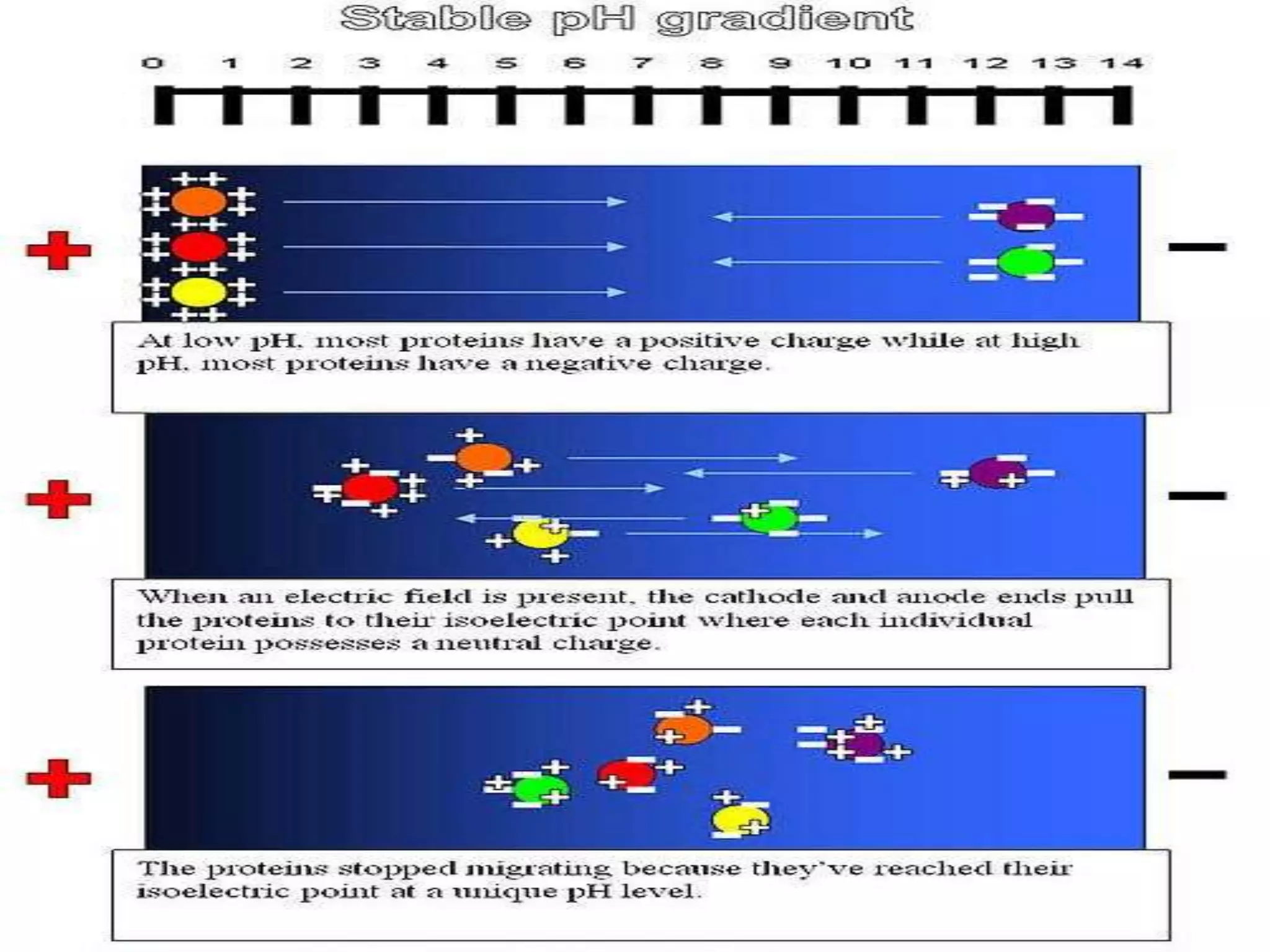
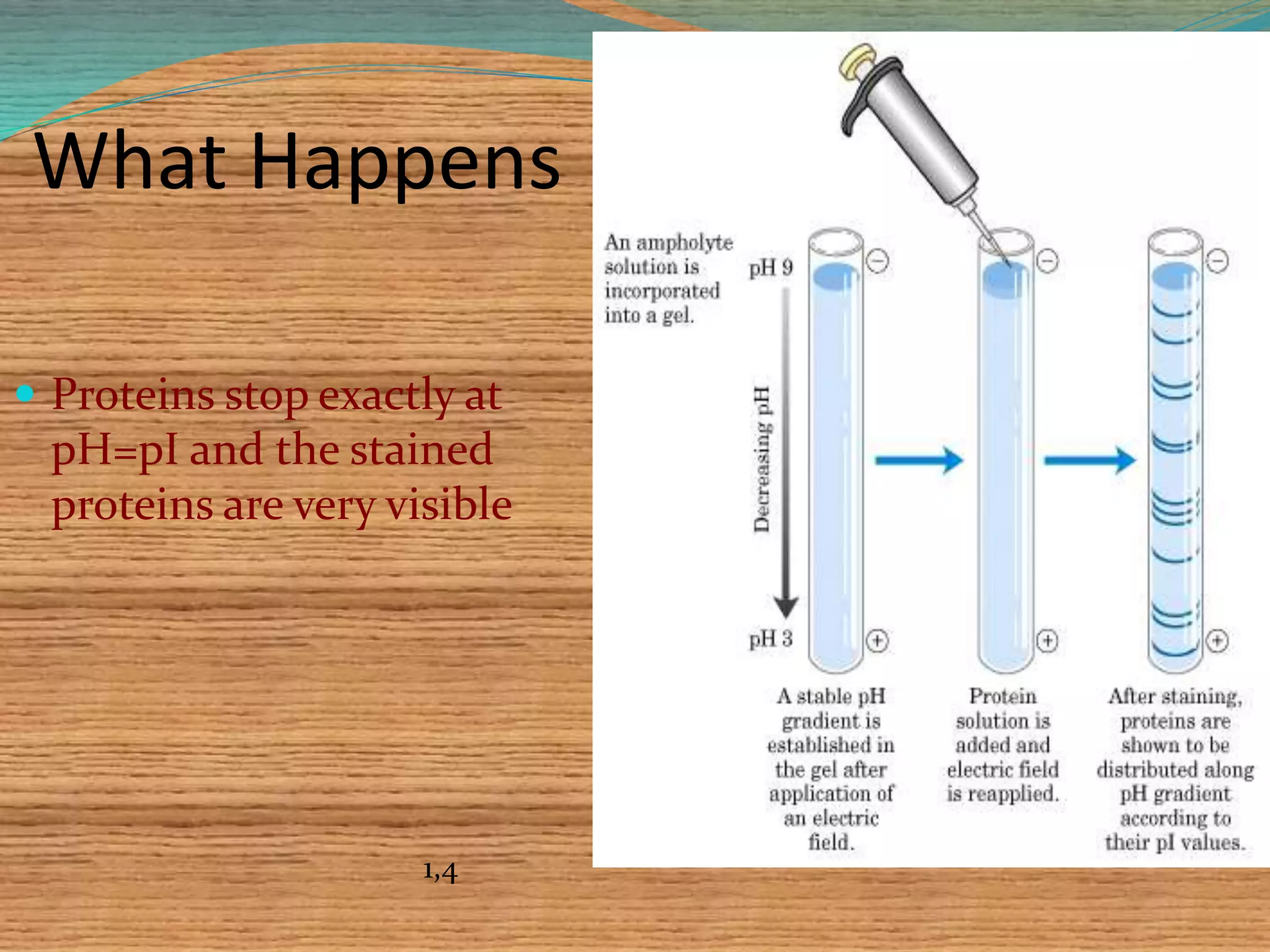
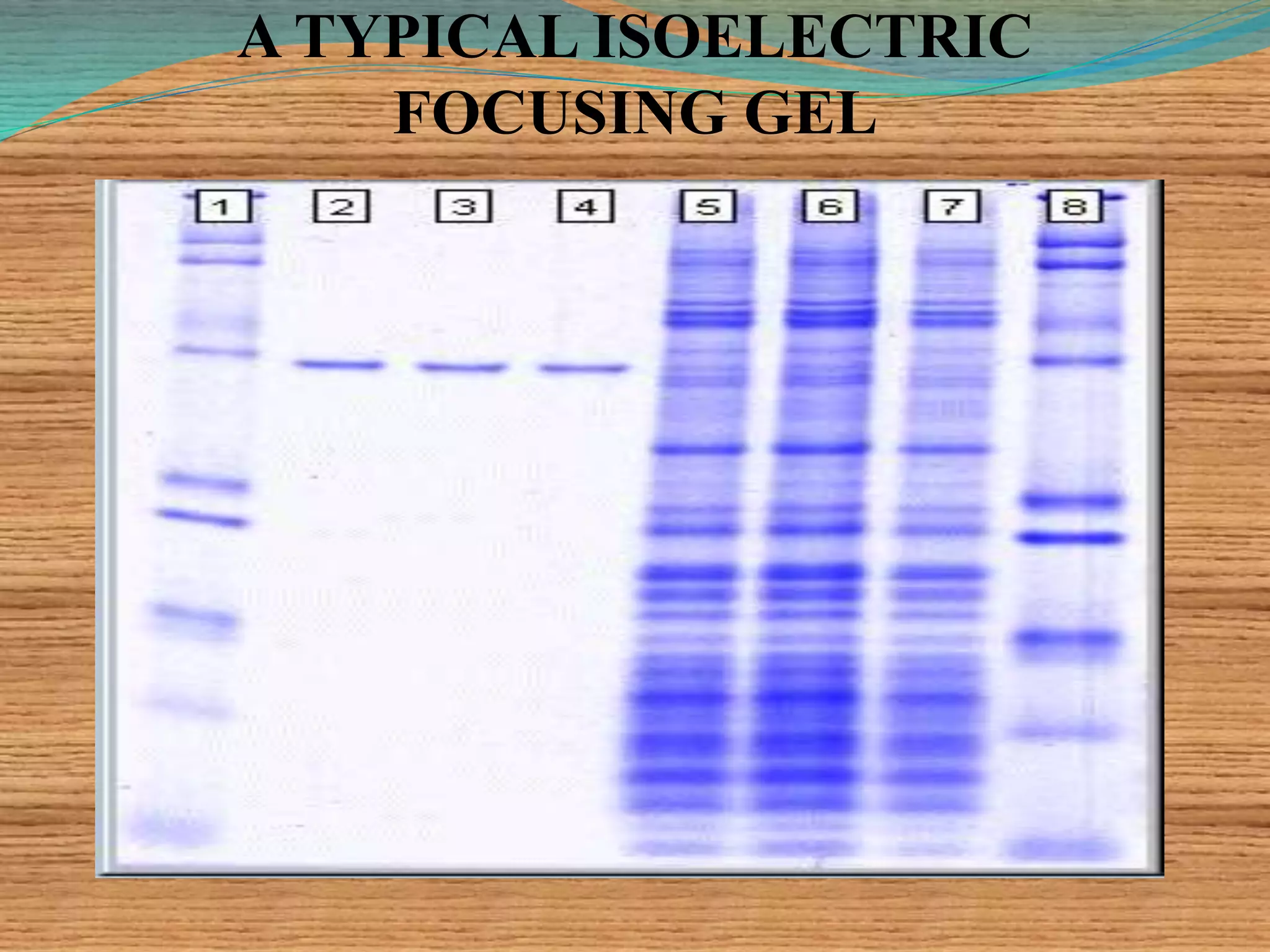
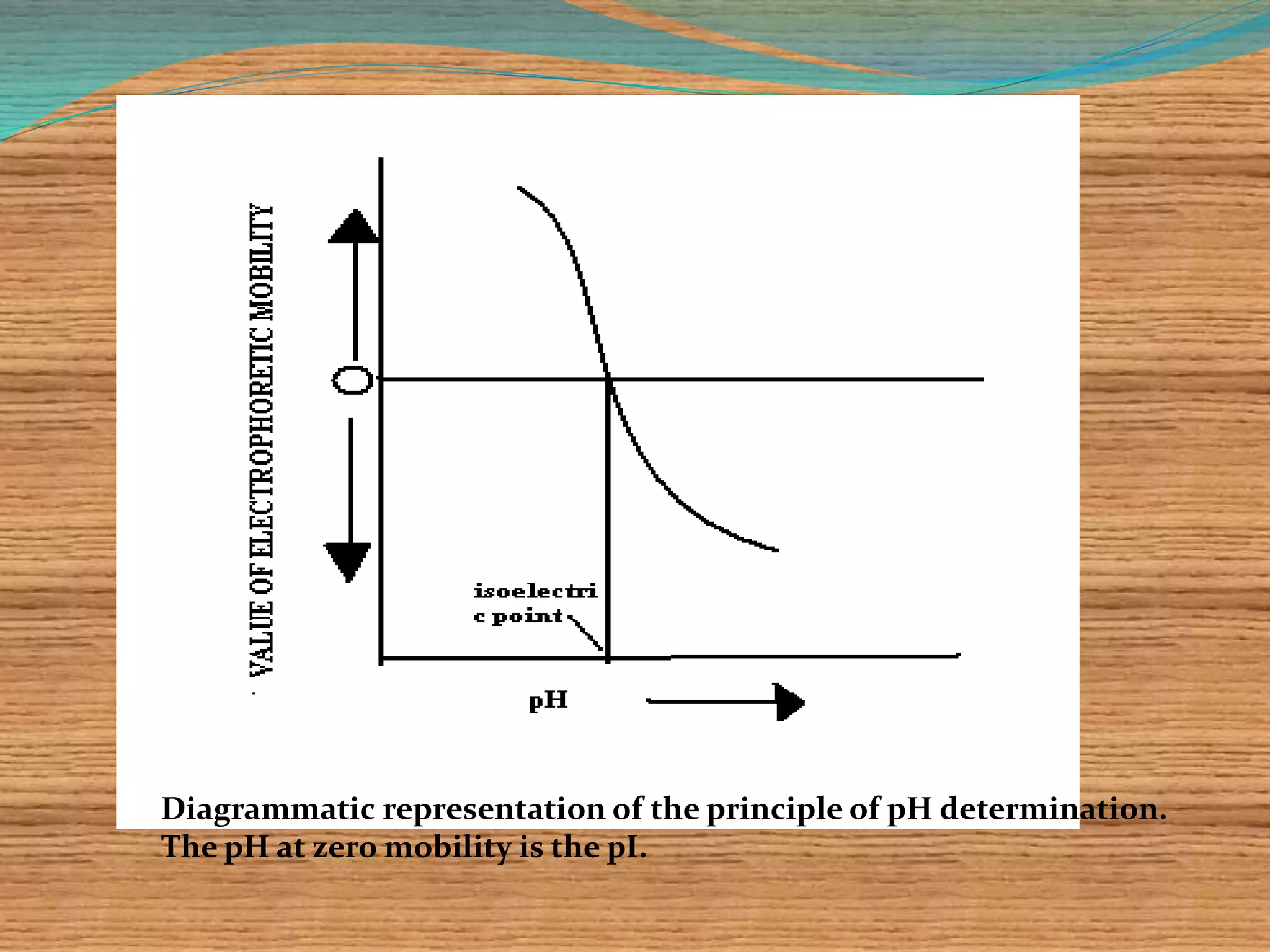
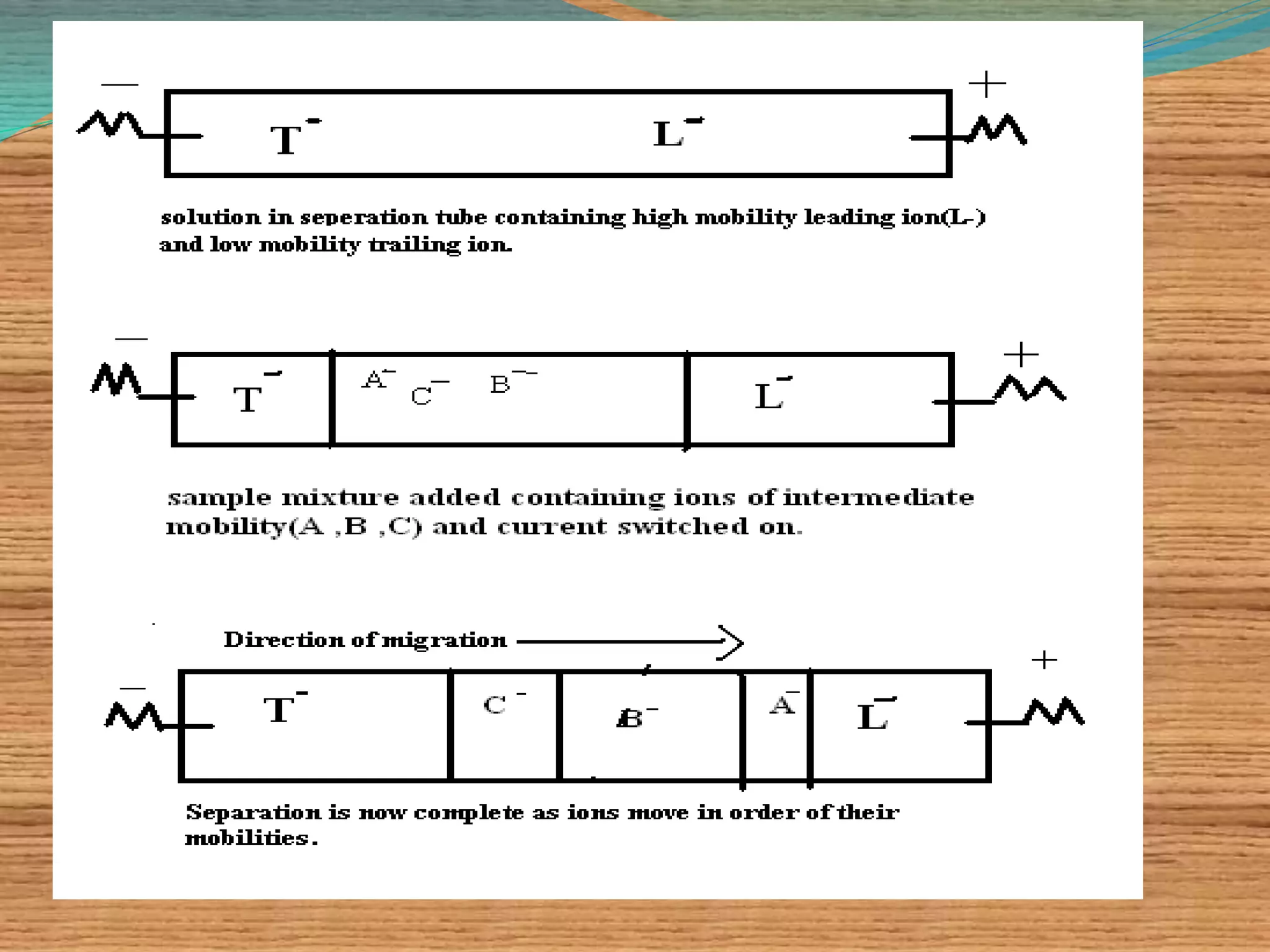
This document provides an overview of isoelectric focusing and isotachophoresis. Isoelectric focusing separates proteins according to their isolectric point (pI), which is the pH at which a protein has no net charge. It works by applying a potential across an immobilized pH gradient gel containing ampholytes. Proteins will migrate within the gel until they reach the pH that matches their pI and stop. Isotachophoresis separates ions based on their electrophoretic mobility by creating discrete zones within a discontinuous electrolyte system. Both techniques provide high resolution separation and have various applications in research, quality control, and identification of substances.