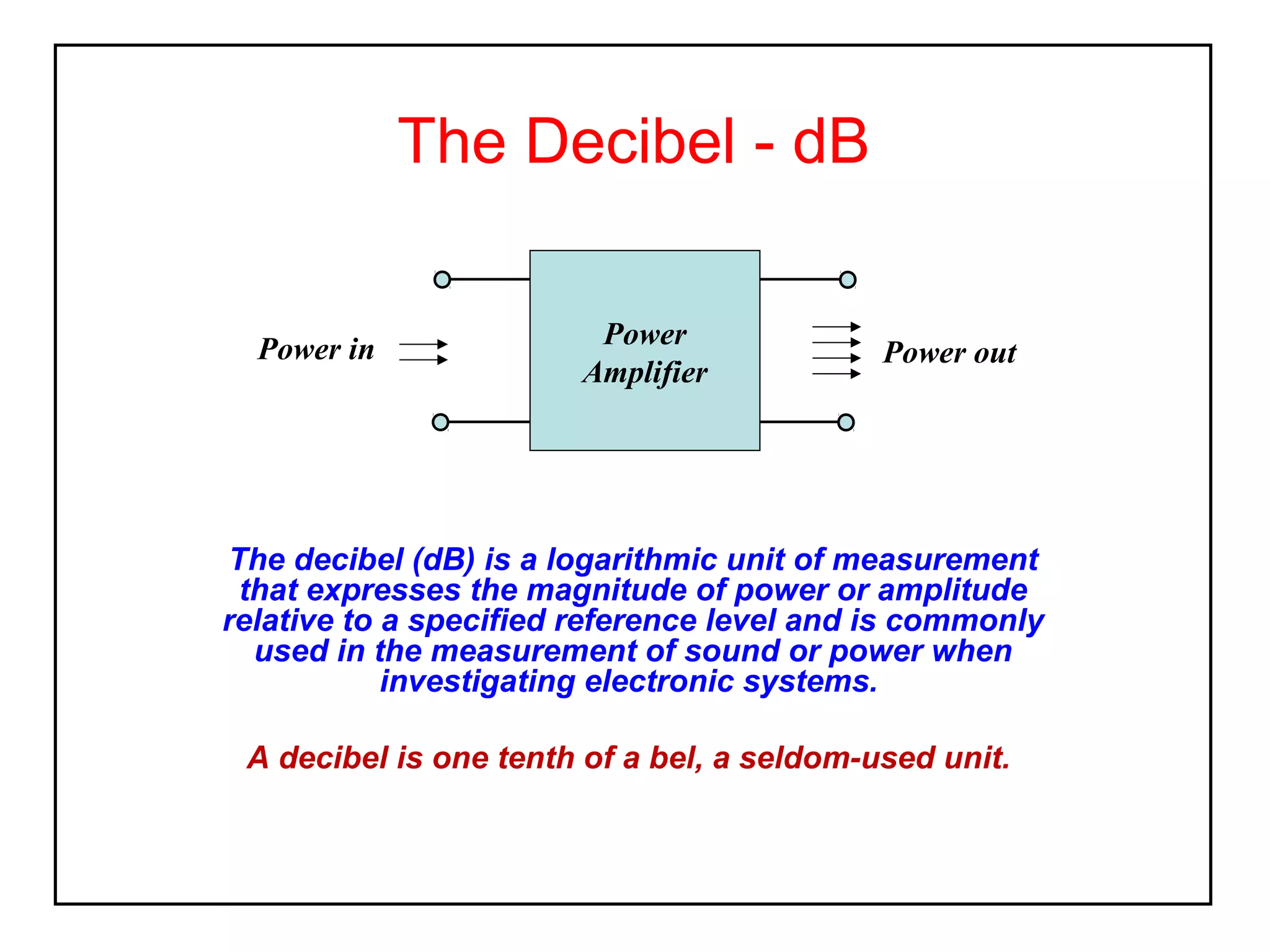
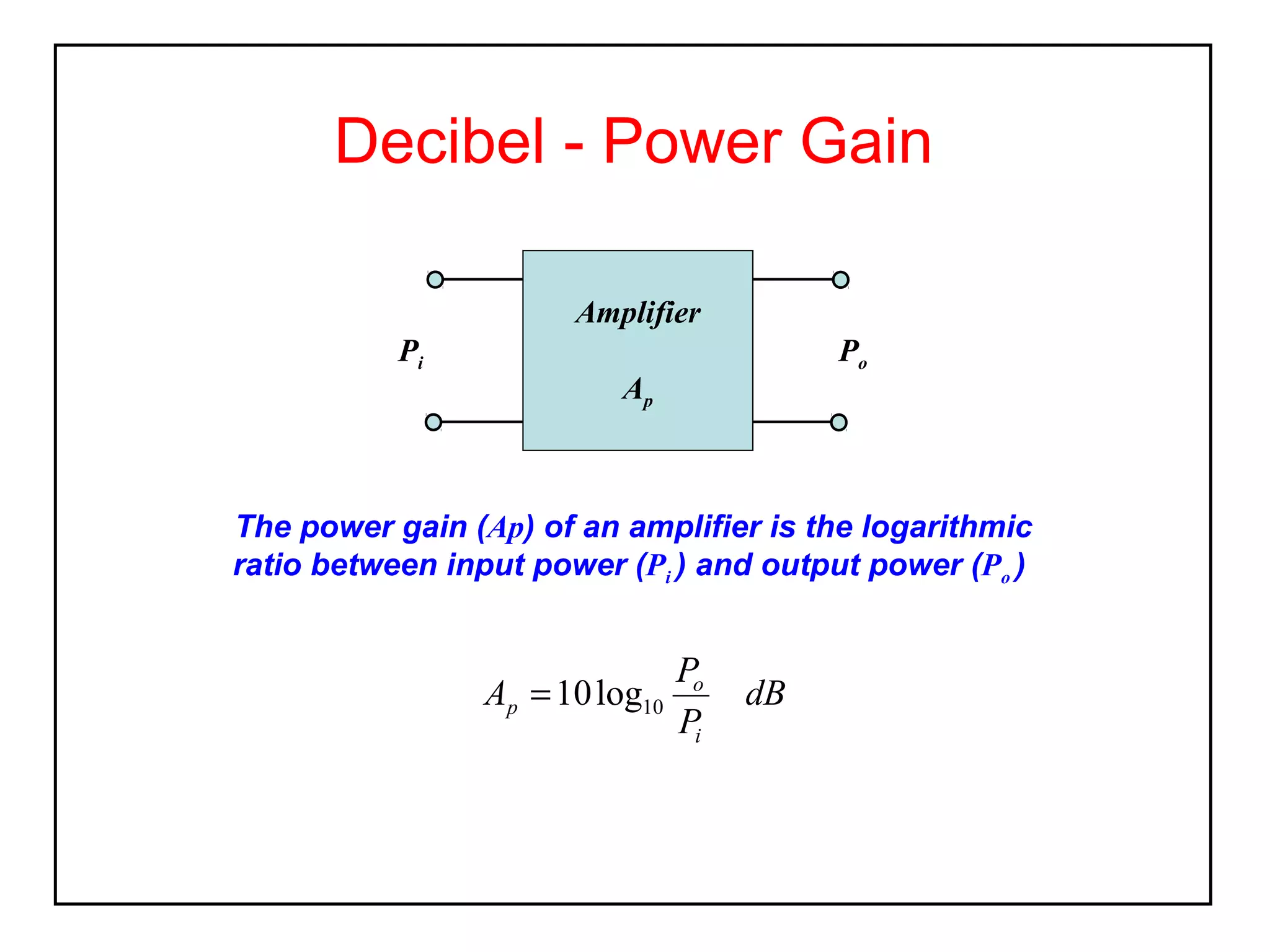
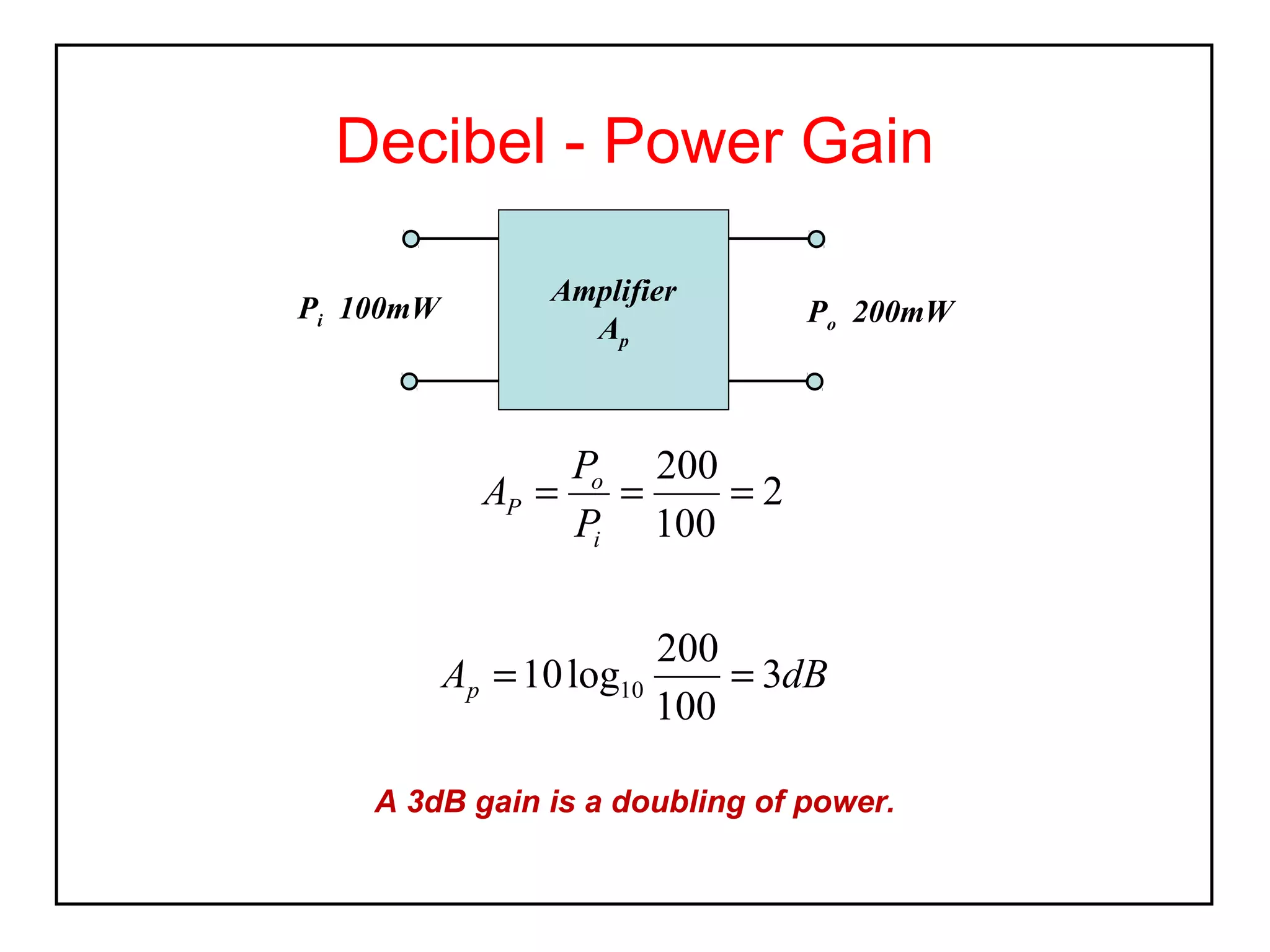
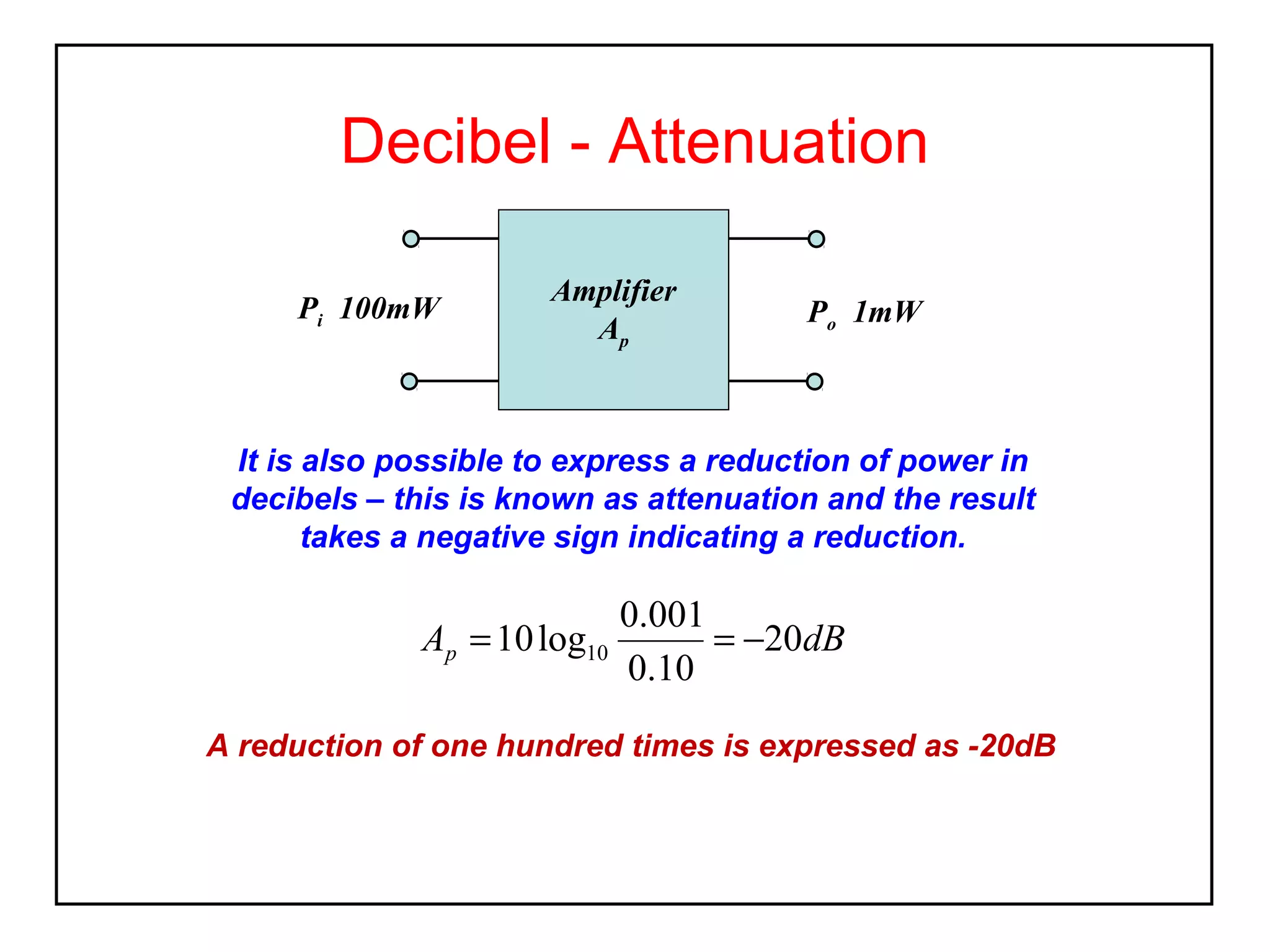
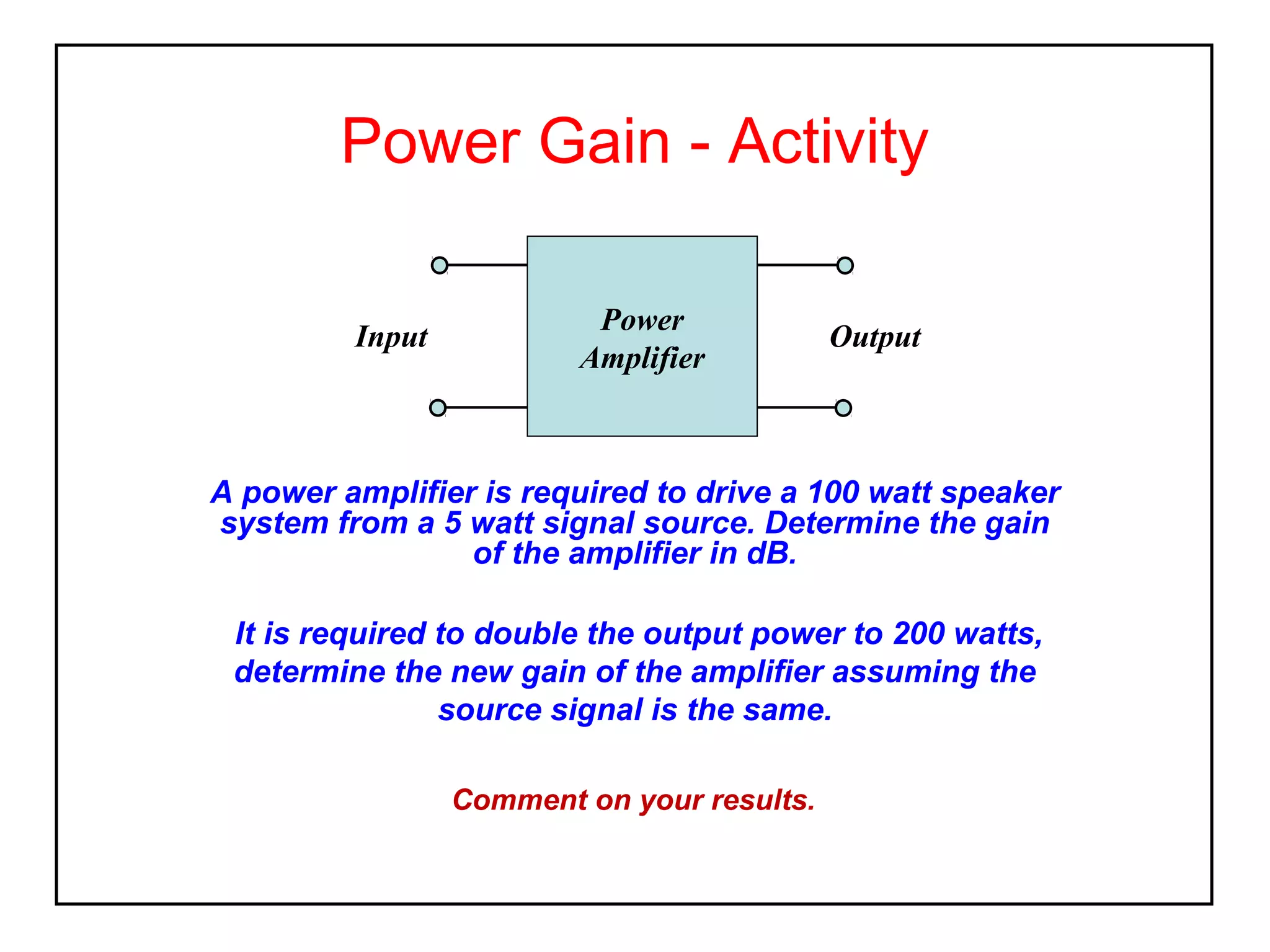
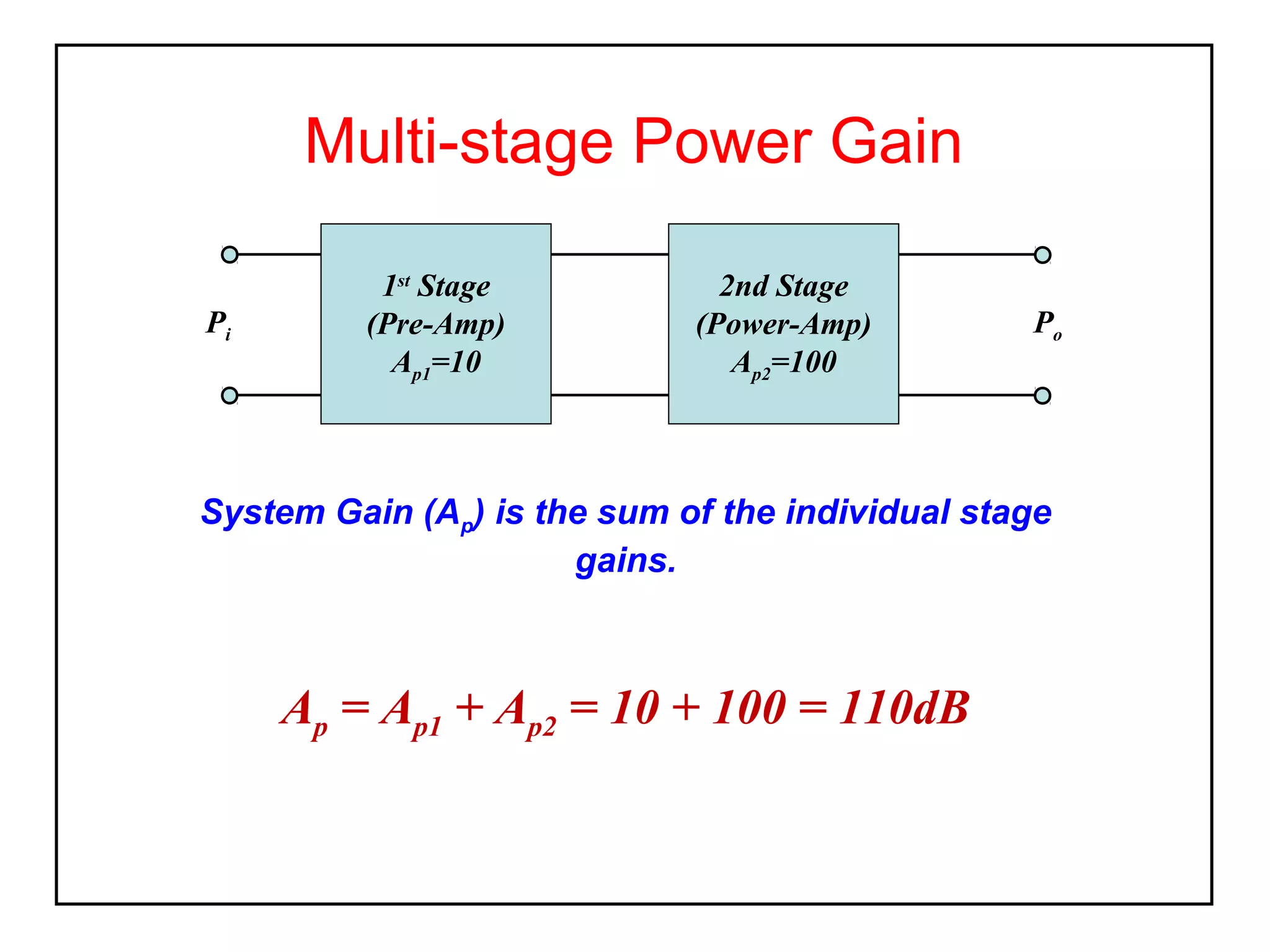
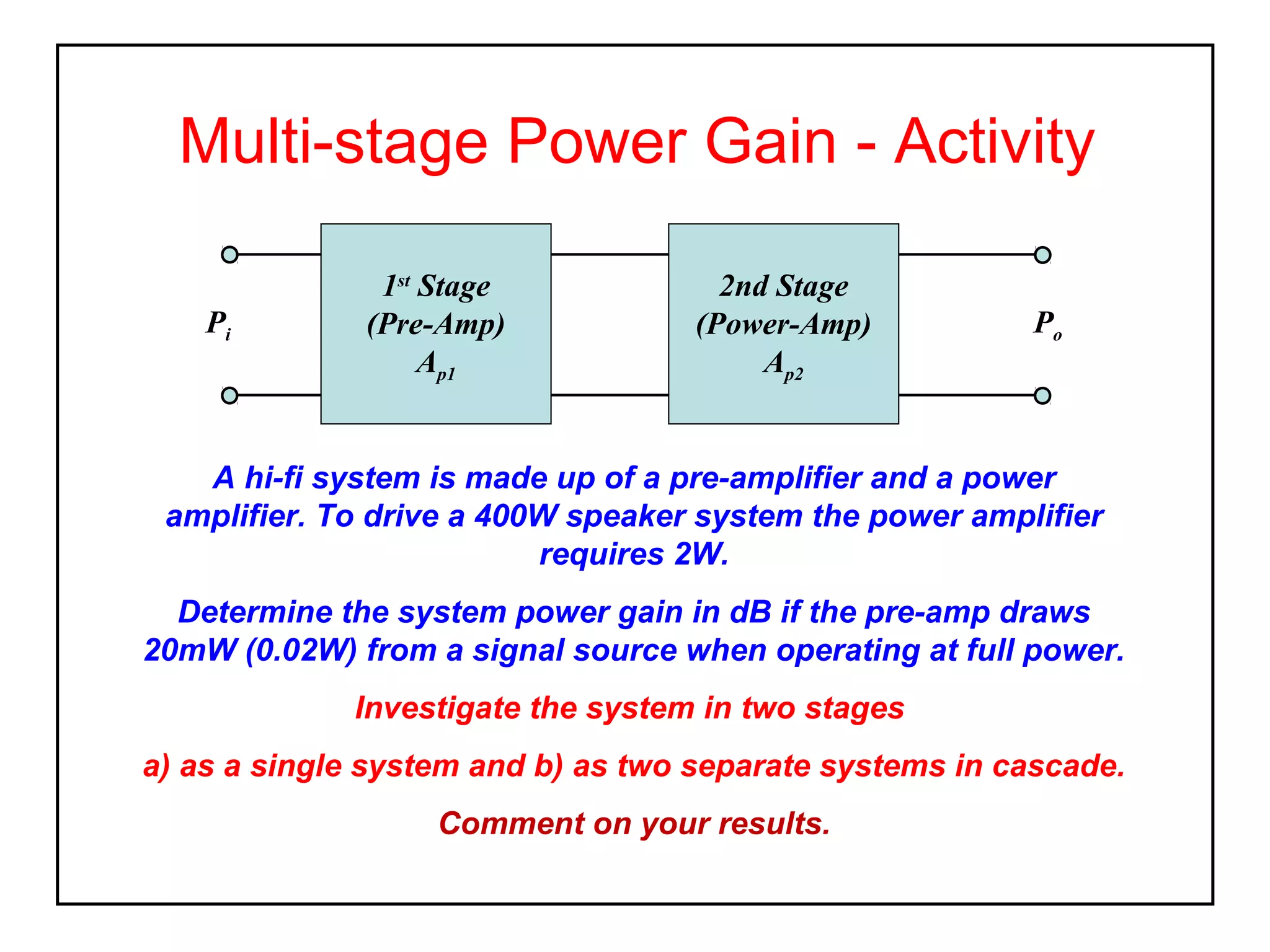
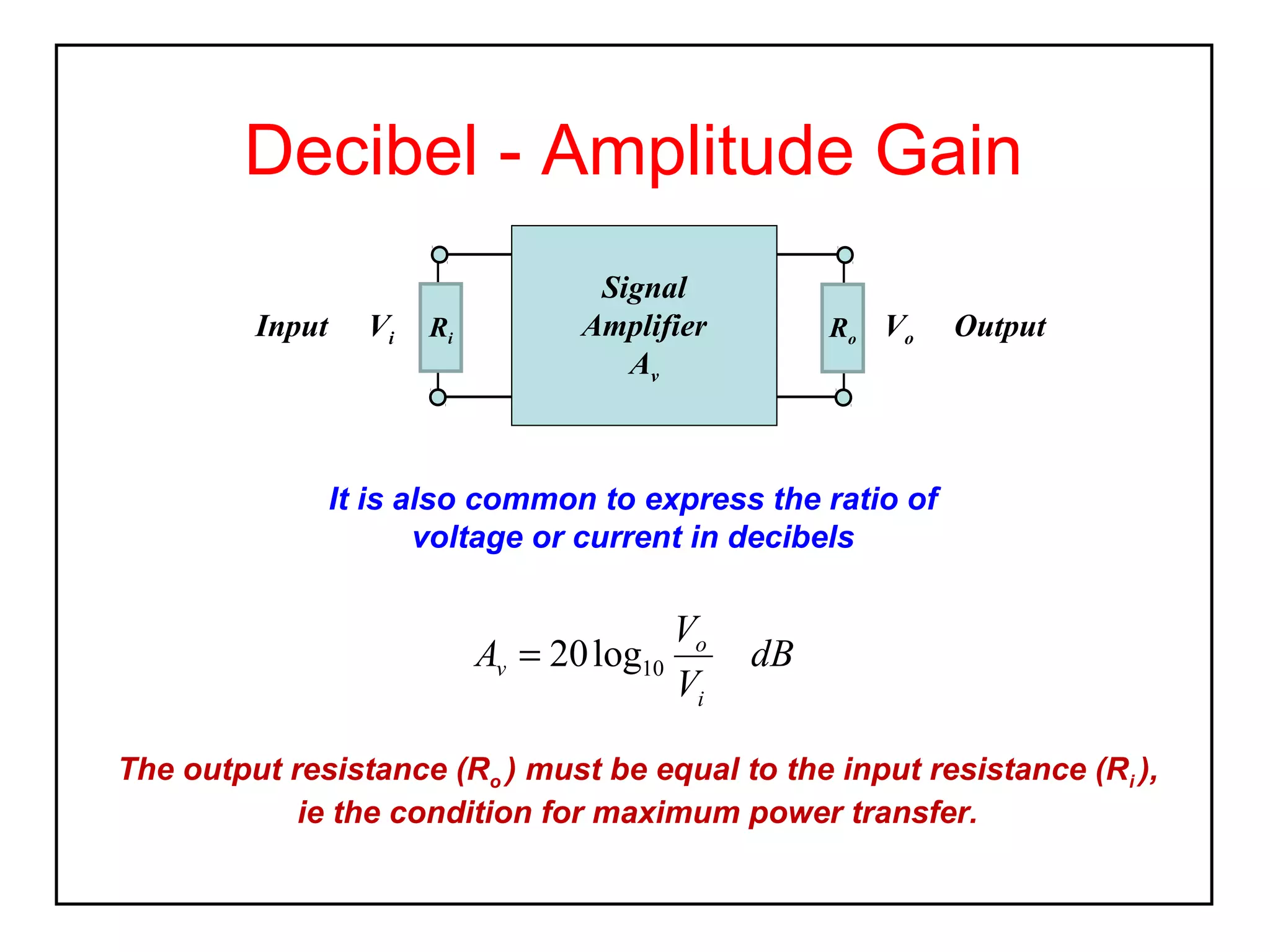
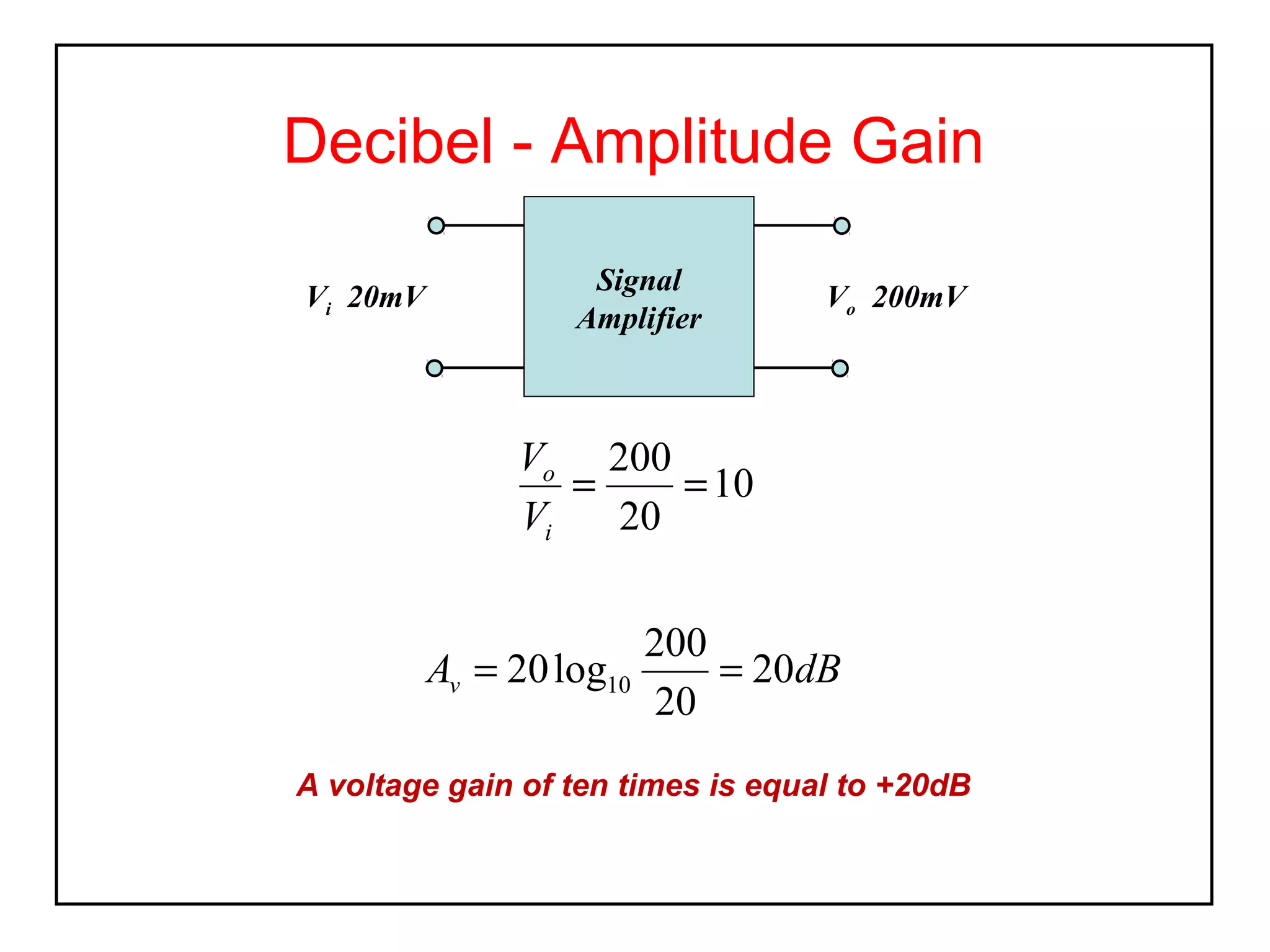
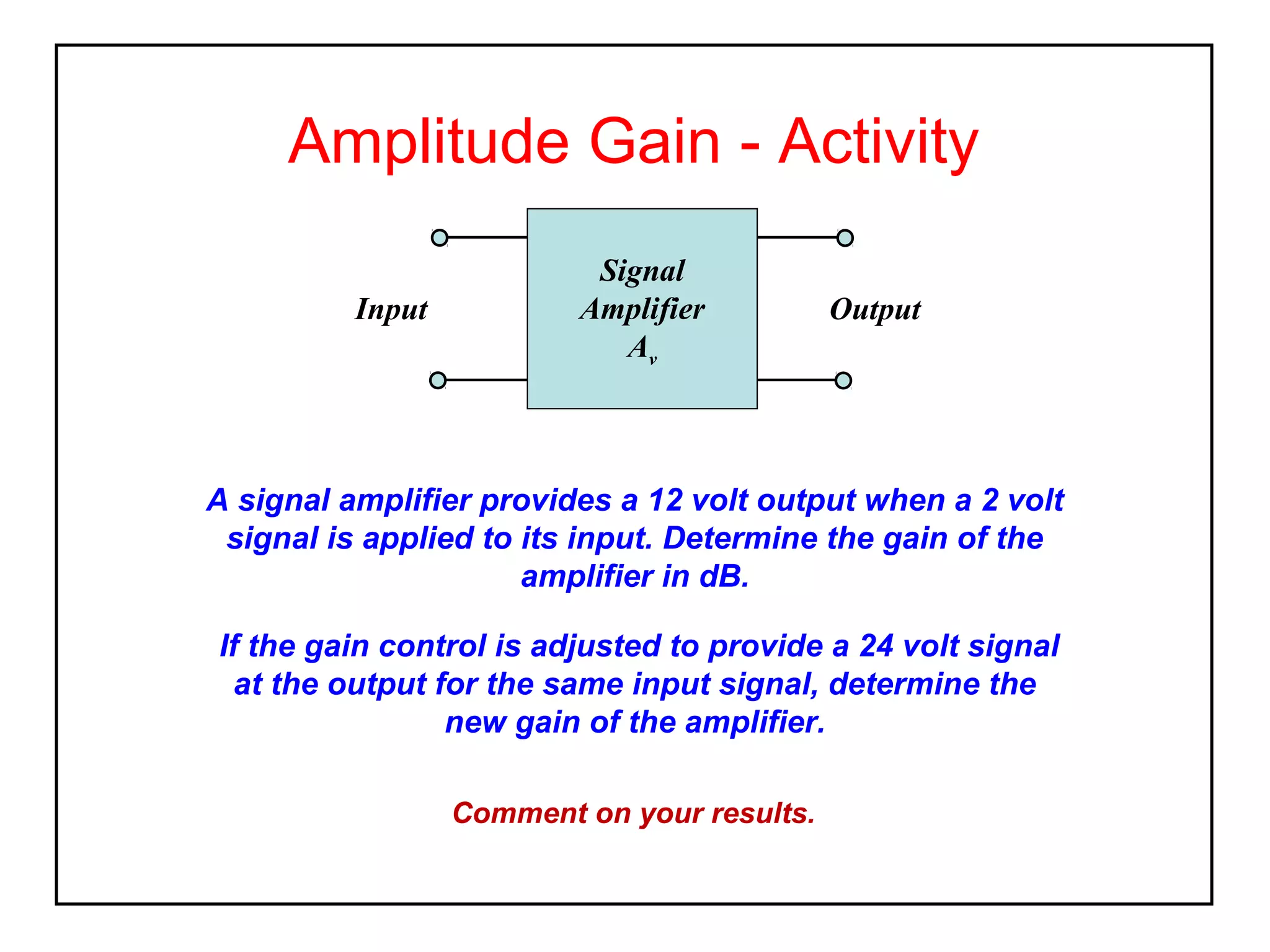
The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two power levels or amplitudes. It is commonly used to measure sound levels and power in electronic systems. A decibel represents one tenth of a bel and can express power gain or attenuation. Power gain is calculated as 10 times the log of the ratio between output and input power. A 3dB gain doubles the power. Attenuation is expressed as a negative value and represents a reduction in power. Gain can also be expressed for voltage or current using 20 times the log of the output to input ratio. Multiple stage amplifiers have a total gain equal to the sum of the individual stage gains.