Electronics noise
•Download as PPT, PDF•
2 likes•2,796 views
Noise is always present in electronic systems due to fluctuations in the atomic structure of components. There are several common types of noise including thermal noise caused by heat from random atom movement, flicker noise from random charge carrier variations, and shot noise from uneven charge distributions. The signal-to-noise ratio is used to quantify signal quality and is the ratio of signal power to noise power expressed in decibels, with a higher ratio indicating less noise corruption of the signal.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
FM demodulation using PLL

The document discusses FM demodulation using a phase-locked loop (PLL). A PLL consists of a phase detector, loop filter, and voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) connected in a feedback loop. It works by using the phase detector to compare the input signal frequency to the VCO output frequency. Any difference or error signal is fed through the loop filter to control the VCO frequency, adjusting it until the two frequencies are synchronized and phase-locked. In this way, a PLL can track the frequency and phase of an incoming FM signal to demodulate it.
Fm receiver

The document describes an FM receiver project. It includes the group members, an overview of radio receivers and how they work, classifications of receivers, details on AM and FM receivers, the circuit diagram and components of the FM receiver, and descriptions of the main sections in the block diagram including the RF amplifier, mixer, filter, IF amplifier, limiter, demodulator, AF amplifier, and oscillator.
Adaptive delta modulation

Adaptive delta modulation is a technique that makes the step size adaptive to variations in the input signal in order to overcome quantization errors from slope overload and granular noise. It works by increasing the step size in sections of the signal where it is changing rapidly and decreasing it where the signal is changing slowly. The transmitter uses adaptive logic to continuously or discretely change the step size based on the one-bit quantizer output. The receiver reproduces the step size and uses an accumulator and low-pass filter to reconstruct the original signal from the transmitted bit sequence and adaptively changing step sizes. Adaptive delta modulation provides better signal-to-noise ratio, wider dynamic range, and more efficient bandwidth utilization than regular delta modulation.
Emi unit iii ppt

A signal generator produces standardized electronic signals that can be modulated in amplitude, frequency, or other properties. It is used to test electronic devices and components. A standard signal generator generates stable, controllable voltages that can be amplitude or frequency modulated. It is commonly used to test radios and transmitters. A function generator produces common waveform types like sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth waves over a wide frequency range for testing purposes.
Amplitude modulation & demodulation 

This document discusses amplitude modulation and demodulation. It defines amplitude modulation as varying the amplitude of a carrier wave linearly with a message signal while keeping frequency and phase constant. Modulation is used to transmit signals over long distances and allow multiple signals over the same channel. Demodulation recovers the signal intelligence by reversing the modulation process through rectification and filtering. The document describes amplitude modulation and different types of AM demodulation techniques.
Filters

The document discusses different types of filters including low pass, high pass, band pass, and band reject filters. It provides details on passive and active low pass and high pass filters. For low pass filters, it explains that they pass low frequencies and attenuate high frequencies, with the cutoff frequency determining where signals start to be reduced. For high pass filters, it describes that they pass high frequencies and attenuate low frequencies below the cutoff point. Examples are given of simple passive RC low and high pass filter circuits and how to create active versions using op-amps for amplification and gain control while maintaining the same frequency response.
Instrumentation amplifier

The document discusses the instrumentation amplifier (IA). It begins by introducing the IA, noting its high input impedance, precisely adjustable gain using a single resistor, and high common mode rejection. It then describes the two stages of an IA: the first offers high input impedance and sets the gain, while the second is a differential amplifier with feedback and grounding that offers very high input impedance. Applications discussed include using a thermistor in a bridge circuit with an IA to indicate temperature.
Pre-emphasis and De-emphasis.pptx

This document discusses pre-emphasis and de-emphasis in analog communication systems. Pre-emphasis is used at the transmitter to boost higher modulating frequencies, reducing noise effects. It involves passing the audio through a high-pass filter. De-emphasis is used at the receiver to remove the boosting, involving a low-pass filter. Both use time constants of 50 microseconds according to standards. Pre-emphasis increases modulation index for higher frequencies while de-emphasis removes this at the receiver.
Recommended
FM demodulation using PLL

The document discusses FM demodulation using a phase-locked loop (PLL). A PLL consists of a phase detector, loop filter, and voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) connected in a feedback loop. It works by using the phase detector to compare the input signal frequency to the VCO output frequency. Any difference or error signal is fed through the loop filter to control the VCO frequency, adjusting it until the two frequencies are synchronized and phase-locked. In this way, a PLL can track the frequency and phase of an incoming FM signal to demodulate it.
Fm receiver

The document describes an FM receiver project. It includes the group members, an overview of radio receivers and how they work, classifications of receivers, details on AM and FM receivers, the circuit diagram and components of the FM receiver, and descriptions of the main sections in the block diagram including the RF amplifier, mixer, filter, IF amplifier, limiter, demodulator, AF amplifier, and oscillator.
Adaptive delta modulation

Adaptive delta modulation is a technique that makes the step size adaptive to variations in the input signal in order to overcome quantization errors from slope overload and granular noise. It works by increasing the step size in sections of the signal where it is changing rapidly and decreasing it where the signal is changing slowly. The transmitter uses adaptive logic to continuously or discretely change the step size based on the one-bit quantizer output. The receiver reproduces the step size and uses an accumulator and low-pass filter to reconstruct the original signal from the transmitted bit sequence and adaptively changing step sizes. Adaptive delta modulation provides better signal-to-noise ratio, wider dynamic range, and more efficient bandwidth utilization than regular delta modulation.
Emi unit iii ppt

A signal generator produces standardized electronic signals that can be modulated in amplitude, frequency, or other properties. It is used to test electronic devices and components. A standard signal generator generates stable, controllable voltages that can be amplitude or frequency modulated. It is commonly used to test radios and transmitters. A function generator produces common waveform types like sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth waves over a wide frequency range for testing purposes.
Amplitude modulation & demodulation 

This document discusses amplitude modulation and demodulation. It defines amplitude modulation as varying the amplitude of a carrier wave linearly with a message signal while keeping frequency and phase constant. Modulation is used to transmit signals over long distances and allow multiple signals over the same channel. Demodulation recovers the signal intelligence by reversing the modulation process through rectification and filtering. The document describes amplitude modulation and different types of AM demodulation techniques.
Filters

The document discusses different types of filters including low pass, high pass, band pass, and band reject filters. It provides details on passive and active low pass and high pass filters. For low pass filters, it explains that they pass low frequencies and attenuate high frequencies, with the cutoff frequency determining where signals start to be reduced. For high pass filters, it describes that they pass high frequencies and attenuate low frequencies below the cutoff point. Examples are given of simple passive RC low and high pass filter circuits and how to create active versions using op-amps for amplification and gain control while maintaining the same frequency response.
Instrumentation amplifier

The document discusses the instrumentation amplifier (IA). It begins by introducing the IA, noting its high input impedance, precisely adjustable gain using a single resistor, and high common mode rejection. It then describes the two stages of an IA: the first offers high input impedance and sets the gain, while the second is a differential amplifier with feedback and grounding that offers very high input impedance. Applications discussed include using a thermistor in a bridge circuit with an IA to indicate temperature.
Pre-emphasis and De-emphasis.pptx

This document discusses pre-emphasis and de-emphasis in analog communication systems. Pre-emphasis is used at the transmitter to boost higher modulating frequencies, reducing noise effects. It involves passing the audio through a high-pass filter. De-emphasis is used at the receiver to remove the boosting, involving a low-pass filter. Both use time constants of 50 microseconds according to standards. Pre-emphasis increases modulation index for higher frequencies while de-emphasis removes this at the receiver.
Frequency Modulation

This document discusses frequency modulation (FM) and its types: phase modulation and frequency modulation. It describes the key characteristics of FM including its constant amplitude, higher signal-to-noise ratio, and infinite bandwidth. FM is classified as narrowband FM (NBFM) or wideband FM (WBFM) based on the modulation index. The document also covers pre-emphasis and de-emphasis circuits, methods for generating NBFM and WBFM signals including the direct and indirect (Armstrong's) methods.
Superhetrodyne receiver

The document describes the key components and operation of a super heterodyne receiver. It has five main sections: RF section, mixer/converter section, IF section, audio detector section, and audio amplifier section. The RF section captures the signal and RF amplifier boosts it. The mixer downconverts the RF signal to an intermediate frequency. The IF section filters and amplifies the IF signal before the audio detector extracts the audio signal, which is then amplified in the audio section. Benefits of this receiver design include simplicity, good fidelity, selectivity, and adaptability.
3.Frequency Domain Representation of Signals and Systems

This document provides an overview of frequency domain representation of signals and systems. It defines key concepts such as the Fourier transform, which converts a signal from the time domain to the frequency domain. The frequency spectrum shows the distribution of frequencies within a signal. Periodic signals can be represented using Fourier series, while aperiodic signals use the Fourier transform. Properties of the Fourier transform such as linearity, time shifting, and the convolution theorem are also covered.
Low pass filters

low pass filters in detail
Low Pass Filters
RC Low Pass Filter
Critical or cutoff frequency
Response curve
Cutoff frequency of RC LPF
RL Low Pass Filter
Cutoff Frequency of RL LPF
Phase Response in Low Pass Filter
Microwave measurements in detail

This document discusses various microwave measurement techniques, including:
- Power, VSWR, impedance, frequency, cavity Q, and wavelength measurements.
- Common measurement devices are vector network analyzers, spectrum analyzers, power meters, tunable detectors, slotted sections, and VSWR meters.
- Power is typically measured using diode detectors, bolometers, or thermocouples, which convert RF power to a measurable DC signal.
Quadrature amplitude modulation

Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is a modulation technique that encodes data by changing both the amplitude and phase of carrier waves. It allows more data to be transmitted over a given bandwidth compared to techniques that only vary the amplitude or phase. QAM modulators use two carrier waves shifted in phase by 90 degrees that are modulated by separate data streams before being combined. Higher order QAM schemes use constellations with more points that allow more bits to be encoded per symbol. While this improves bandwidth efficiency, it also makes the system more susceptible to noise. QAM is widely used in technologies like DSL, wireless networks, cable TV, and microwave backhaul systems.
Phase locked loop

This document provides an overview of phase locked loops (PLL) including:
1. The basic components of a PLL including a phase detector, low pass filter, and voltage controlled oscillator that work together in a closed loop to lock the output frequency and phase to the input signal.
2. Examples of PLL applications such as frequency multiplication, FM demodulation, and motor speed control.
3. A more detailed description of the 565 PLL IC including its pin configuration and characteristics such as operating frequency range and drift with temperature/voltage.
Fm transmitter and receivers

FM transmitters and receivers are used for sending and receiving FM signals. Transmitters modulate a carrier wave with an audio signal to generate an FM signal, which is transmitted through a band. Receivers receive the modulated signal, demodulate it to extract the original audio signal. FM offers advantages over AM like noise reduction, improved fidelity, and more efficient power use, though it requires more complex circuits and a larger bandwidth. Applications of FM include radio broadcasting, mobile radio, TV sound, and cellular/satellite communication.
Noise in communication system

The document discusses different types of noise that affect communication systems, including thermal noise, shot noise, flicker noise, excess resistor noise, and popcorn noise. It provides details on thermal noise generation and its relation to temperature and resistance. The analysis section examines thermal noise in resistors in series and parallel and defines signal-to-noise ratio and noise factor. Additive white Gaussian noise is described as noise that is additive, has a constant spectral density (white), and has a Gaussian amplitude distribution.
EEG (ELECTROENCEPALOGRAM)

This slide has been prepared in detaied manner and will help you.
The topics covered are:-
1- introduction
2.circuit diagram and its explaination
3.working
4. features
5.advantages / disadvantages
6. the top vendors
Generation of fm

This document discusses the generation of frequency modulation (FM) using direct and indirect methods. The direct method uses a reactance modulator like a varactor diode or FET placed across an LC oscillator tank circuit to vary the capacitance or inductance in proportion to the modulating voltage. The indirect method generates FM through phase modulation using a crystal oscillator and phase modulator, then detecting the phase changes to create FM. Vector diagrams are also presented to illustrate phase modulation. Effects of frequency changing like multiplication and mixing on FM signals are explained.
Phase Locked Loop (PLL)

The document discusses a Phase Locked Loop (PLL). It describes PLL as a circuit that synchronizes an output signal generated by an oscillator to match the frequency and phase of a reference input signal. The key functional blocks of a PLL are a phase detector, low pass filter, and voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). The phase detector compares the input and feedback frequencies and provides an error signal. The low pass filter removes noise and the VCO generates the output frequency controlled by the error signal voltage. A PLL goes through free running, capture, and phase locked stages of operation. Applications of PLL include frequency modulation/demodulation and signal synchronization.
Attenuators and phase shifters 24

This document discusses attenuators and phase shifters. It describes how attenuators are used to reduce signal power without distortion, and includes fixed and variable types. Fixed attenuators are commonly used where a fixed amount of power is needed, while variable attenuators provide continuous or stepwise adjustable attenuation using methods like flap or vane designs. Phase shifters are also discussed, including ferrite and semiconductor types. Applications of phase shifters include communication systems, radar, and industrial uses. Key specifications for digital phase shifters are provided.
Demodulation of AM wave

AM wave demodulation, Envelop detector, Square law detection, Difference between AM modulation and FM modulation
Frequency modulation and its application

This document discusses frequency modulation (FM) including its definition, modulation index, spectrum characteristics, types of FM modulation, generation of FM using phase modulation, advantages and disadvantages compared to other modulation techniques, and applications of FM such as in radio broadcasting, television sound, and satellite television. FM provides noise immunity and allows adjusting the noise level by changing the frequency deviation. It is widely used for radio but requires more complex transmission and reception equipment than other modulation methods.
Signal Filtering

This document discusses signal filtering techniques. It introduces electronic filters and their characteristics such as cut-off frequency, stop band, and pass band. It describes different types of filters and provides examples of their applications. The document then focuses on 1D signal filtering, specifically analyzing audio signals. It explains the Butterworth filter and Wiener filter, applying each to a noisy speech signal to suppress frequencies and reduce noise. The Wiener filter is found to have better noise reduction capabilities. In conclusion, signal filtering is important for signal processing, and the Butterworth and Wiener filters can be used to filter 1D noisy signals.
Phase modulation

Phase modulation (PM) is a form of modulation where information is represented by variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. The phase angle of the complex envelope is changed in direct proportion to the message signal. PM can be considered a special case of FM where the carrier frequency modulation is given by the time derivative of the phase modulation. The bandwidth of PM for a single sinusoidal signal is approximately equal to the modulation index multiplied by the carrier frequency.
Microwave

Microwave engineering involves the design of communication and navigation systems that operate in the microwave frequency range. Key topics in microwave engineering include microwave networks, scattering parameters, power dividers, couplers, filters, and amplifiers. Microwave systems have applications in areas like microwave ovens, radar, satellite communications, and personal communication systems.
Signal generators

This document provides an overview of signal generators. It discusses the basic components and applications of signal generators, including providing waveforms for testing electronic circuits at low powers. It describes the oscillator that provides the output signal and different waveform options. It also covers the requirements for frequency, amplitude, and distortion for the output signal. The document then discusses different frequency bands and types of fixed and variable frequency oscillators. It provides examples of basic, standard, and modern laboratory signal generators. It describes the front panel controls of an AF sine and square wave generator and includes block diagrams of a square and pulse generator and sweep frequency generator.
Eeng 3810 chapter 4

This document discusses amplitude modulation (AM) and covers topics like:
1. Generation of AM signals using double sideband full carrier (DSBFC) modulation.
2. Calculating sideband frequencies and bandwidth for different modulation scenarios.
3. Examining the voltage spectrum and time-domain representation of AM signals.
4. Looking at different AM transmitter and receiver circuit designs including single sideband techniques.
Electronics amplifiers

The push-pull amplifier uses two complementary power transistors arranged in a symmetrical configuration to amplify an input signal. There are different classes of linear amplifiers - Class A always conducts but is inefficient, Class B has zero quiescent current but high distortion, and Class AB balances these tradeoffs. The class is determined by the quiescent current. Feedback amplifiers have gains that are stable over temperature and reduce distortion.
Electronics decibel

The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two power levels or amplitudes. It is commonly used to measure sound levels and power in electronic systems. A decibel represents one tenth of a bel and can express power gain or attenuation. Power gain is calculated as 10 times the log of the ratio between output and input power. A 3dB gain doubles the power. Attenuation is expressed as a negative value and represents a reduction in power. Gain can also be expressed for voltage or current using 20 times the log of the output to input ratio. Multiple stage amplifiers have a total gain equal to the sum of the individual stage gains.
More Related Content
What's hot
Frequency Modulation

This document discusses frequency modulation (FM) and its types: phase modulation and frequency modulation. It describes the key characteristics of FM including its constant amplitude, higher signal-to-noise ratio, and infinite bandwidth. FM is classified as narrowband FM (NBFM) or wideband FM (WBFM) based on the modulation index. The document also covers pre-emphasis and de-emphasis circuits, methods for generating NBFM and WBFM signals including the direct and indirect (Armstrong's) methods.
Superhetrodyne receiver

The document describes the key components and operation of a super heterodyne receiver. It has five main sections: RF section, mixer/converter section, IF section, audio detector section, and audio amplifier section. The RF section captures the signal and RF amplifier boosts it. The mixer downconverts the RF signal to an intermediate frequency. The IF section filters and amplifies the IF signal before the audio detector extracts the audio signal, which is then amplified in the audio section. Benefits of this receiver design include simplicity, good fidelity, selectivity, and adaptability.
3.Frequency Domain Representation of Signals and Systems

This document provides an overview of frequency domain representation of signals and systems. It defines key concepts such as the Fourier transform, which converts a signal from the time domain to the frequency domain. The frequency spectrum shows the distribution of frequencies within a signal. Periodic signals can be represented using Fourier series, while aperiodic signals use the Fourier transform. Properties of the Fourier transform such as linearity, time shifting, and the convolution theorem are also covered.
Low pass filters

low pass filters in detail
Low Pass Filters
RC Low Pass Filter
Critical or cutoff frequency
Response curve
Cutoff frequency of RC LPF
RL Low Pass Filter
Cutoff Frequency of RL LPF
Phase Response in Low Pass Filter
Microwave measurements in detail

This document discusses various microwave measurement techniques, including:
- Power, VSWR, impedance, frequency, cavity Q, and wavelength measurements.
- Common measurement devices are vector network analyzers, spectrum analyzers, power meters, tunable detectors, slotted sections, and VSWR meters.
- Power is typically measured using diode detectors, bolometers, or thermocouples, which convert RF power to a measurable DC signal.
Quadrature amplitude modulation

Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is a modulation technique that encodes data by changing both the amplitude and phase of carrier waves. It allows more data to be transmitted over a given bandwidth compared to techniques that only vary the amplitude or phase. QAM modulators use two carrier waves shifted in phase by 90 degrees that are modulated by separate data streams before being combined. Higher order QAM schemes use constellations with more points that allow more bits to be encoded per symbol. While this improves bandwidth efficiency, it also makes the system more susceptible to noise. QAM is widely used in technologies like DSL, wireless networks, cable TV, and microwave backhaul systems.
Phase locked loop

This document provides an overview of phase locked loops (PLL) including:
1. The basic components of a PLL including a phase detector, low pass filter, and voltage controlled oscillator that work together in a closed loop to lock the output frequency and phase to the input signal.
2. Examples of PLL applications such as frequency multiplication, FM demodulation, and motor speed control.
3. A more detailed description of the 565 PLL IC including its pin configuration and characteristics such as operating frequency range and drift with temperature/voltage.
Fm transmitter and receivers

FM transmitters and receivers are used for sending and receiving FM signals. Transmitters modulate a carrier wave with an audio signal to generate an FM signal, which is transmitted through a band. Receivers receive the modulated signal, demodulate it to extract the original audio signal. FM offers advantages over AM like noise reduction, improved fidelity, and more efficient power use, though it requires more complex circuits and a larger bandwidth. Applications of FM include radio broadcasting, mobile radio, TV sound, and cellular/satellite communication.
Noise in communication system

The document discusses different types of noise that affect communication systems, including thermal noise, shot noise, flicker noise, excess resistor noise, and popcorn noise. It provides details on thermal noise generation and its relation to temperature and resistance. The analysis section examines thermal noise in resistors in series and parallel and defines signal-to-noise ratio and noise factor. Additive white Gaussian noise is described as noise that is additive, has a constant spectral density (white), and has a Gaussian amplitude distribution.
EEG (ELECTROENCEPALOGRAM)

This slide has been prepared in detaied manner and will help you.
The topics covered are:-
1- introduction
2.circuit diagram and its explaination
3.working
4. features
5.advantages / disadvantages
6. the top vendors
Generation of fm

This document discusses the generation of frequency modulation (FM) using direct and indirect methods. The direct method uses a reactance modulator like a varactor diode or FET placed across an LC oscillator tank circuit to vary the capacitance or inductance in proportion to the modulating voltage. The indirect method generates FM through phase modulation using a crystal oscillator and phase modulator, then detecting the phase changes to create FM. Vector diagrams are also presented to illustrate phase modulation. Effects of frequency changing like multiplication and mixing on FM signals are explained.
Phase Locked Loop (PLL)

The document discusses a Phase Locked Loop (PLL). It describes PLL as a circuit that synchronizes an output signal generated by an oscillator to match the frequency and phase of a reference input signal. The key functional blocks of a PLL are a phase detector, low pass filter, and voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). The phase detector compares the input and feedback frequencies and provides an error signal. The low pass filter removes noise and the VCO generates the output frequency controlled by the error signal voltage. A PLL goes through free running, capture, and phase locked stages of operation. Applications of PLL include frequency modulation/demodulation and signal synchronization.
Attenuators and phase shifters 24

This document discusses attenuators and phase shifters. It describes how attenuators are used to reduce signal power without distortion, and includes fixed and variable types. Fixed attenuators are commonly used where a fixed amount of power is needed, while variable attenuators provide continuous or stepwise adjustable attenuation using methods like flap or vane designs. Phase shifters are also discussed, including ferrite and semiconductor types. Applications of phase shifters include communication systems, radar, and industrial uses. Key specifications for digital phase shifters are provided.
Demodulation of AM wave

AM wave demodulation, Envelop detector, Square law detection, Difference between AM modulation and FM modulation
Frequency modulation and its application

This document discusses frequency modulation (FM) including its definition, modulation index, spectrum characteristics, types of FM modulation, generation of FM using phase modulation, advantages and disadvantages compared to other modulation techniques, and applications of FM such as in radio broadcasting, television sound, and satellite television. FM provides noise immunity and allows adjusting the noise level by changing the frequency deviation. It is widely used for radio but requires more complex transmission and reception equipment than other modulation methods.
Signal Filtering

This document discusses signal filtering techniques. It introduces electronic filters and their characteristics such as cut-off frequency, stop band, and pass band. It describes different types of filters and provides examples of their applications. The document then focuses on 1D signal filtering, specifically analyzing audio signals. It explains the Butterworth filter and Wiener filter, applying each to a noisy speech signal to suppress frequencies and reduce noise. The Wiener filter is found to have better noise reduction capabilities. In conclusion, signal filtering is important for signal processing, and the Butterworth and Wiener filters can be used to filter 1D noisy signals.
Phase modulation

Phase modulation (PM) is a form of modulation where information is represented by variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. The phase angle of the complex envelope is changed in direct proportion to the message signal. PM can be considered a special case of FM where the carrier frequency modulation is given by the time derivative of the phase modulation. The bandwidth of PM for a single sinusoidal signal is approximately equal to the modulation index multiplied by the carrier frequency.
Microwave

Microwave engineering involves the design of communication and navigation systems that operate in the microwave frequency range. Key topics in microwave engineering include microwave networks, scattering parameters, power dividers, couplers, filters, and amplifiers. Microwave systems have applications in areas like microwave ovens, radar, satellite communications, and personal communication systems.
Signal generators

This document provides an overview of signal generators. It discusses the basic components and applications of signal generators, including providing waveforms for testing electronic circuits at low powers. It describes the oscillator that provides the output signal and different waveform options. It also covers the requirements for frequency, amplitude, and distortion for the output signal. The document then discusses different frequency bands and types of fixed and variable frequency oscillators. It provides examples of basic, standard, and modern laboratory signal generators. It describes the front panel controls of an AF sine and square wave generator and includes block diagrams of a square and pulse generator and sweep frequency generator.
Eeng 3810 chapter 4

This document discusses amplitude modulation (AM) and covers topics like:
1. Generation of AM signals using double sideband full carrier (DSBFC) modulation.
2. Calculating sideband frequencies and bandwidth for different modulation scenarios.
3. Examining the voltage spectrum and time-domain representation of AM signals.
4. Looking at different AM transmitter and receiver circuit designs including single sideband techniques.
What's hot (20)
3.Frequency Domain Representation of Signals and Systems

3.Frequency Domain Representation of Signals and Systems
Viewers also liked
Electronics amplifiers

The push-pull amplifier uses two complementary power transistors arranged in a symmetrical configuration to amplify an input signal. There are different classes of linear amplifiers - Class A always conducts but is inefficient, Class B has zero quiescent current but high distortion, and Class AB balances these tradeoffs. The class is determined by the quiescent current. Feedback amplifiers have gains that are stable over temperature and reduce distortion.
Electronics decibel

The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two power levels or amplitudes. It is commonly used to measure sound levels and power in electronic systems. A decibel represents one tenth of a bel and can express power gain or attenuation. Power gain is calculated as 10 times the log of the ratio between output and input power. A 3dB gain doubles the power. Attenuation is expressed as a negative value and represents a reduction in power. Gain can also be expressed for voltage or current using 20 times the log of the output to input ratio. Multiple stage amplifiers have a total gain equal to the sum of the individual stage gains.
Components transistors

The document discusses the transistor, the basic building block of electronics. It describes the two main types - bipolar junction transistors and field effect transistors. Transistors can be used as amplifiers or switches to increase signal amplitude or turn devices on/off. Characteristics like packaging, markings, and applications of small signal and power transistors are covered. Circuit examples show how transistors function as amplifiers and switches.
Components 555 timer

The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit that can be used to generate precise timing pulses or oscillations. It can operate from 3-15V and works in either monostable (one-shot) mode to produce a single pulse, or astable (multivibrator) mode to produce a continuous train of pulses. The duration of pulses in monostable mode or frequency in astable mode is determined by external resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer. Common applications include timers, flashing indicators, and pulse generation.
Electronics power supplies

1. Power supplies convert the 240V AC mains supply into suitable DC voltages between 5-30V for electronic equipment through transformers, rectifiers, and regulators.
2. Transformers convert the AC voltage to a lower isolated AC voltage, which is then rectified to DC and smoothed by capacitors.
3. Various rectifier circuits like half-wave, full-wave, and bridge are used to rectify different portions of the AC cycle. Smoothing circuits use large capacitors to reduce ripple in the DC output.
4. Regulator circuits like zener diodes and integrated circuits are used to stabilize the output DC voltage against fluctuations in the input voltage and load. Heat sinks are required to dissip
Components resistors

Resistors are commonly used electronic components that restrict the flow of electric current. They have a circuit symbol of a zigzag line. Most resistors have four color bands that indicate their resistance value and tolerance according to the resistor color code. Potentiometers are variable resistors that allow adjusting resistance between zero and a maximum value, and are often used as volume controls. Light dependent resistors have a resistance that varies with the amount of light shining on them.
Record audio in Studio One V2 - Stefano Ribaudo

This document provides a step-by-step tutorial for recording audio in a digital audio workstation (DAW). It outlines preparing the DAW project, creating audio tracks, setting the click and countdown, and efficiently recording audio. The tutorial uses Presonus Studio One and a Focusrite audio interface to record vocal audio over multiple takes through a microphone and XLR cable.
Pro tools 8

This chapter provides an overview of how to use Pro Tools. It covers starting up Pro Tools and configuring audio and MIDI hardware. It describes the main user interface elements like the transport controls, edit window, and mix window. It explains how to navigate sessions, zoom and scroll windows, and work with tracks, channels and regions. Key features like muting, soloing, and track heights are demonstrated. The chapter aims to introduce the basic workflow and navigation within the Pro Tools interface.
Hearing Conservation 2010

The document discusses noise exposure at work and hearing conservation programs. It covers the effects of noise on hearing, types of hearing protection, audiometric testing, noise measurement records, and an employer's responsibilities regarding noise exposure and hearing protection. Examples of noisy equipment and their decibel levels are provided, as well as allowable daily noise exposure times without hearing protection.
Decibel insight measurefest october2013_external

This document discusses analytics and insights for website optimization. It provides a strategic framework with 3 questions: 1) What's useful to stakeholders? 2) What's useful to you? 3) What tools do you need? For question 1, it lists top key performance indicators (KPIs) like unique visitors and bounce rates. For question 2, it discusses measuring traffic, content, user experience (UX), and conversion through the success funnel. It provides a 6-step guide to measuring UX and content through audience segmentation, browser testing, visitor playback, popular content analysis, ensuring the right content is seen, and learning navigation patterns. It concludes by stating traditional analytics are missing visual and actionable insights into how users interact with websites
LO4: The decibel scale

The document discusses the decibel scale used to measure sound intensity levels. It explains that the decibel scale is logarithmic since sound intensities detected by the human ear can range from 10-12 W/m2 to 10 W/m2, or 1013 W/m2. The reference point for the decibel scale is set at the lowest intensity the human ear can detect, 0 decibels (10-12 W/m2). Any other sound intensity (I) can be expressed in decibels using the formula: β(I) = 0dB + 10 log10 (I/I0). Two examples are provided showing how decibel increases correspond to multiplicative increases in sound intensity.
The Patchbay

What is a Patchbay?
Connections
Configuration
Inserts points
Compressors and Gates
FX Units and Auxes
Synths and others
Audient patchbay
Pro tools HD Systems

The document discusses Pro Tools systems, including the Control 24 audio interface, HD 192 interface, and Accel Core Card. It covers the basic signal flow and connections of a Pro Tools studio setup. Monitoring, synchronization using SMPTE, MTC, and MIDI Clock are explained. The document also briefly mentions the plug-in architecture and includes a bibliography of additional resources.
Testing

An oscilloscope displays varying signal voltages over time. It plots voltage on the y-axis and time on the x-axis. Trigger controls allow stable displays of periodic or non-periodic signals. Accuracy refers to how close measurements are to the true value and can drift over time. Bandwidth is the range of frequencies over which accurate measurements can be made. Resolution is the smallest change that can alter the reading.
Components operational amplifiers

The operational amplifier (op-amp) is an integrated circuit that can provide voltage gain and be used as a signal amplifier or comparator. It has high input resistance, virtually infinite voltage gain, and two inputs - inverting and non-inverting - and one output. Common op-amp configurations include the inverting amplifier, non-inverting amplifier, summing amplifier, and comparator. The op-amp is a versatile active component used in various circuit applications.
Components the diode

The diode allows current to pass in one direction only. It is used as a rectifier in power supplies to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). The diode uses a single P-N junction made of semiconductor material. The zener diode can operate in reverse bias and maintains a stable voltage, making it useful for voltage regulation and reference circuits. Diodes come in different package styles and are identified by alphanumeric codes and cathode markings.
Microphones

Microphones convert sound waves into electrical signals by using a diaphragm that vibrates when hit by sound waves. This vibration is then converted into a varying electrical current through different mechanisms depending on the microphone type. The main types are dynamic, condenser and ribbon microphones. Microphones can also be classified by their directional properties and application.
Microphone types and characteristics essay

The document summarizes the history and types of microphones. It describes how the first microphone was invented in 1876 and key developments like the ribbon microphone in 1931 and electric microphone in 1964. It then explains how microphones work by transforming sound waves into electrical signals. The main types of microphones are described - dynamic, condenser, ribbon, carbon, crystal - along with their characteristics. Polar patterns like omni-directional, bi-directional and cardioid are also covered. The document concludes by discussing the purpose of different microphones and their appropriate uses.
Microphone 

Microphone is a type of acoustic transducer or sensor.
A microphone, is an acoustic-to-electrical transducer or sensor that converts sound in air into an electrical signal.
Viewers also liked (19)
Similar to Electronics noise
Noise

Noise is an unwanted random fluctuation in an electrical signal that is inherent in all electronic systems. There are two main types of noise: internal noise generated within components like thermal noise and shot noise, and external noise from outside sources such as atmospheric noise. Noise can have detrimental effects on signal quality and effective communication, so techniques are used to quantify noise levels and maximize the signal-to-noise ratio.
Unit 2_Noise.pdf

Noise is any unwanted signal that interferes with the desired signal. There are two main categories of noise - interference from human-made sources and naturally occurring random noise. Naturally occurring noise comes from atmospheric disturbances, solar noise, cosmic noise, and thermal noise within electronic components. Thermal noise arises from the random movement of electrons in conductors and follows Johnson's and Nyquist's laws. Shot noise results from the random arrival of charge carriers. Flicker noise is a low frequency noise that follows a 1/f relationship. Receiver noise comes from internal components and includes thermal noise, shot noise, partition noise, and avalanche noise. The signal-to-noise ratio is a measure of the desired signal strength relative to the
Electrical noise and signal to noise ratio

Electrical noise is any undesirable electrical energy within a signal's pass band. There are several types of noise including man-made, thermal, correlated, and impulse noise. Man-made noise comes from sources like electric motors and lights. Thermal noise results from random electron motion and increases with temperature. Correlated noise is noise related to the signal, like harmonic distortion from nonlinear amplification. Impulse noise consists of short, high amplitude bursts from sources such as electric motors or lightning.
Noise

This document discusses different types of noise in communication systems. It defines noise and describes two main categories of noise: external noise and internal noise. External noise sources include atmospheric noise from lightning, extraterrestrial noise from space objects, and man-made noise from industrial equipment. Internal noise is generated within communication systems and includes thermal noise, shot noise, flicker noise, and intermodulation noise caused by non-linear components. The document provides detailed explanations and examples of different noise sources.
Signals and noise

The document discusses various sources and types of noise in communication systems and instrumentation. It provides details on fundamental, environmental, and instrumental noise. The major types of fundamental noise are thermal, shot, and flicker noise. Thermal noise originates from thermally induced motions in charge carriers and is represented by a formula involving resistance, temperature, and bandwidth. Shot noise arises when current involves the movement of charged particles across a junction, like at a pn interface. Flicker noise is associated with crystal surface defects and decreases with increasing frequency. Hardware techniques for improving signal-to-noise ratio include filtering, grounding/shielding, difference amplifiers, and analog filtering. Narrowing bandwidth and lowering resistance/temperature can reduce thermal noise
Noise....pdf

The signal is the meaningful information that you’re actually trying to detect. The noise is the random, unwanted variation or fluctuation that interferes with the signal. To get a sense of this, imagine trying to tune into a radio station. Ok, you don’t use radio anymore, so imagine your dad can’t call you to get help setting up his Spotify, so is trying to tune into a radio station. He turns the dial but it’s just picking up white noise and, after a few frustrating minutes, he manages to pick up a signal and tune into a station.
The same is true in statistics — there is something you’re trying to actually measure (say, how many Americans want to leave for Canada), but the data could be noisy (by including everyone who just makes a trip over the border to buy affordable medication). Noisy data are data from which it is hard to determine the true effect.Examples of signal vs noise
If I speak German, for most people, there will be no signal, just noise, although Claus can detect the actual signal.
How accurate are the polls in predicting the election? If the data are noisy (for example, because it’s a small sample size, has low external validity, or small effect size), the poll numbers won’t correlate well with a change in the chance of a different President.
Does money make you happier? The signal (correlation between income and happiness) would be noisy because of confounders — you’d expect people who earn more to be happier because they are in positions of higher social status, they have better working conditions, being happier could cause people to be rich etc. Turns out there is some signal amongst the noise though.
Noise in Electronic System

Noise is a fundamental parameter that limits performance in electronic systems. There are many sources of noise, both internal from components and external introduced into the circuit. The main types of internal noise discussed are Johnson noise (thermal noise) which is present in all conductors, shot noise from current flow across barriers, 1/f noise which increases at low frequencies, and photon noise from the quantum nature of radiation. Noise from these various sources adds depending on whether they are correlated or not. Noise is typically expressed as a noise spectral density and most common sources like Johnson noise exhibit white or frequency-independent noise.
Unit III.pptx

This document discusses different types of noise sources and noise theory concepts. It covers shot noise, thermal noise, and white noise. It also discusses noise equivalent temperature, narrowband noise representation, noise figure, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and noise in different communication systems using amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM), and coherent/envelope detection. Key concepts summarized include noise figure determination, narrowband noise representation using in-phase and quadrature components, noise properties, and figures of merit for different modulation schemes in the presence of noise.
16 Noise.pdf

The noise figure of the amplifier is given as 3.2 dB at an ambient temperature of 297K.
Using the formula:
Noise figure (dB) = 10log10(Noise factor)
3.2 dB = 10log10(F)
F = 10^(3.2/10) = 2.09
Noise equivalent temperature, Te = (F - 1)T
= (2.09 - 1)(297K)
= 323K
Therefore, the noise equivalent temperature of the amplifier is 323K.
Chapter 5 -_signal_to_noise

The document discusses sources of noise and techniques for improving the signal-to-noise ratio. It describes different types of noise including thermal, shot, flicker, and environmental noise. It also explains how signal averaging and filtering can be used to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio by reducing random noise through cancellation while preserving the underlying signal. The goal is to improve measurement precision and lower detection limits by increasing the signal compared to the noise.
S@P Noise.pptx

Thermal, shot, and flicker noise are common sources of noise in analytical signals. Signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) quantifies the quality of a measurement by comparing the mean signal to the standard deviation of noise. Higher S/N makes the signal easier to distinguish. Noise can be reduced through hardware methods like shielding, filtering, and lock-in amplifiers or software techniques such as averaging multiple measurements, which improves S/N proportionally to the square root of the number of measurements averaged.
Communication Theory - Noise Characterization.pdf

This document discusses different types of noise that can affect communication systems. It describes two main categories of noise: external noise and internal noise. External noise comes from sources outside the system, such as atmospheric effects, extra-terrestrial sources like the sun, and man-made industrial sources. Internal noise is generated within the system itself and includes thermal noise, shot noise, transit time noise, and other minor sources. The document provides detailed explanations and examples of different noise types in communication systems.
DOC-20231009-WA0000..pdf

This document discusses different types of noise that can interfere with radio transmitters and receivers. It describes noise as an unwanted signal that corrupts the original message signal. The document outlines several sources of internal noise like thermal noise and shot noise, which are produced by components in the receiver. It also discusses external noise sources such as industrial noise and atmospheric noise. The effects of noise are that it limits operating range and affects receiver sensitivity. The document provides detailed explanations of different internal noise types like thermal noise, shot noise, transit-time noise, and flicker noise.
Noise in communication system

The document discusses different types of noise that affect communication systems, including thermal noise, shot noise, flicker noise, excess resistor noise, and popcorn noise. It analyzes noise in terms of thermal noise voltage spectral density, resistors in series and parallel, signal-to-noise ratio, noise factor, noise figure, and additive white Gaussian noise. The document is a presentation on noise in communication systems, identifying key noise sources and how they are analyzed.
Magazine article

The document discusses the use of sound in interactive media products. It provides information on sound theory including waveforms, amplitude, frequency, pitch, and decibel levels. It also covers basics of sound recording such as microphones, mixers, signal levels, and mono versus stereo sound. Finally, it discusses uses of sound in interactive media like DVD interfaces, video games, and mobile phones to add realism, notify users of interactions, and enhance the user experience.
ShriyaMhatre_p21006_Paper1_ppt.pptx

Signal to noise ratio is an important concept to learn while handling various analytical instruements.
3-Basic Acoustics.ppt

The document provides an overview of basic acoustics concepts including quantification of sound through measurements of sound pressure, intensity, and power. It discusses acoustic variables such as sound pressure level and intensity level which are expressed on a logarithmic decibel scale. Key concepts covered include the inverse square law describing how sound pressure/intensity decreases with distance from a point source, effects of multiple sound sources, relationships between frequency and sound perception, and directionality of sound sources. Measurement techniques and standards are also summarized.
Transmission impairments

This document discusses various types of transmission impairments including attenuation, distortion, and noise. Attenuation is the reduction of signal strength during transmission, while distortion alters the original signal shape. There are different types of distortion such as amplitude, delay, and frequency distortion. Noise refers to random electrical signals that interfere with reception, and can come from internal or external sources. Signal-to-noise ratio and noise figure are discussed as ways to measure noise levels relative to signals.
Signals and noise

This document discusses techniques for enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio in analytical measurements. It describes what the signal-to-noise ratio is and explains common sources of noise like thermal noise, shot noise, and flicker noise. It then discusses various hardware and software methods for improving the SNR, such as shielding, grounding, difference amplifiers, filtering (low-pass, high-pass, band-pass), ensemble averaging, and moving averages. Modulation and lock-in amplifiers are also covered as techniques to extract low-level signals from noise.
Similar to Electronics noise (20)
Electronics noise
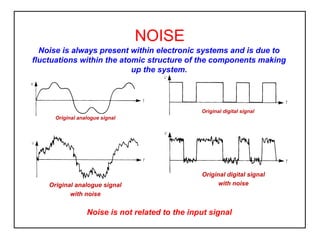
- 1. NOISE Noise is always present within electronic systems and is due to fluctuations within the atomic structure of the components making up the system. Original digital signal Original analogue signal Original analogue signal with noise Original digital signal with noise Noise is not related to the input signal
- 2. COMMON TYPES of NOISE Thermal (Johnson) Noise: Caused by heat generated due to the random movement of atoms within the components. Has an infinite bandwidth with equal noise power. Flicker Noise: Caused by random variations in the diffusion of charge carriers within devices, transistors especially and is a low frequency noise. Shot Noise: Caused by uneven distribution of charge carriers due to the granular nature of semiconductor materials as a result of fluctuations in the diffusion process. Pink Noise: A low frequency noise similar to flicker noise also known as 1/f noise since its power spectrum is inversely proportional to frequency. White Noise: Similar to thermal noise, having noise components at all frequencies with equal noise power across the spectrum.
- 3. SIGNAL to NOISE RATIO The signal-to-noise ratio (S/N ratio) is a quantitative method of describing the quality of a signal in terms of its corruption by noise. That is, the ratio of the magnitude of the signal to that of the noise, usually expressed as the ratio of signal power (Ps) to the noise power (Pn). Ps S N ratio = 10 log10 Pn dB The signal-to-noise ratio within a given system varies with the magnitude of the signal. If the signal becomes very small, the relative size of the noise will increase causing the S/N ratio to decrease, (remember the noise level is independent of signal). Manufacturers of audio equipment often like to quote the signal-to-noise ratio as a selling point for their equipment.