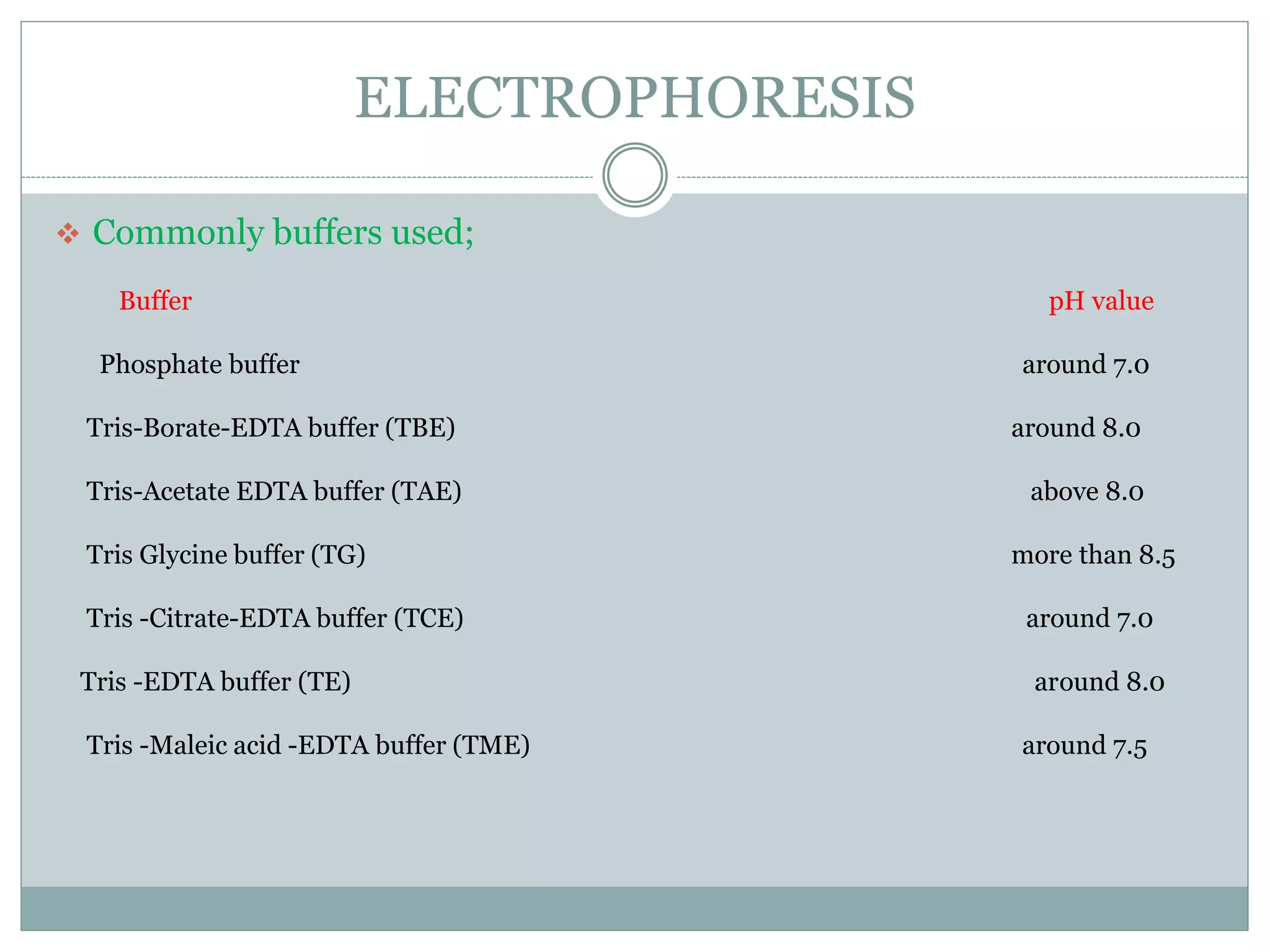
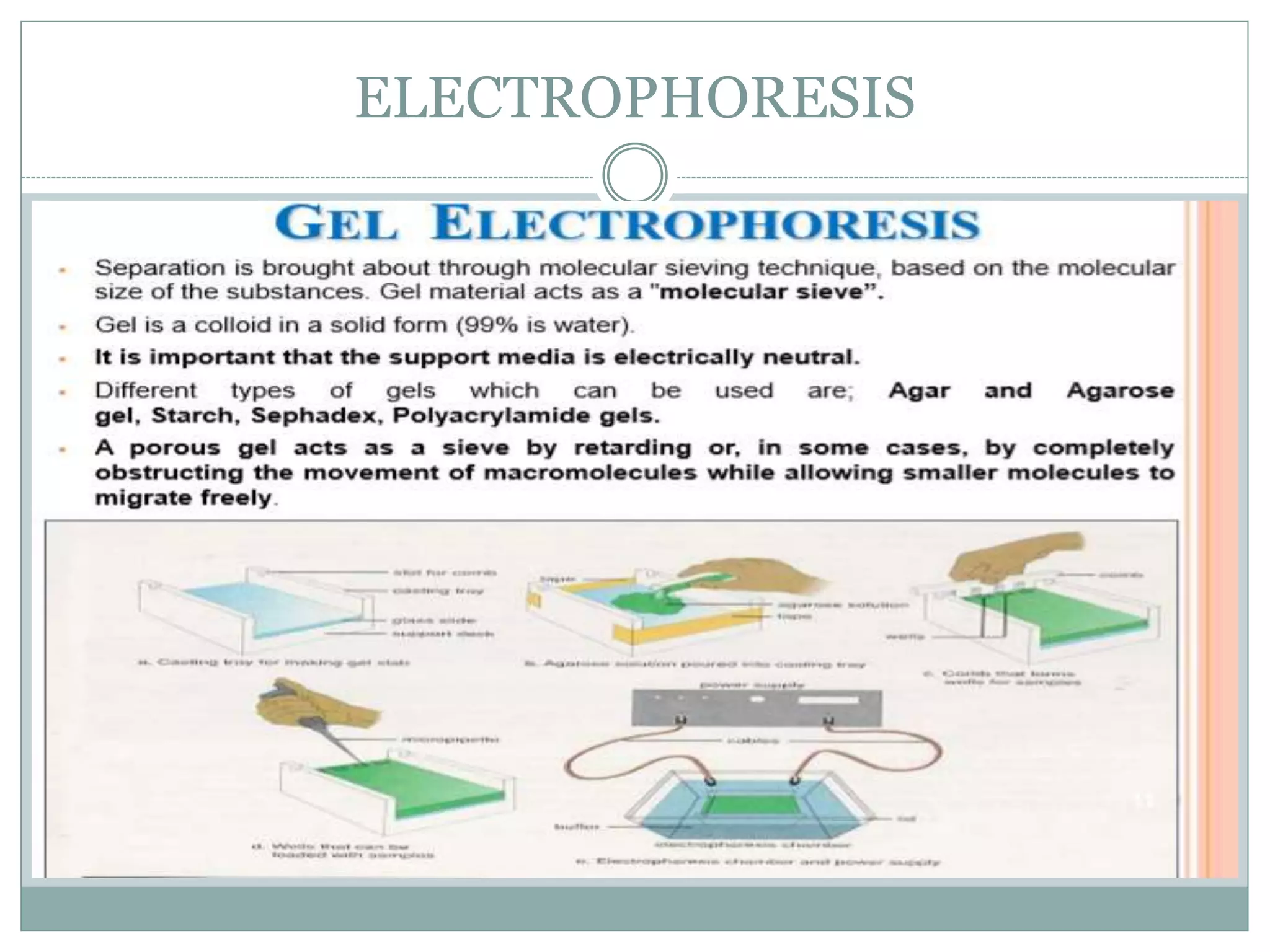
Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate charged molecules like proteins and nucleic acids. It works by applying an electric field to move molecules through a buffer solution or gel based on their size and charge. There are several types of electrophoresis that use different supporting media like agarose gel, polyacrylamide gel, cellulose acetate, or paper to separate molecules. Factors like pH, buffer composition, strength of electric field, and temperature influence how molecules separate during electrophoresis. It has various applications in biomedical research and clinical diagnostics.