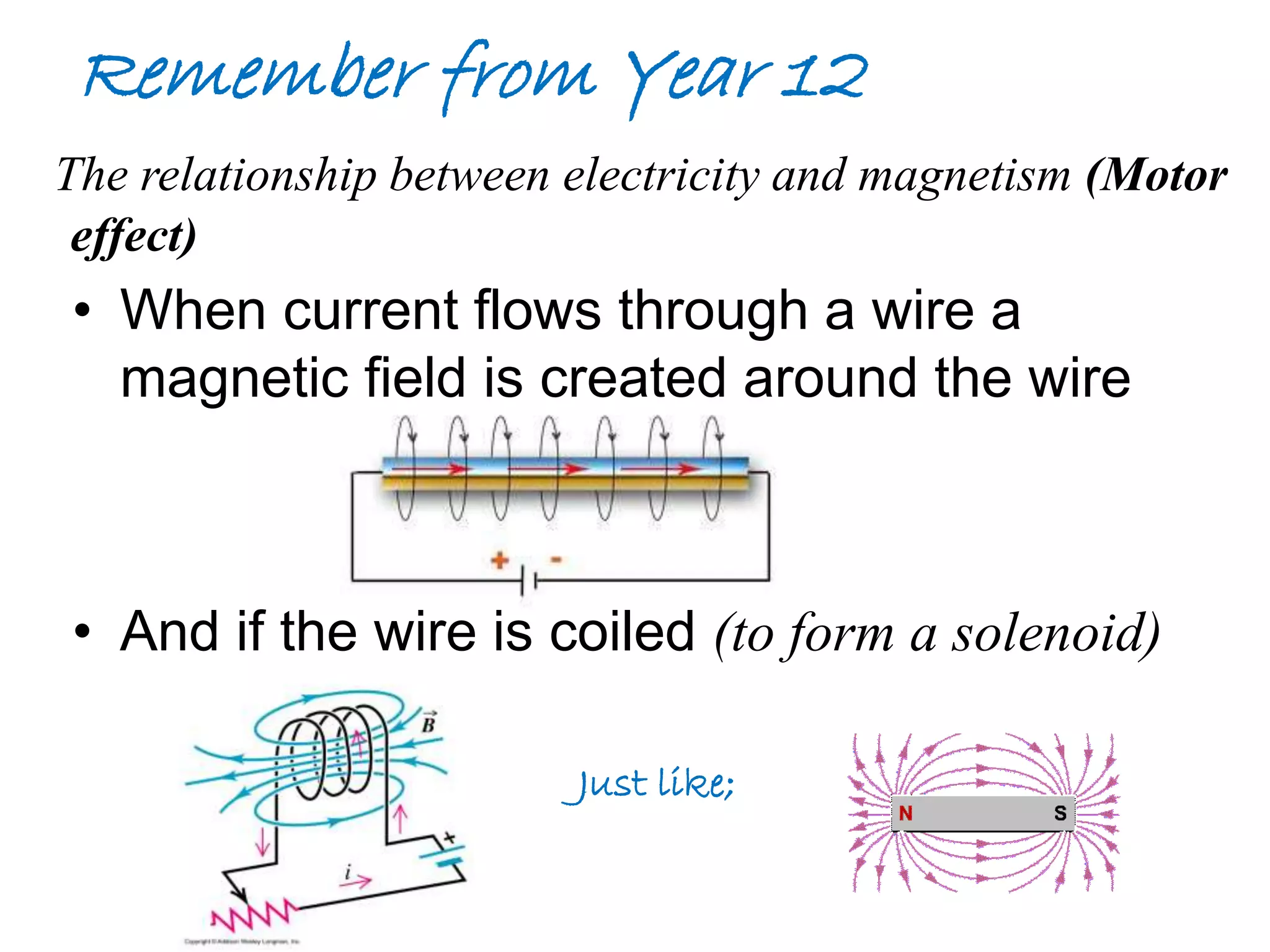
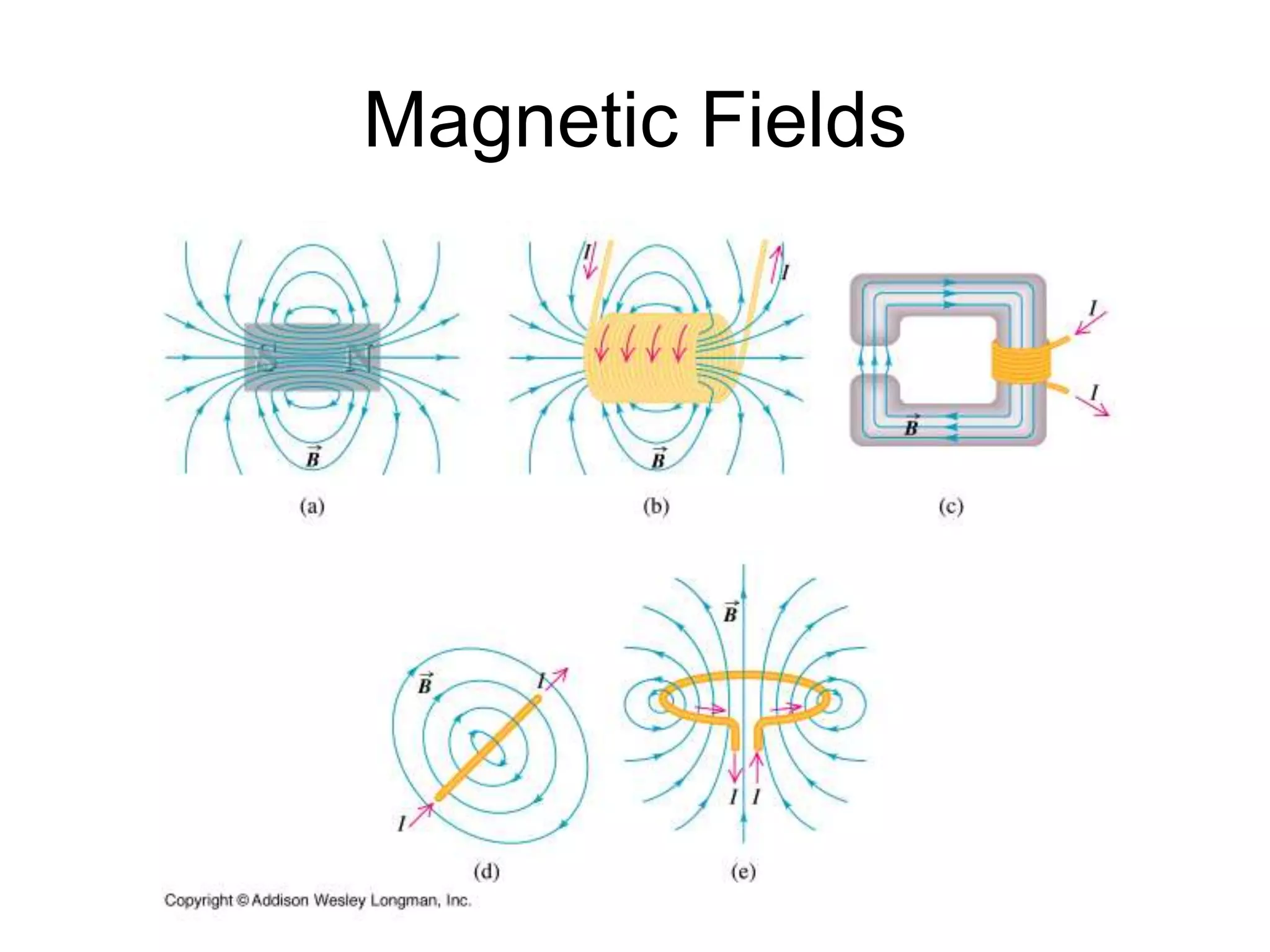
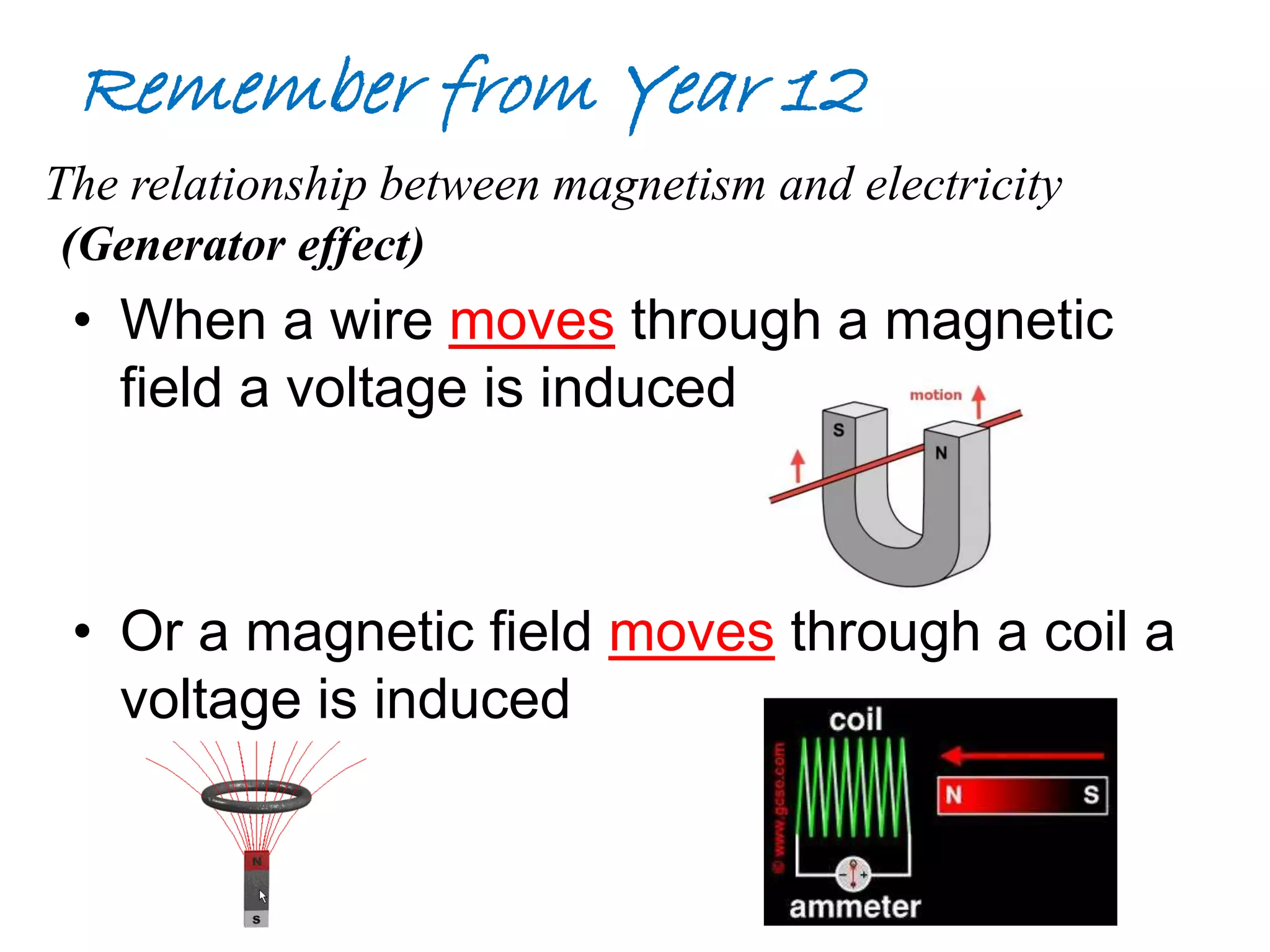
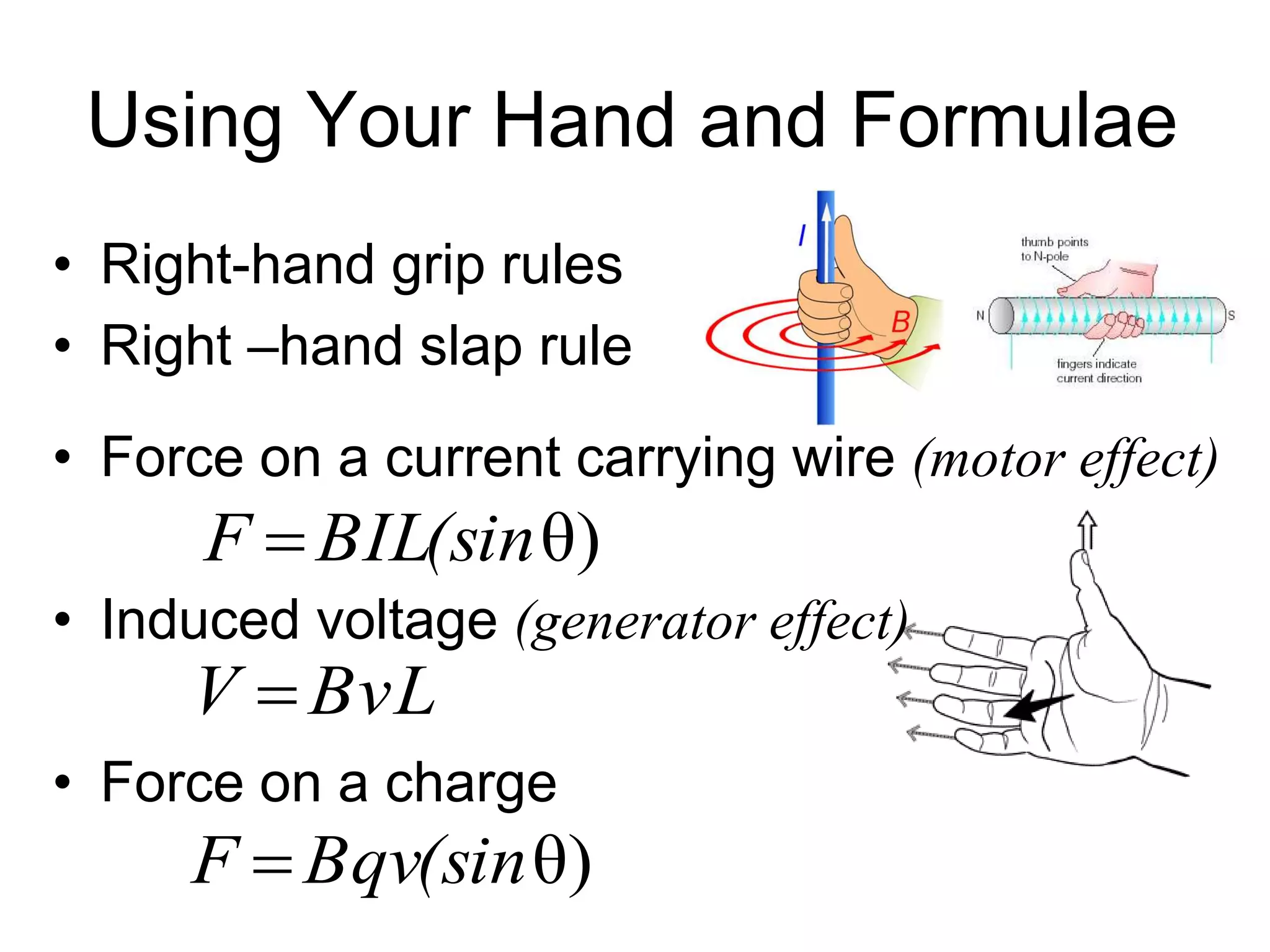
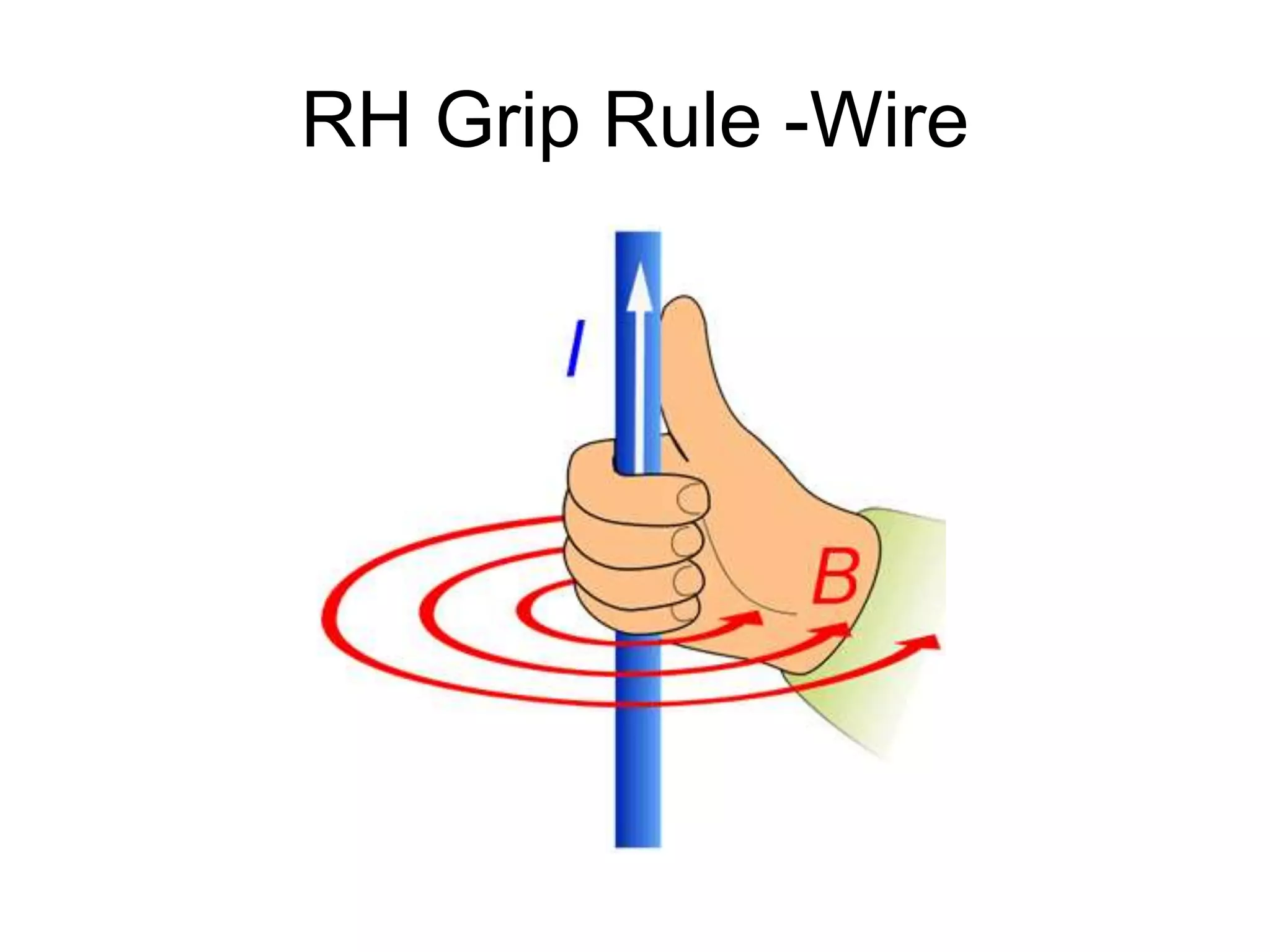
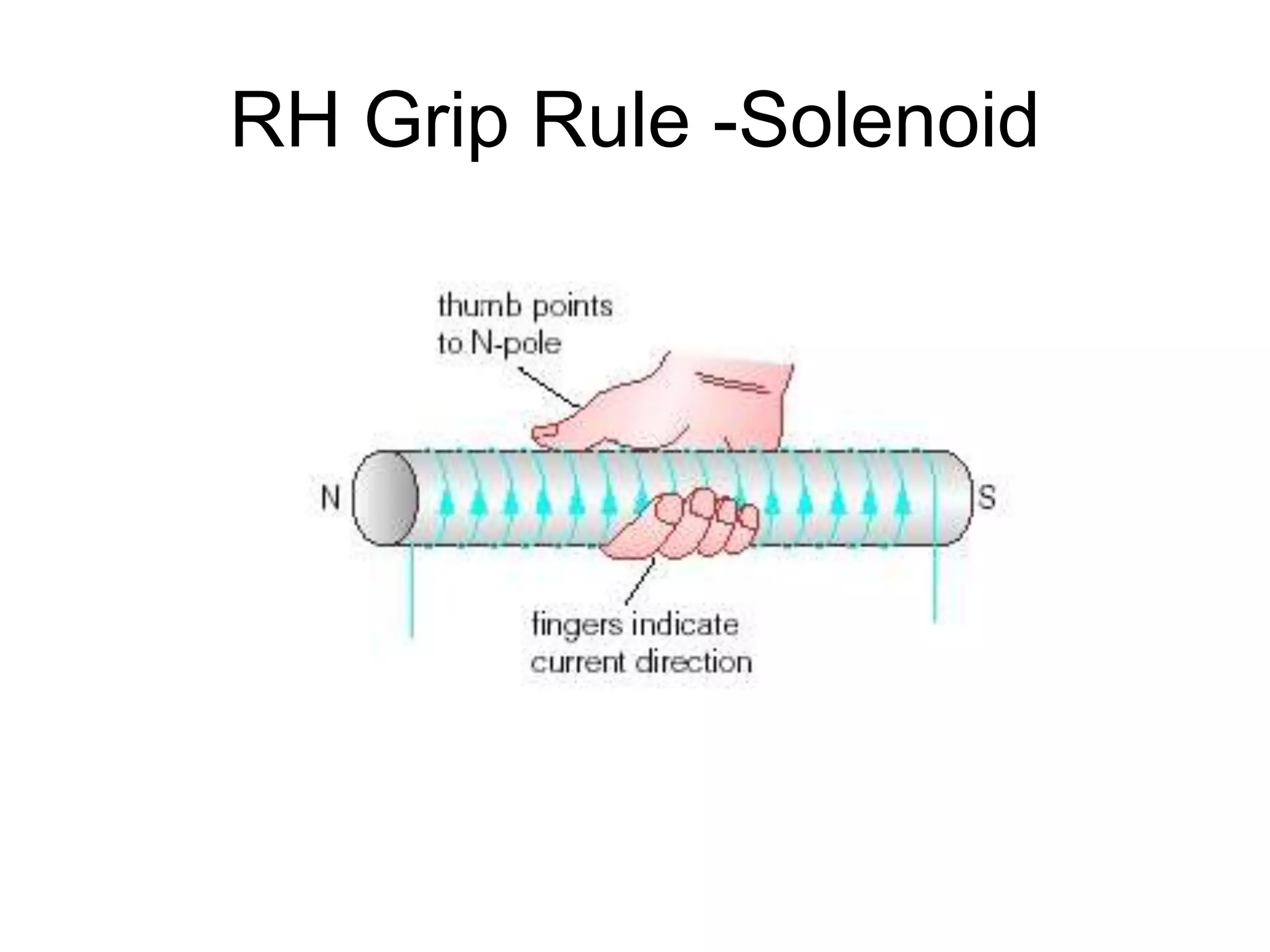
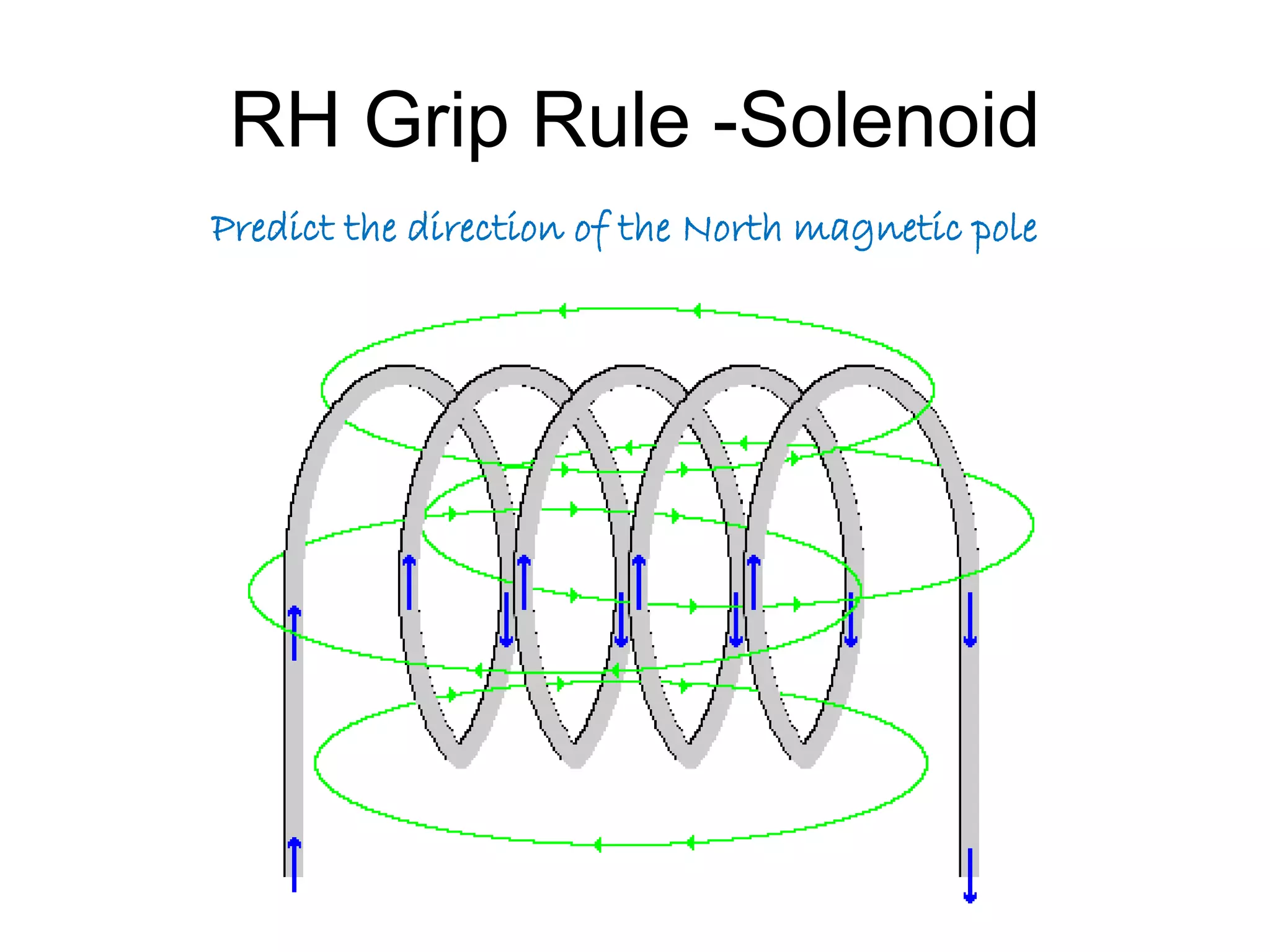
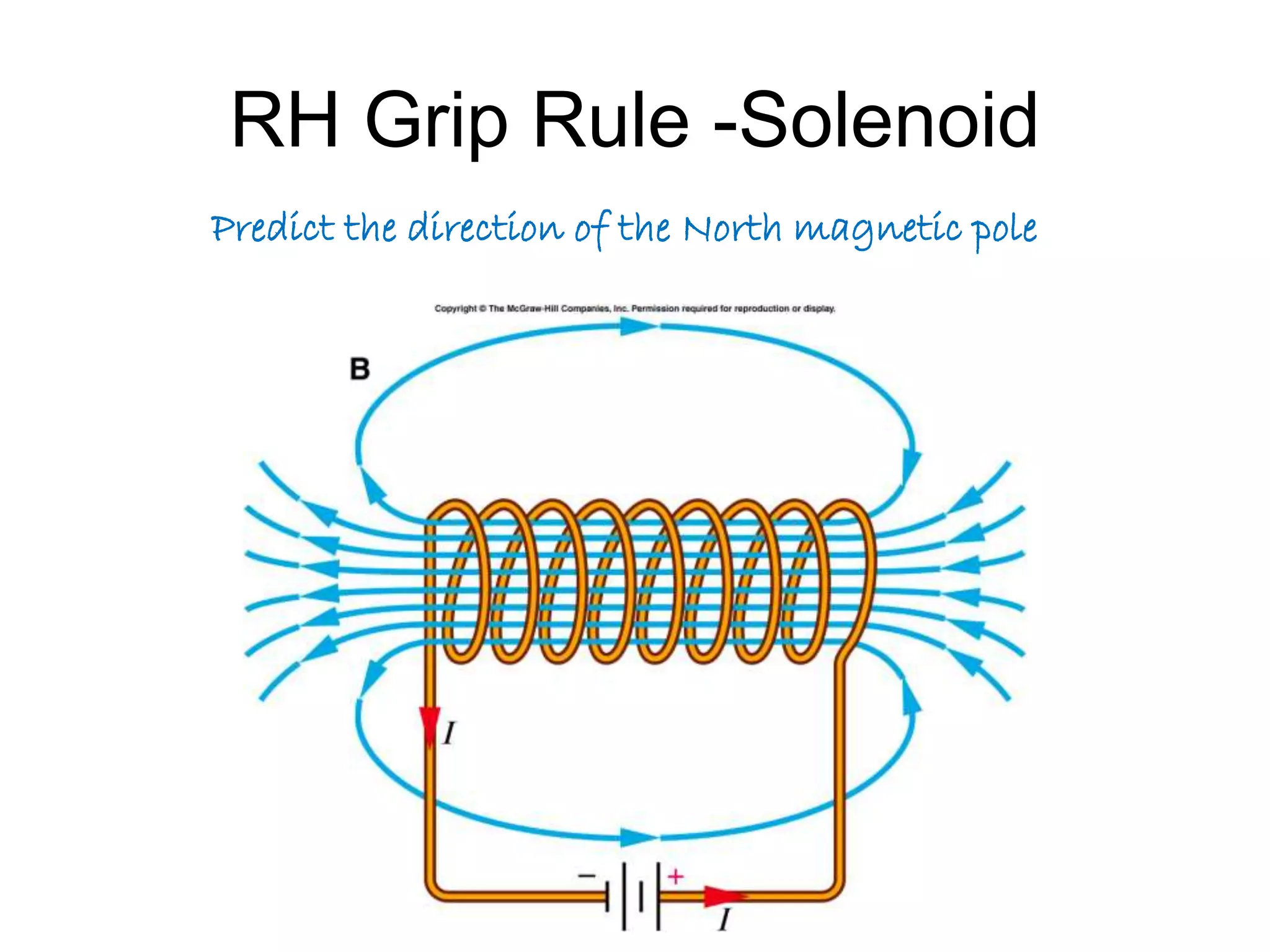
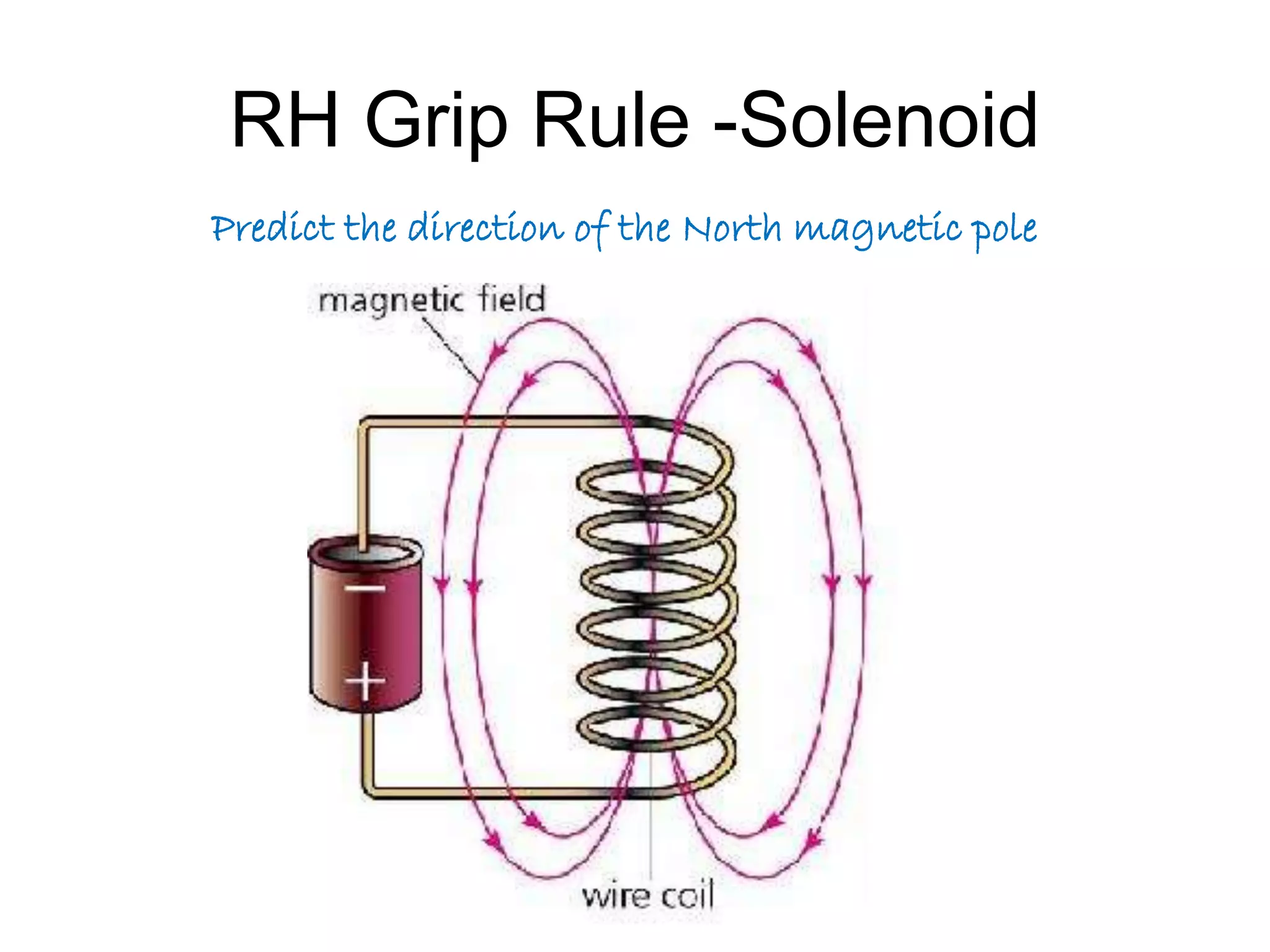
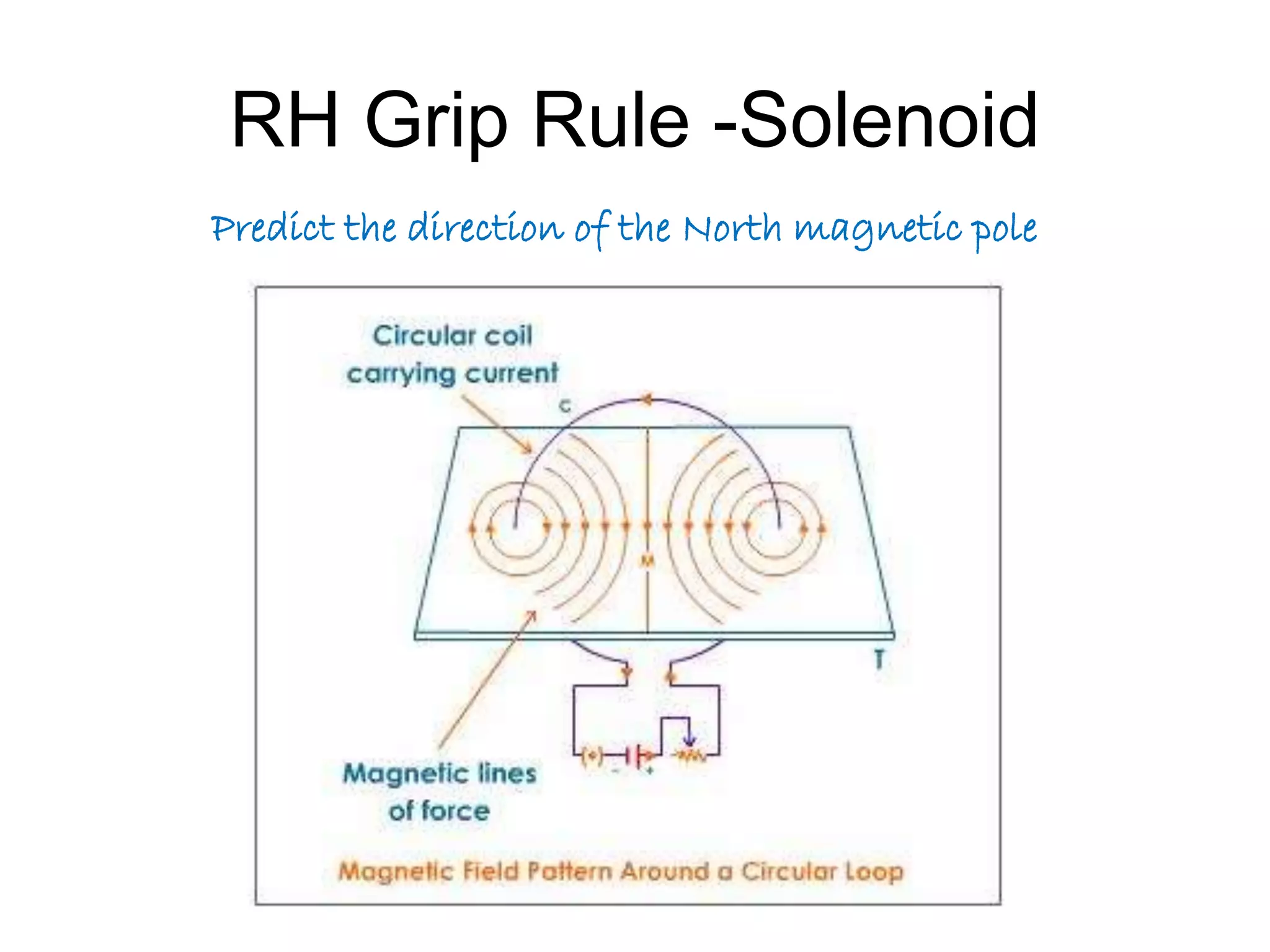
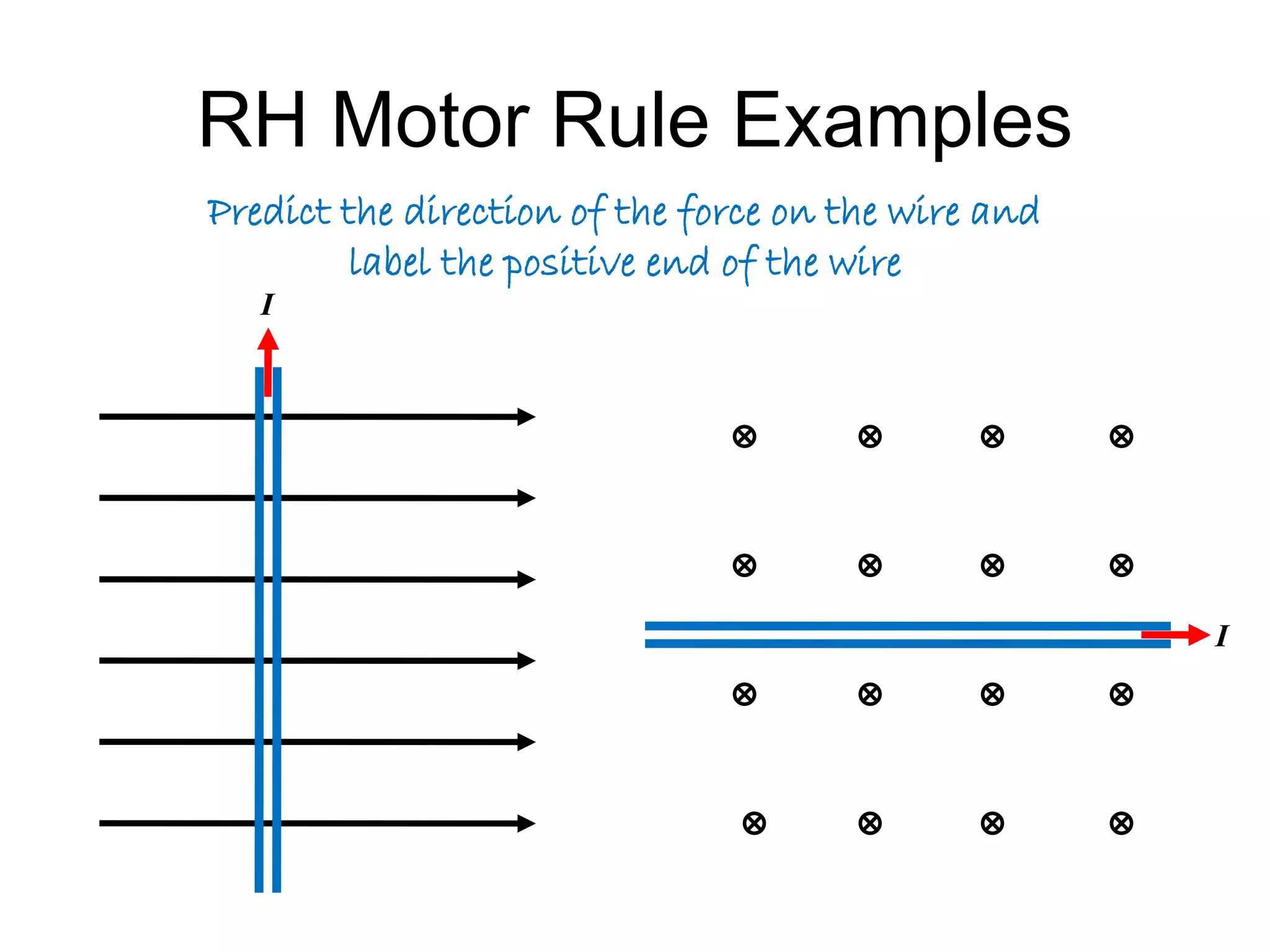
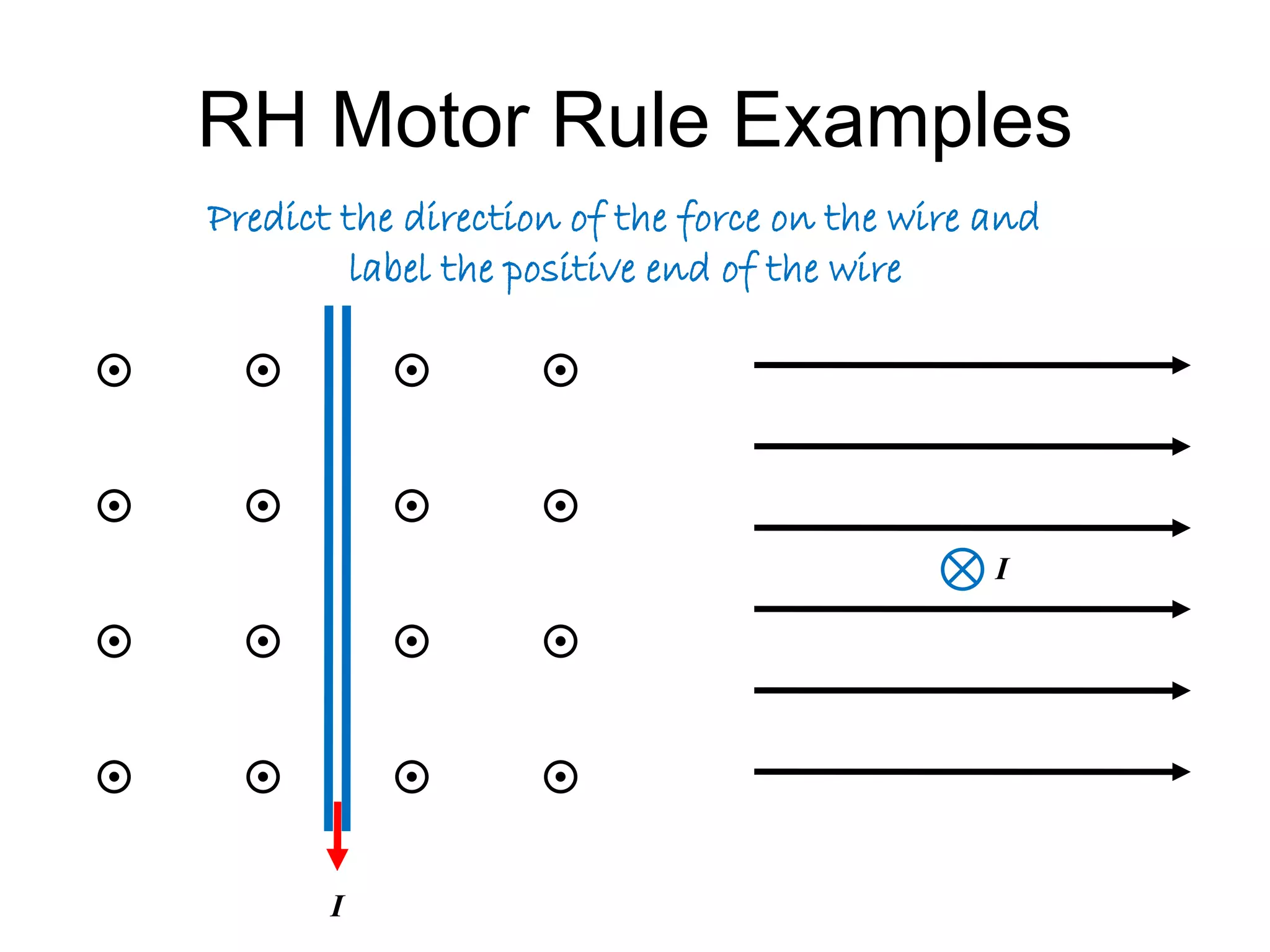
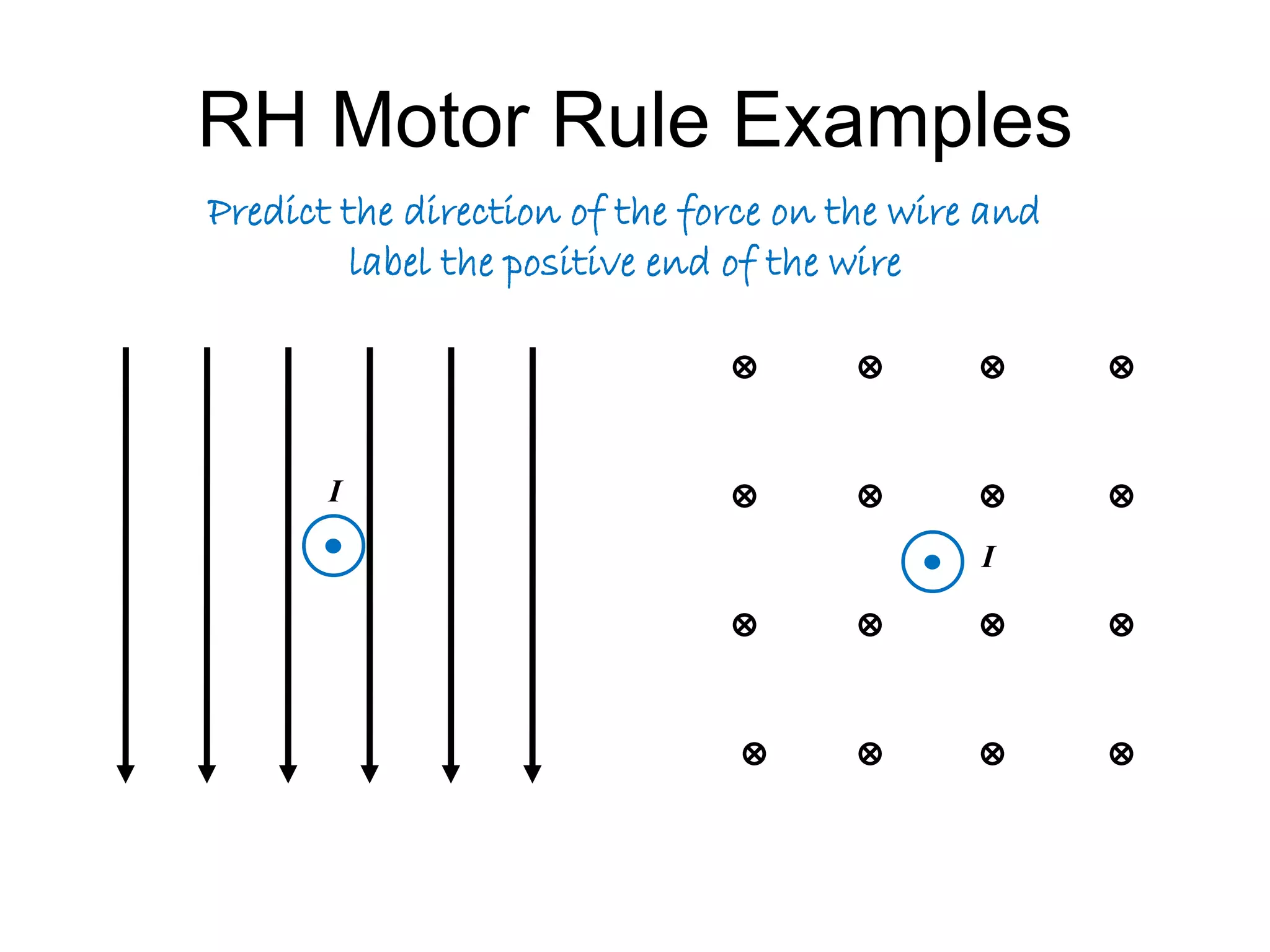
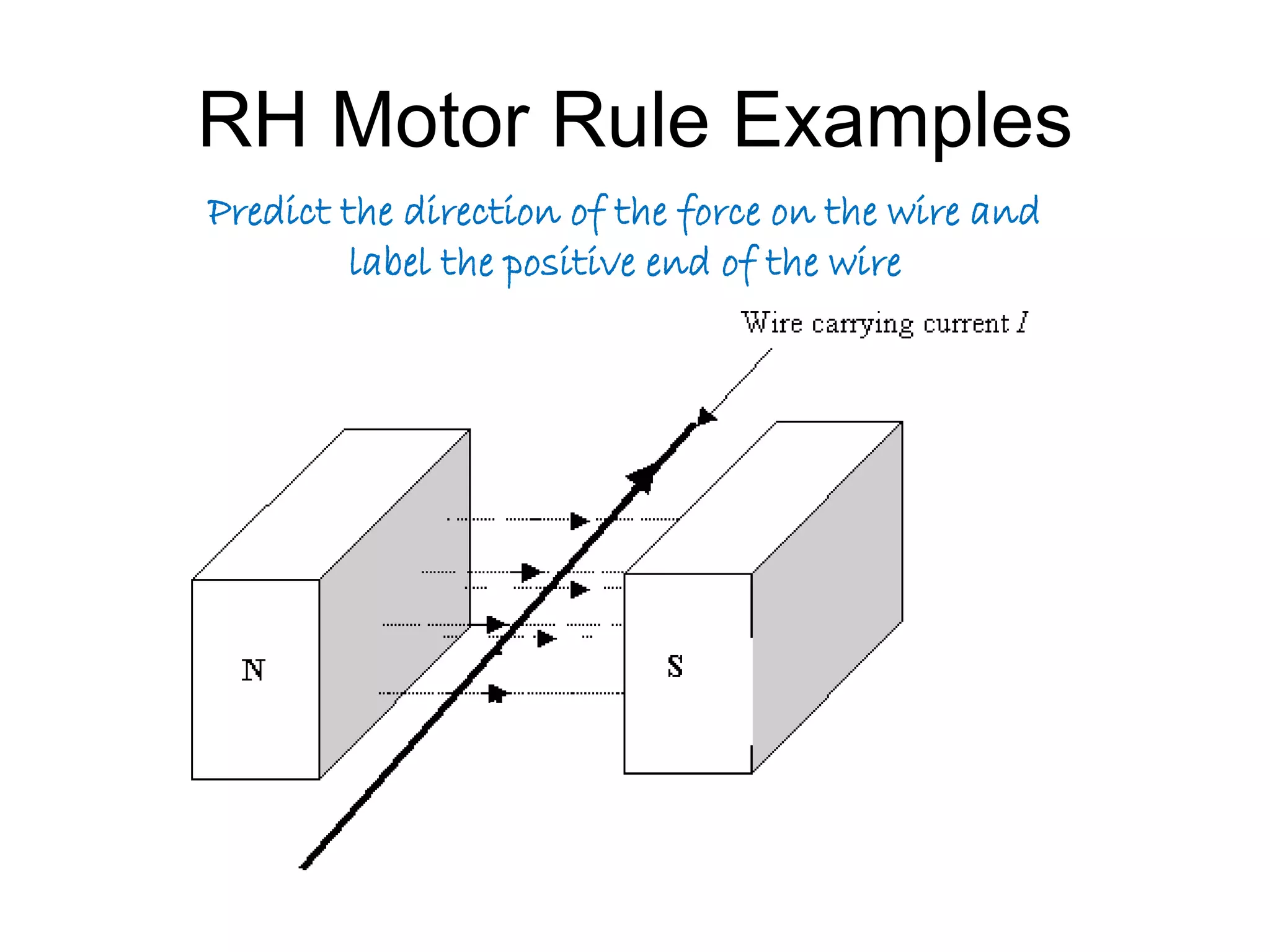
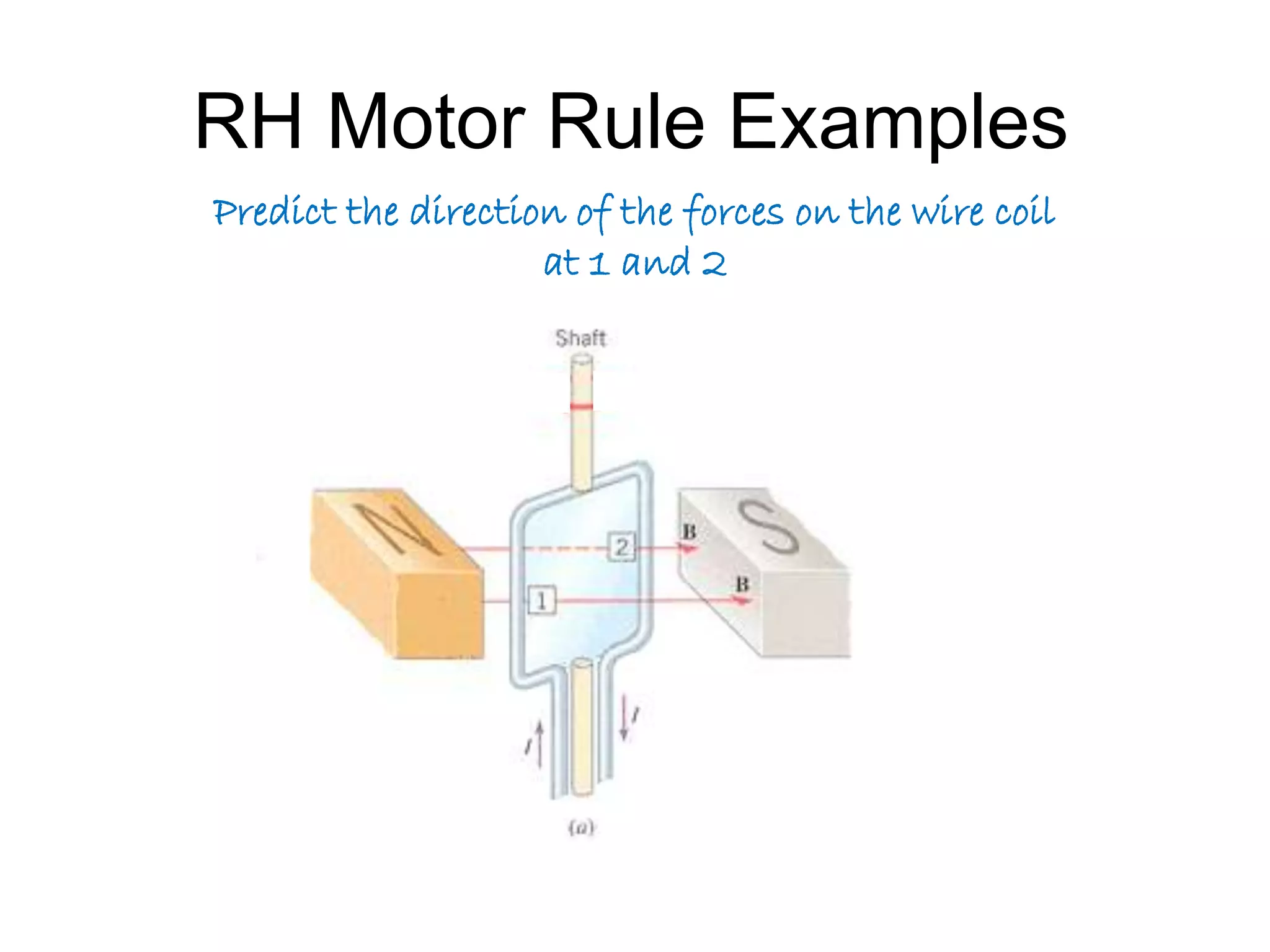
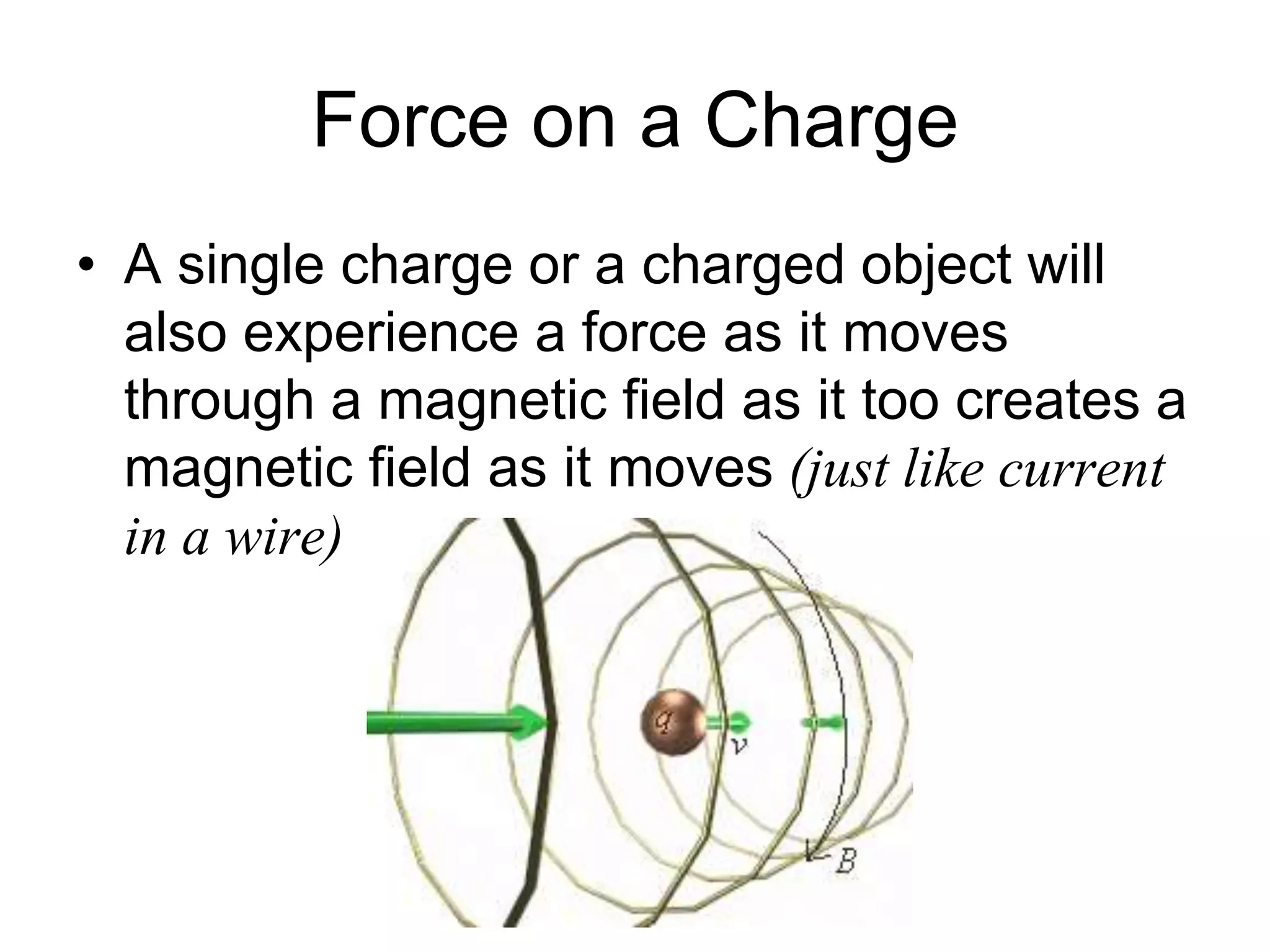
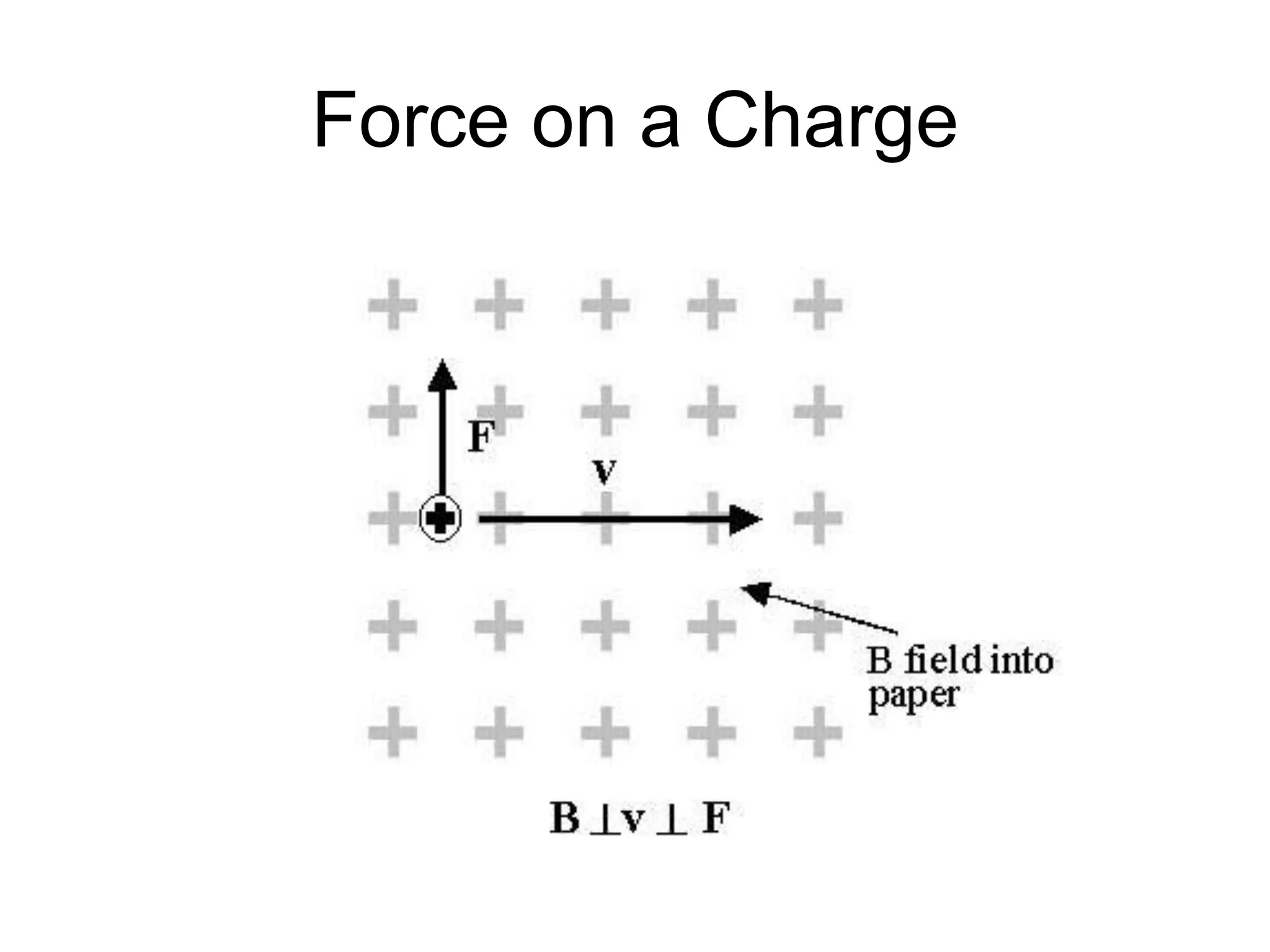
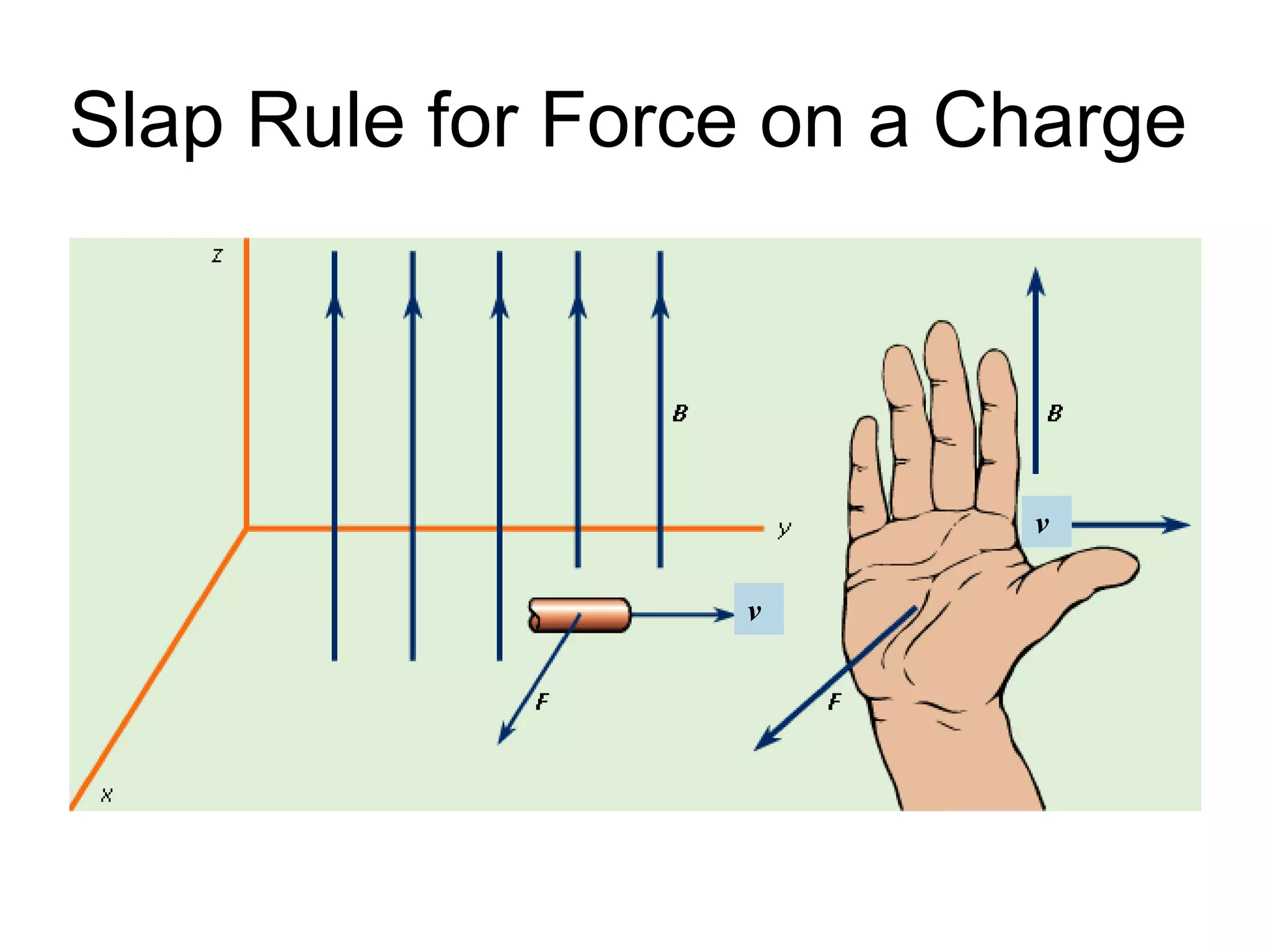
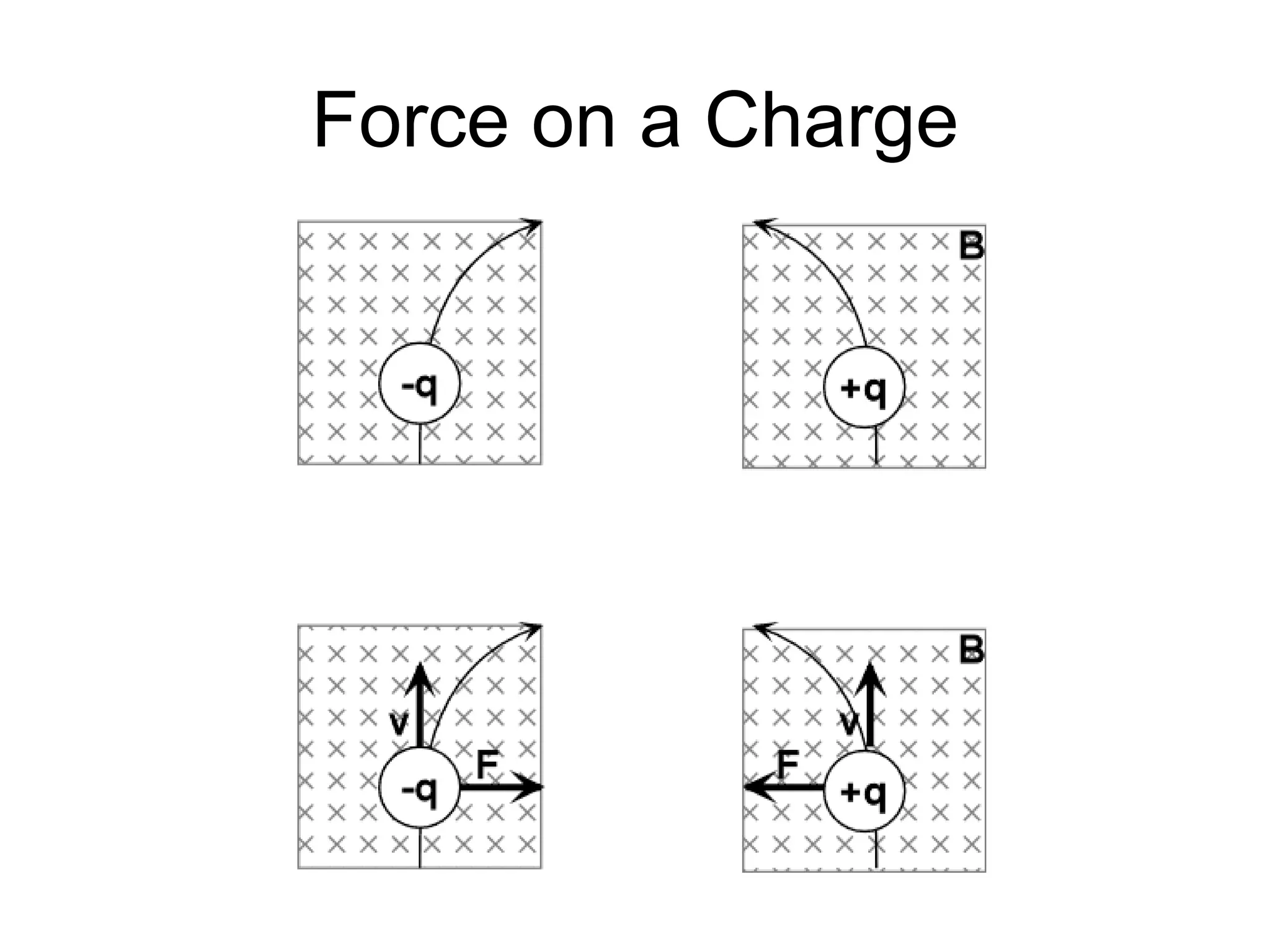
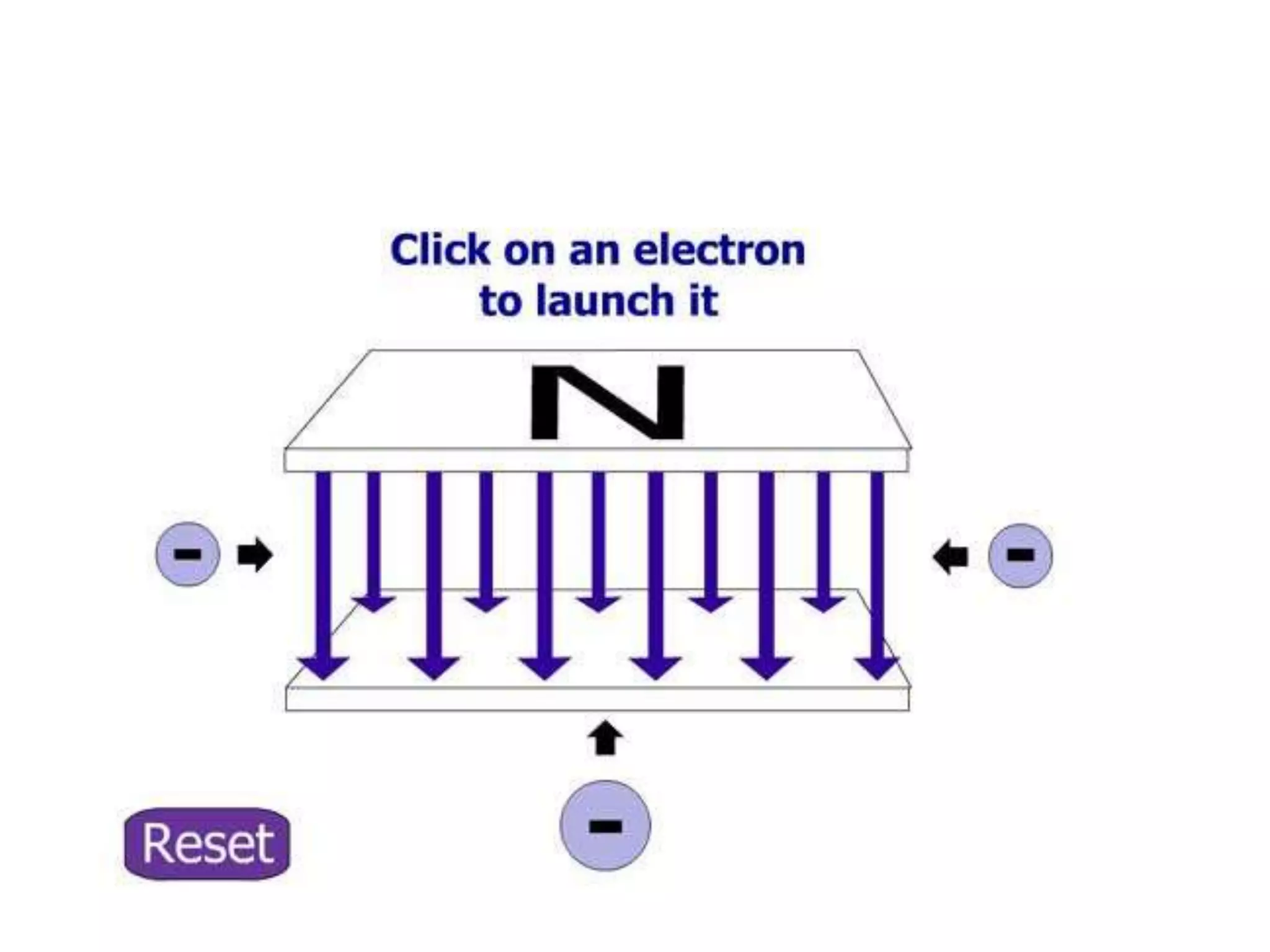
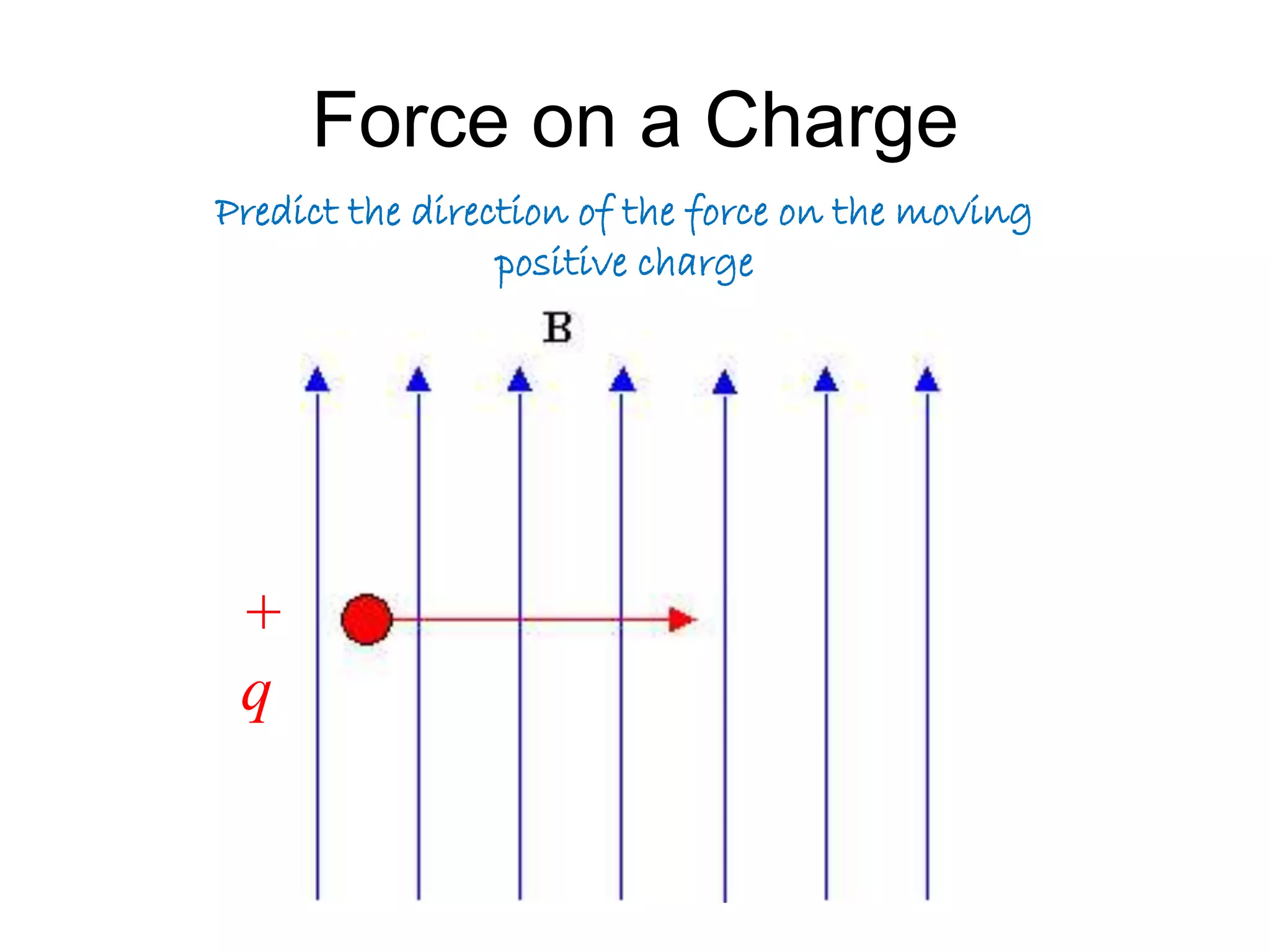
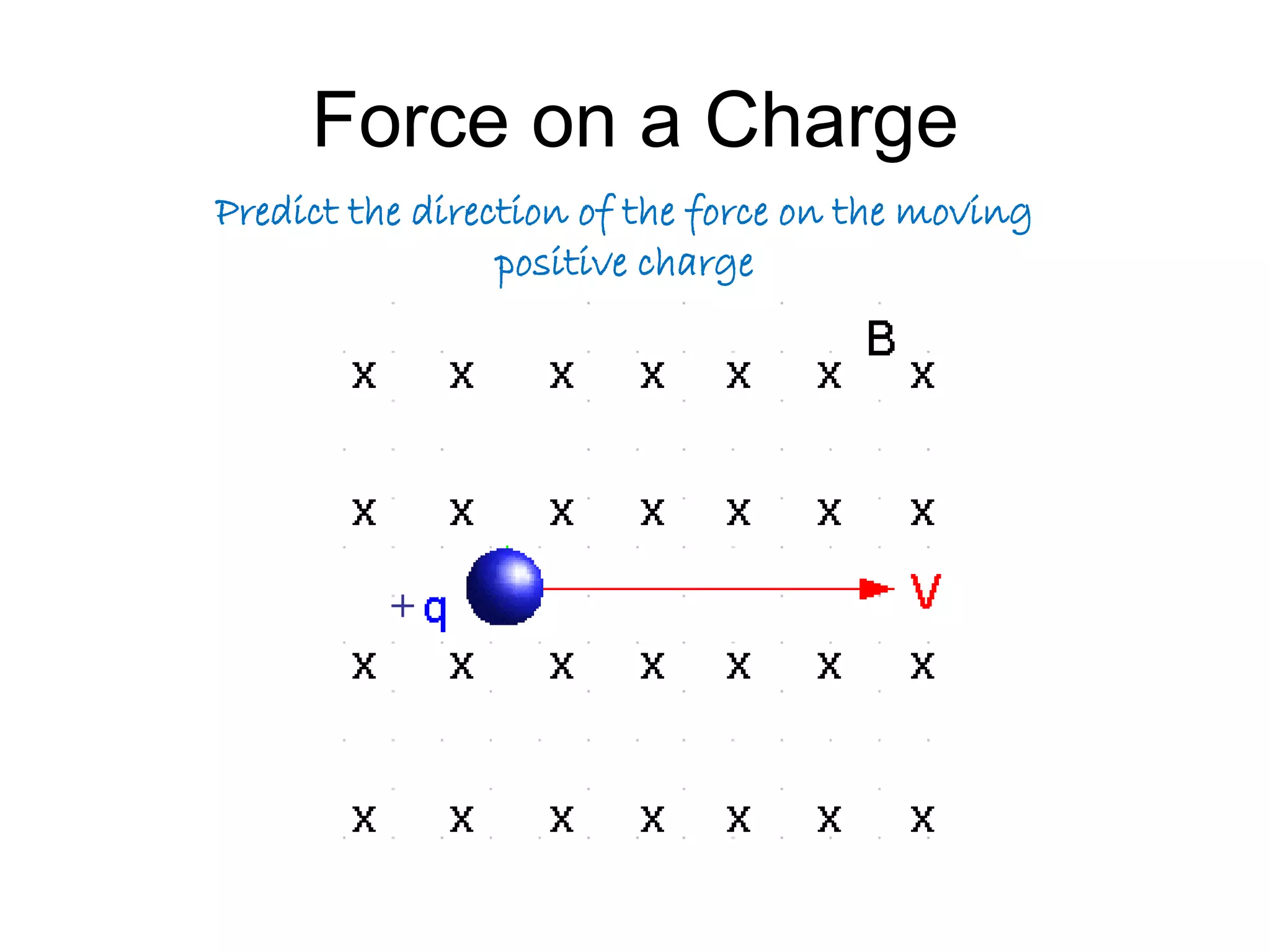
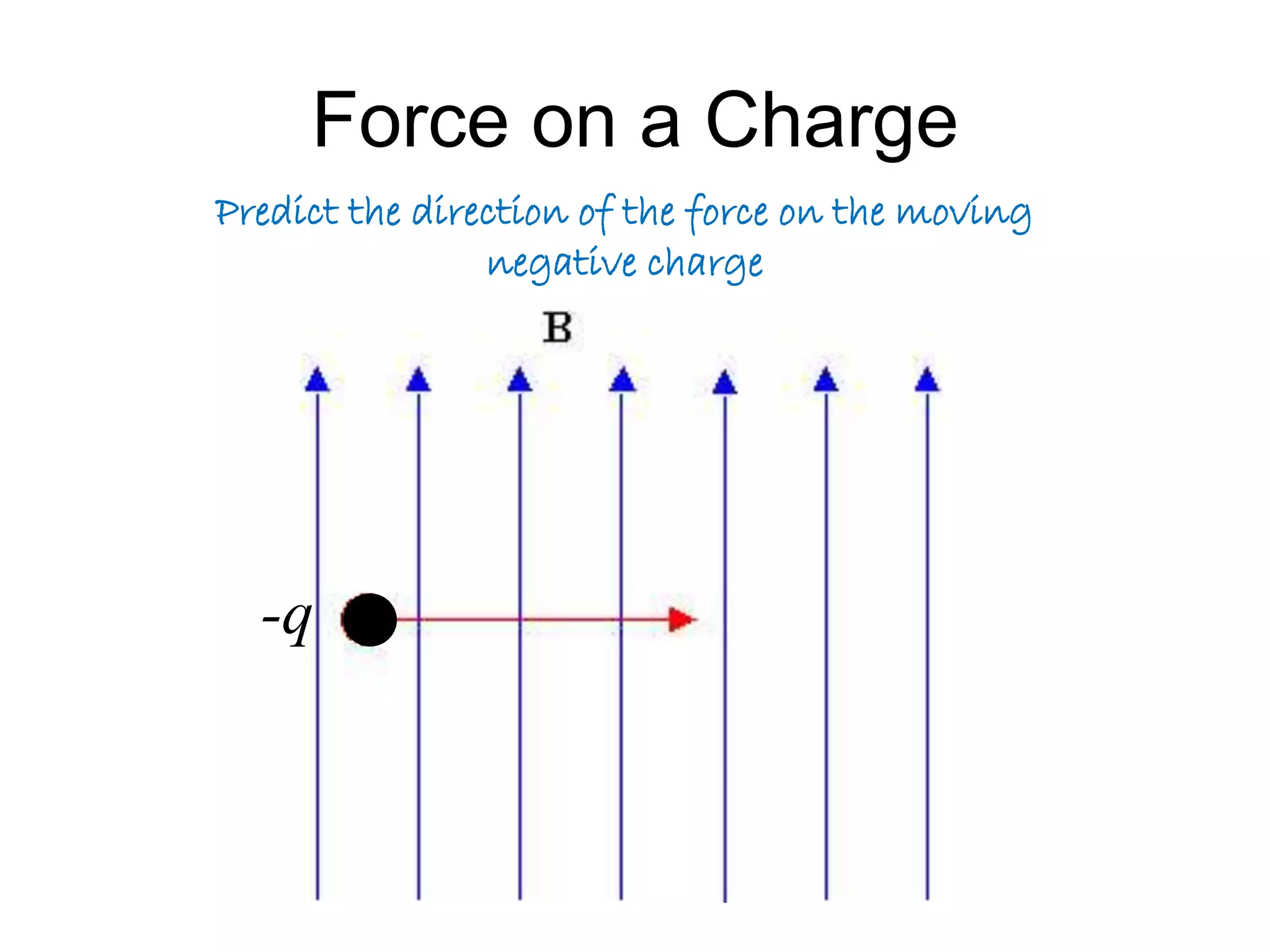
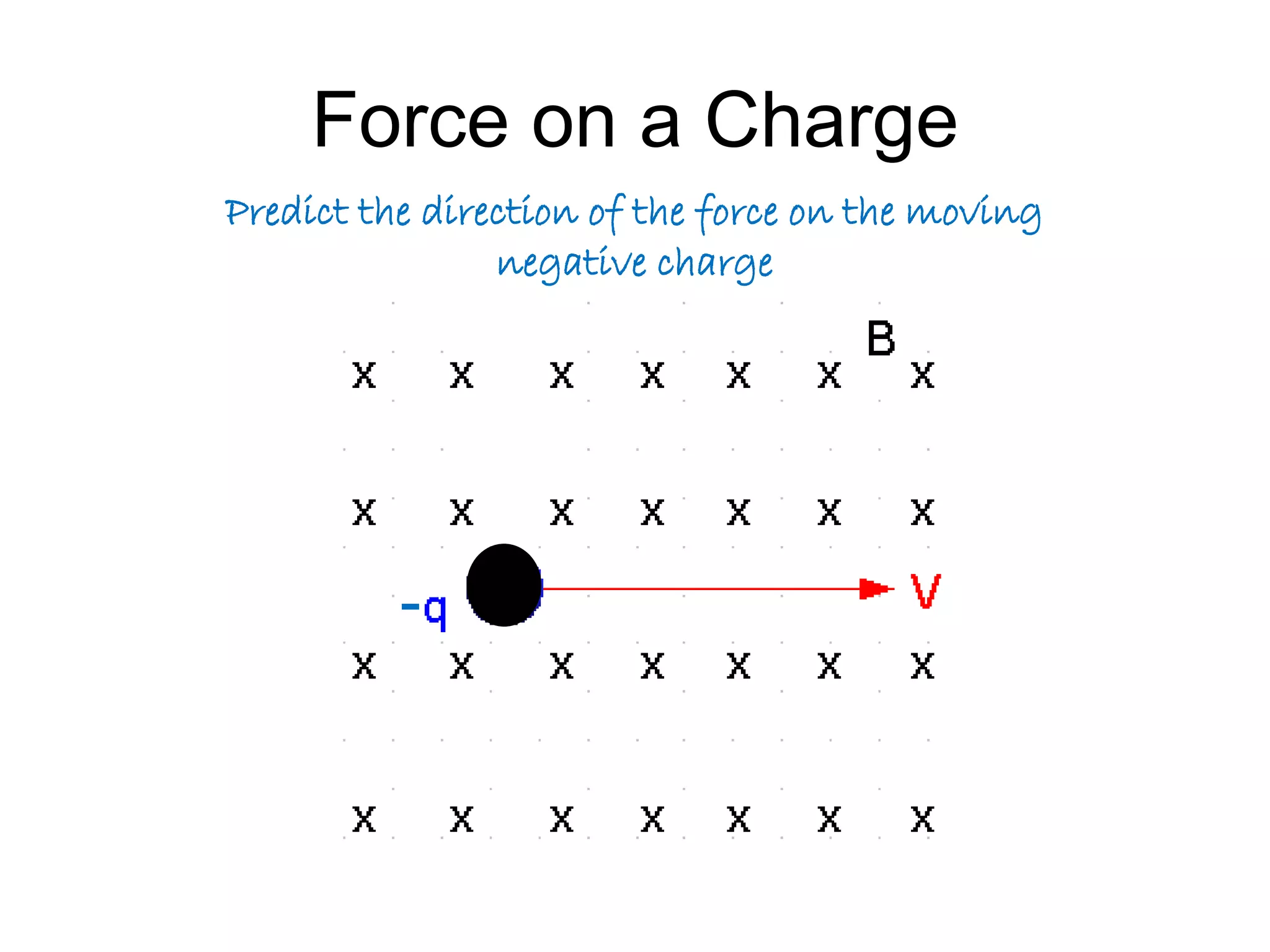
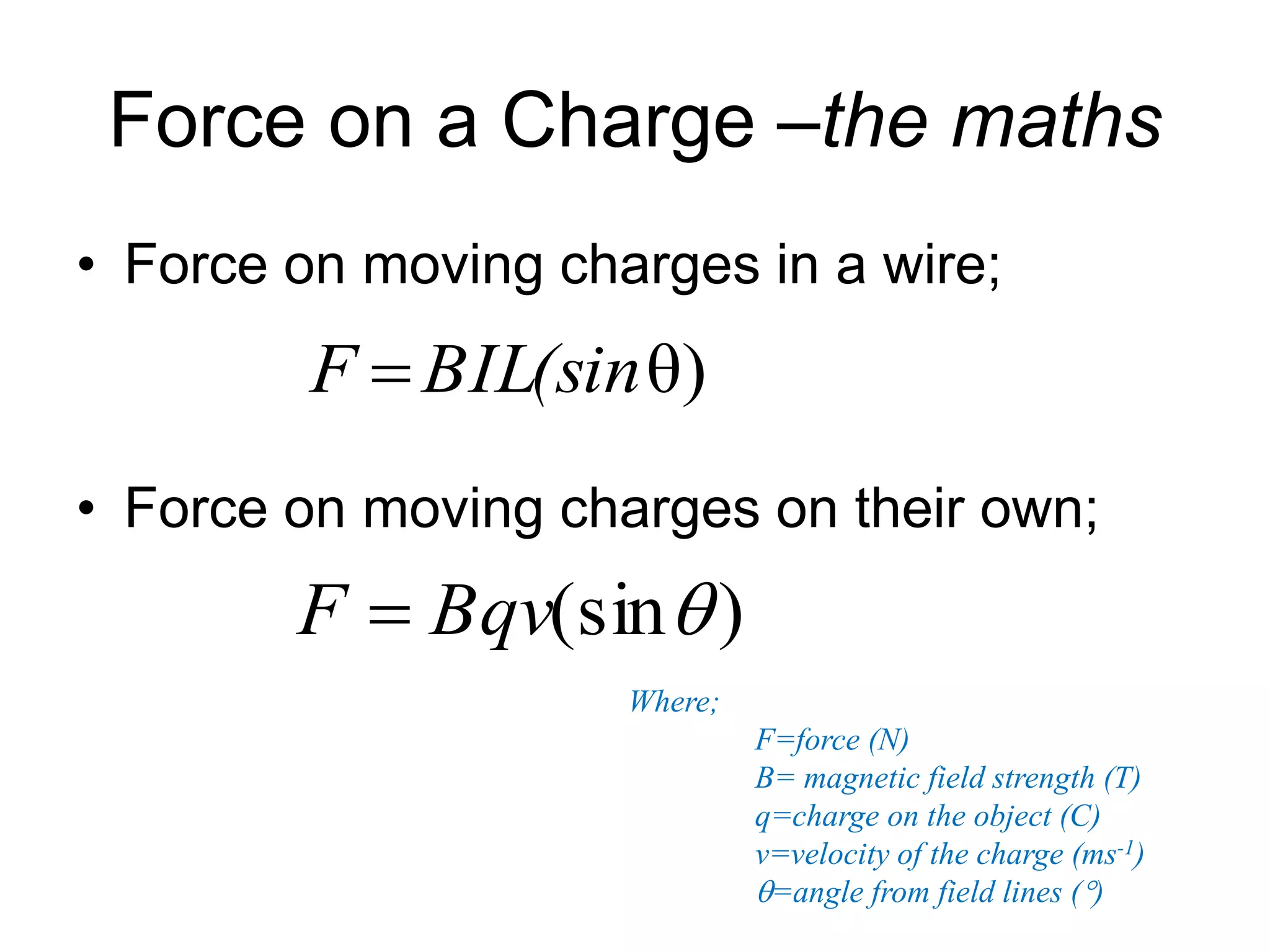
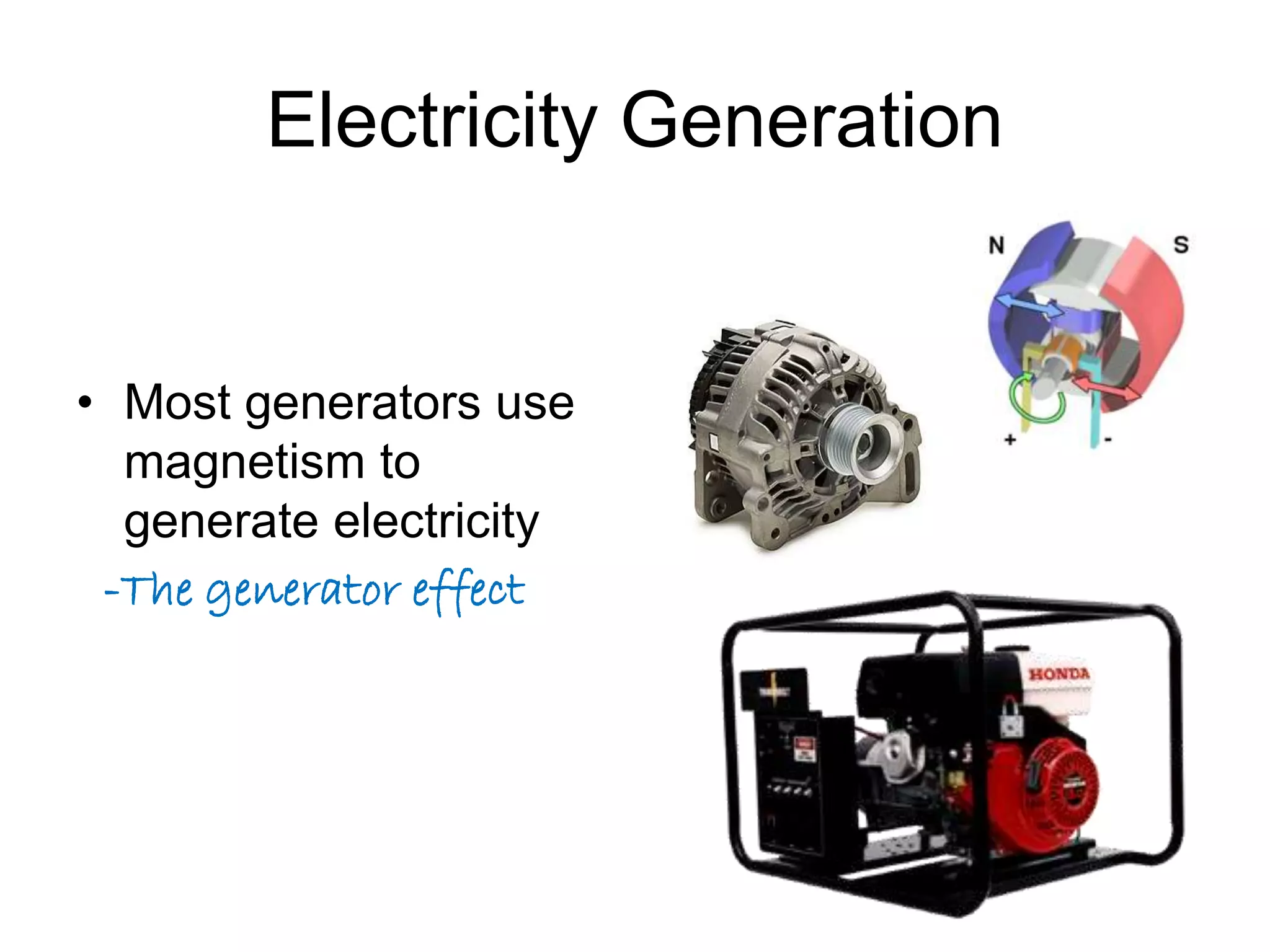
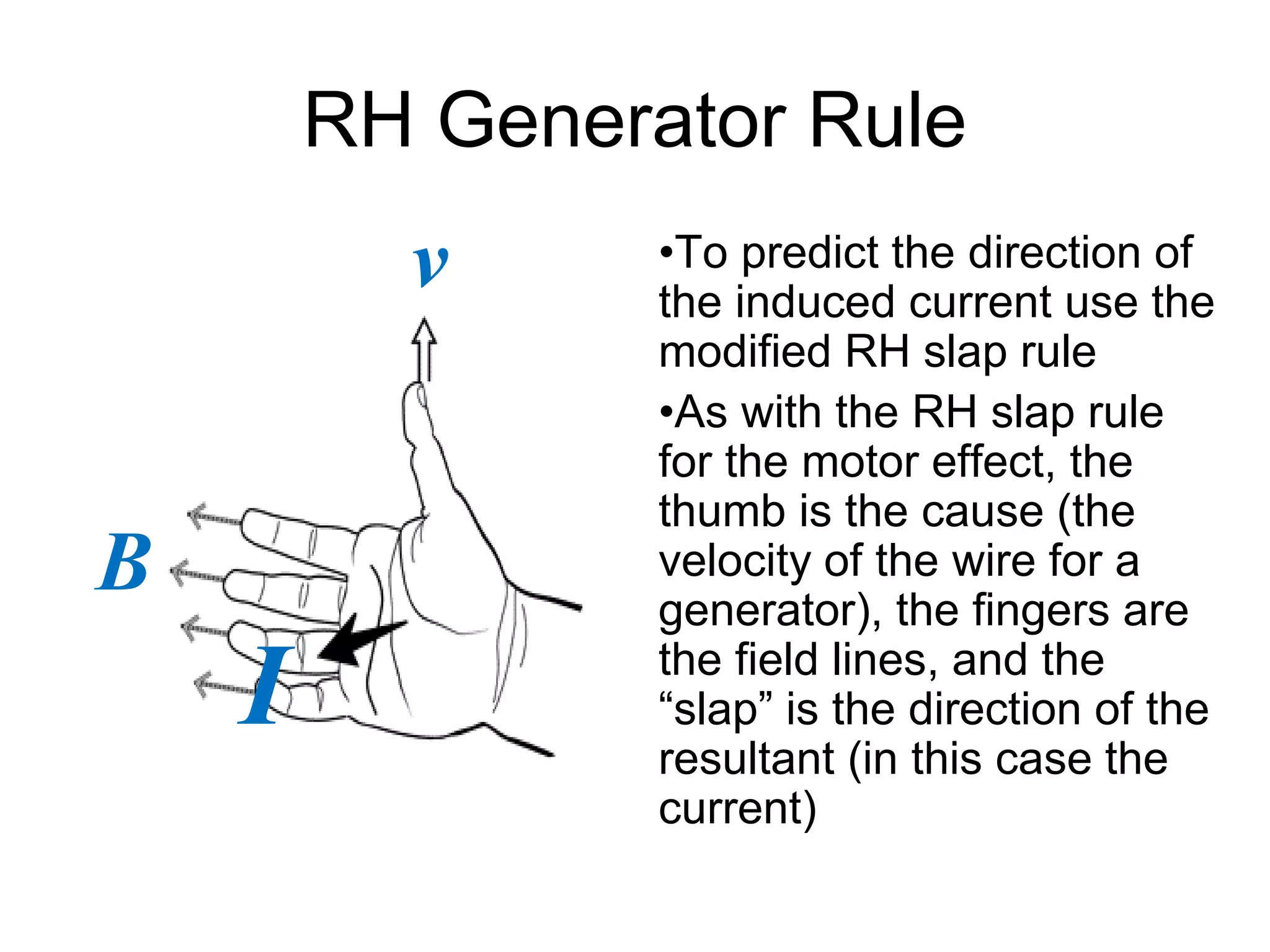
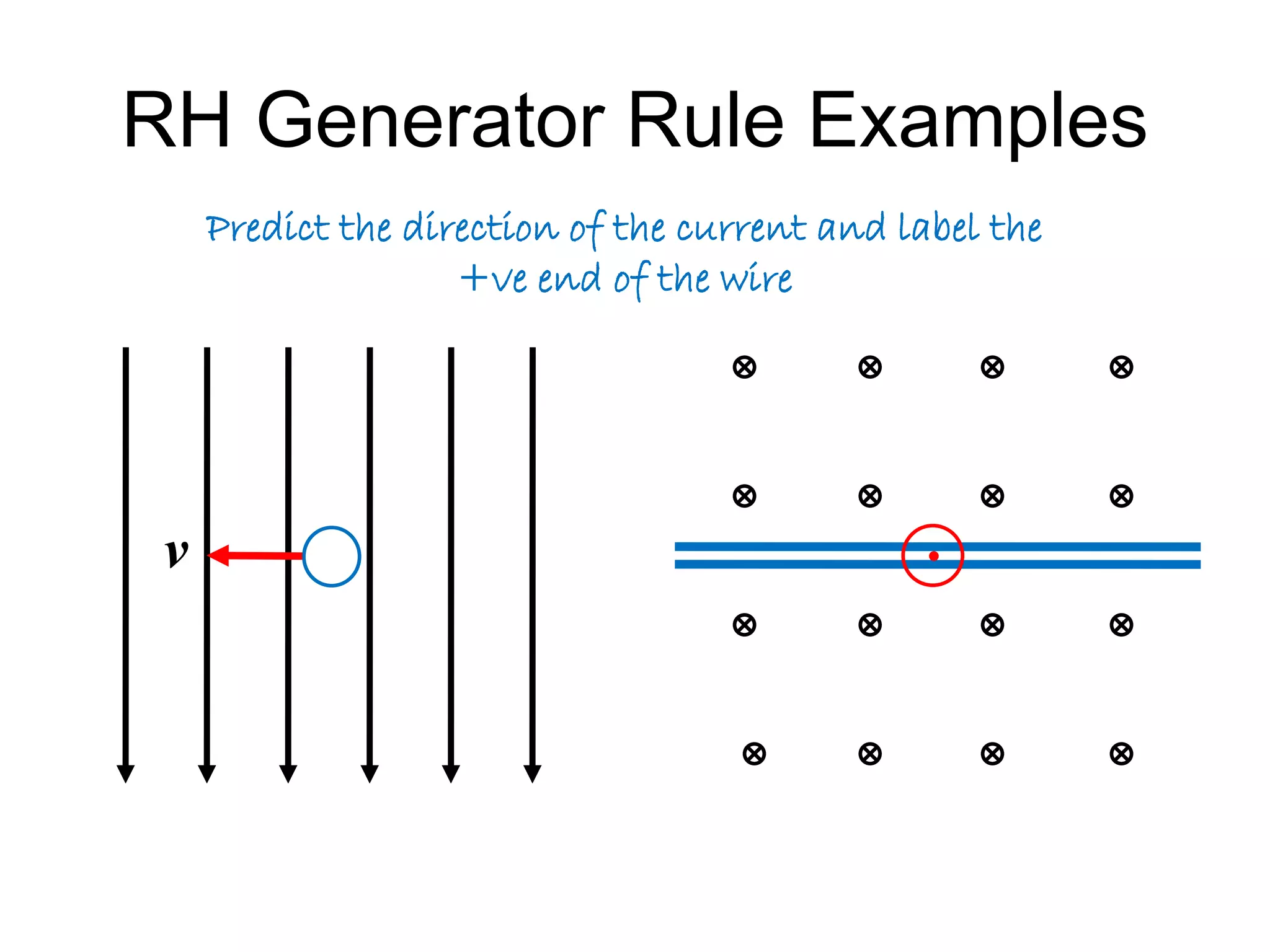
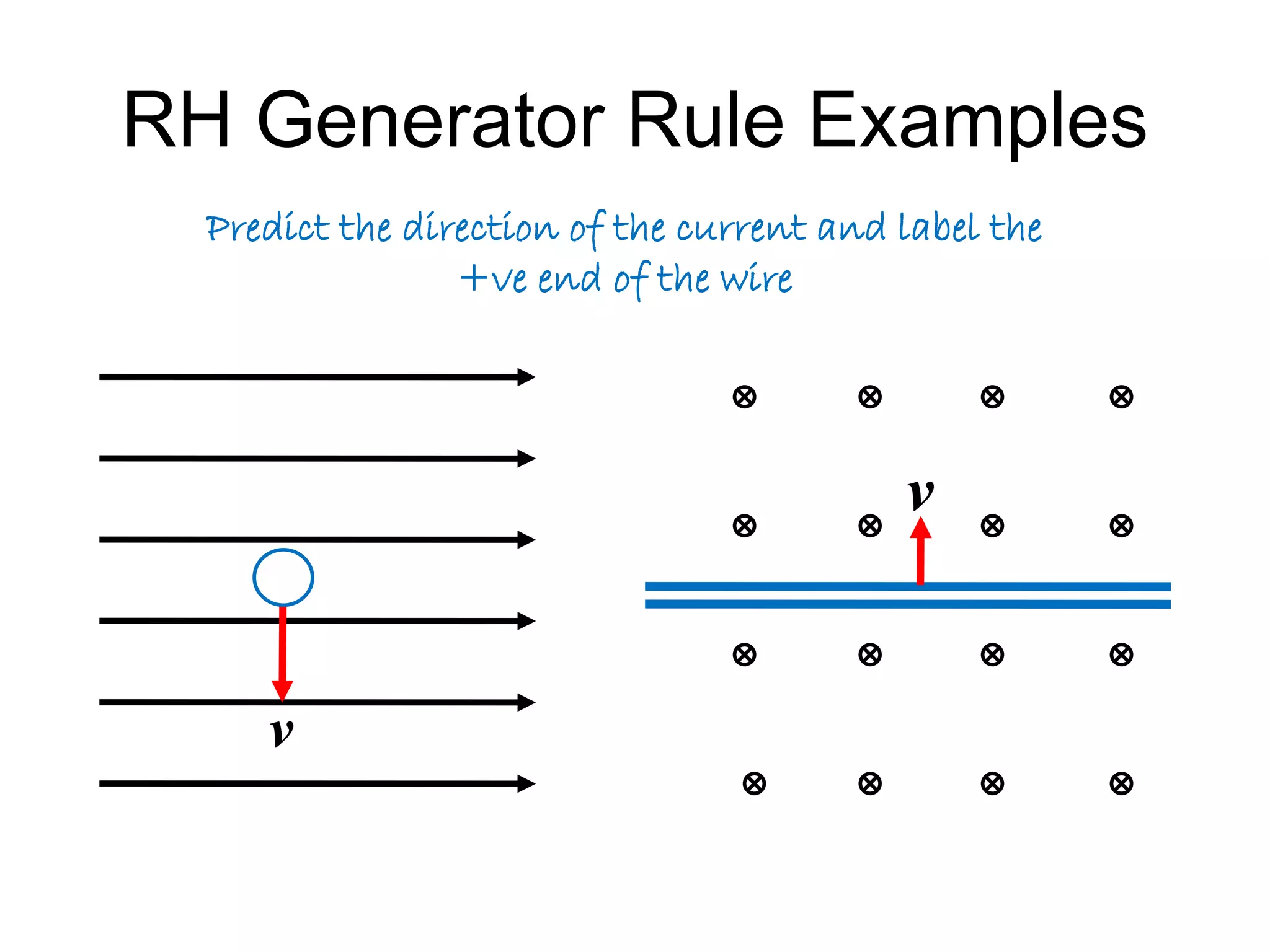
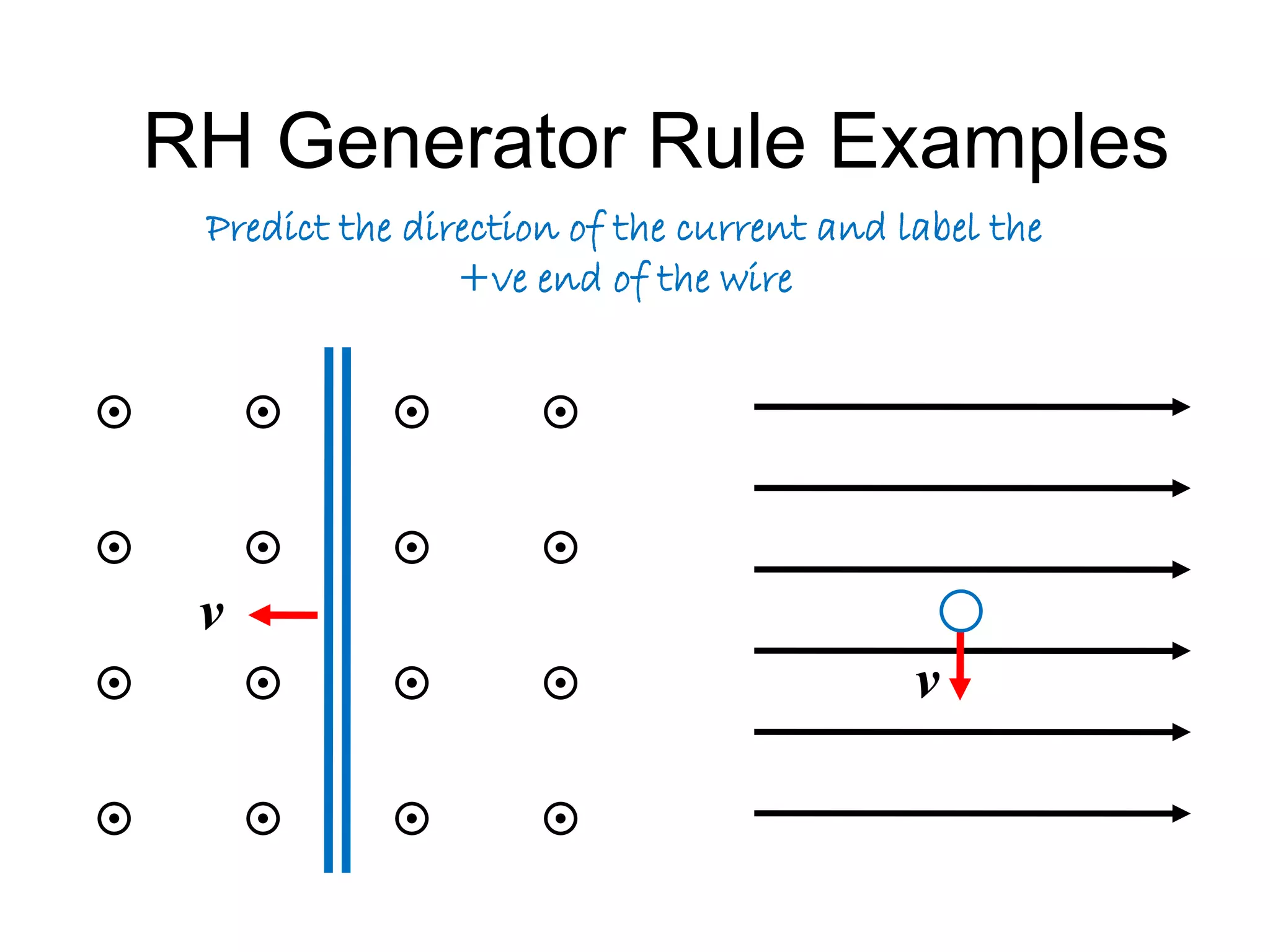
This document discusses electromagnetic induction, including the motor and generator effects. It provides explanations and examples of how current flowing in a wire creates a magnetic field (motor effect), and how a changing magnetic field induces current in a conductor (generator effect). Right-hand rules are introduced to predict the direction of forces and currents. Examples are given for determining the direction of force on current-carrying wires and moving charges in magnetic fields.