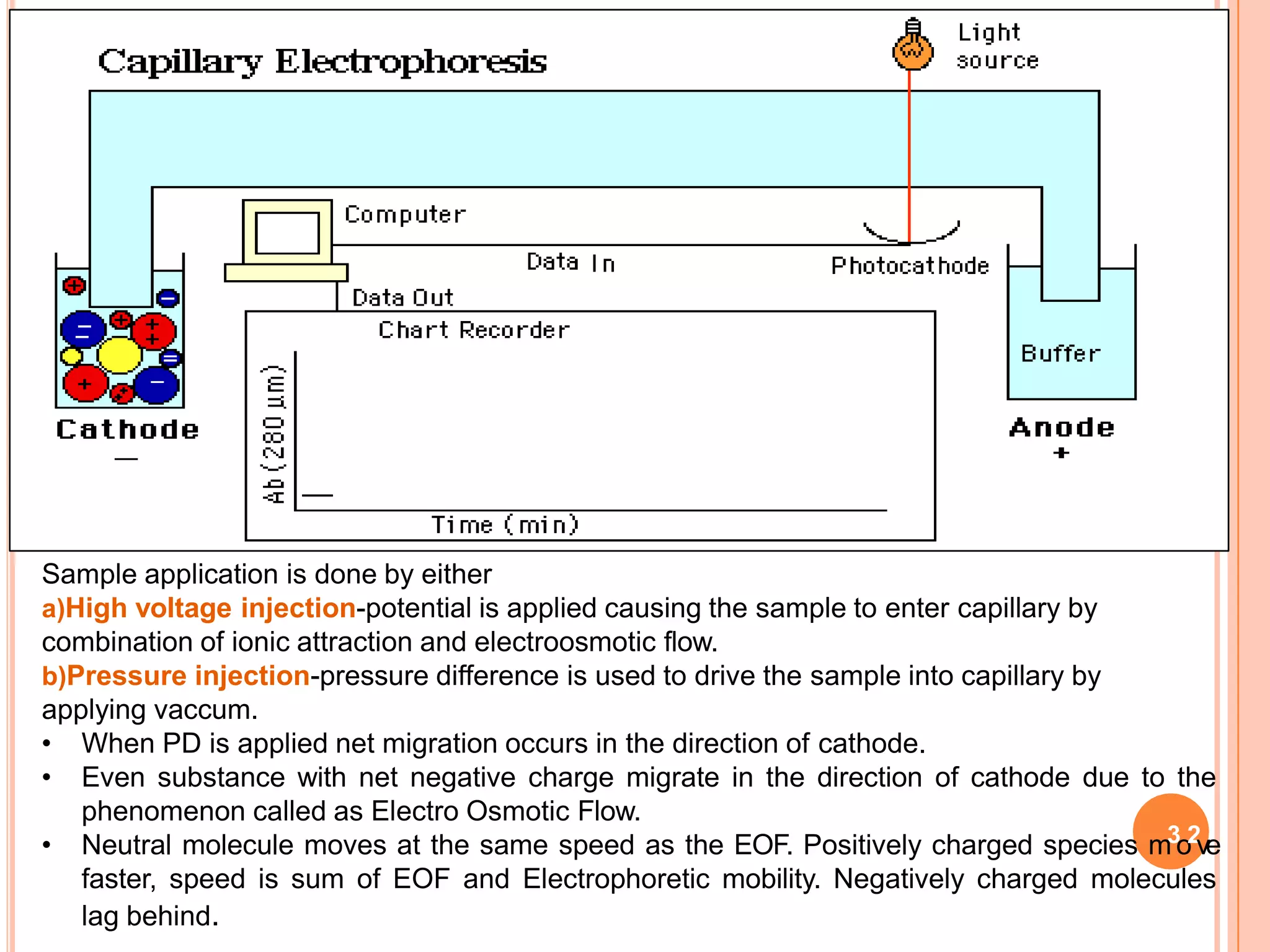
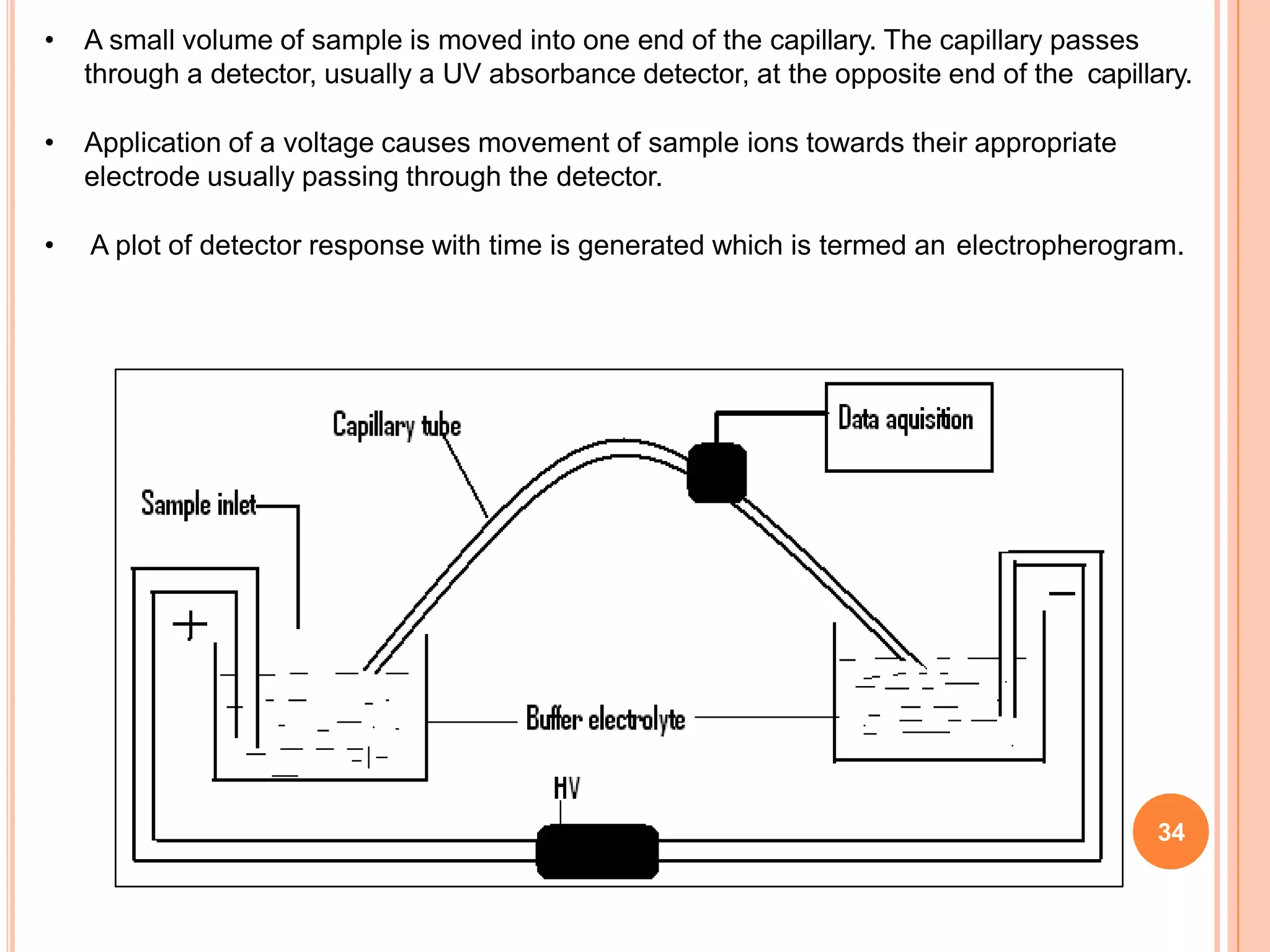
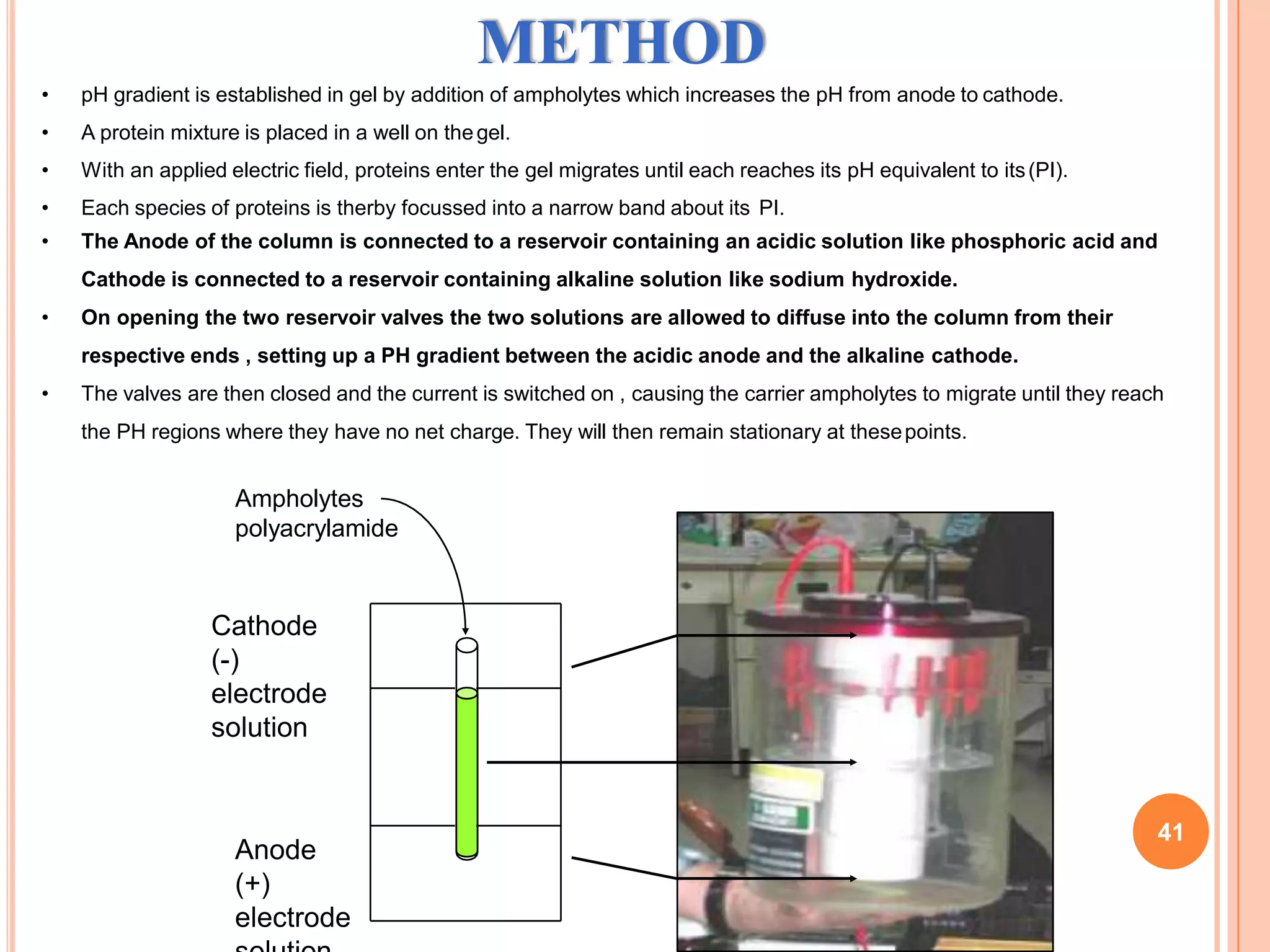
Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate charged molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. It works by applying an electric field to move these molecules through a medium such as a gel or paper. There are different types of electrophoresis based on the medium used and whether the molecules are separated by size alone or by their charge. Zone electrophoresis separates molecules into discrete zones based on their charge and size, while moving boundary electrophoresis separates molecules continuously. SDS-PAGE is a common electrophoresis method that uses SDS detergent to denature proteins and give them a uniform charge-to-size ratio for separation based only on their molecular weight.