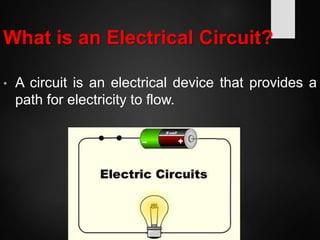
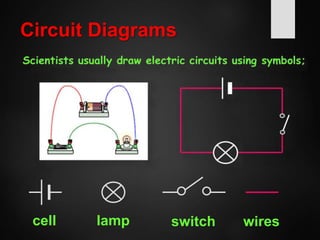
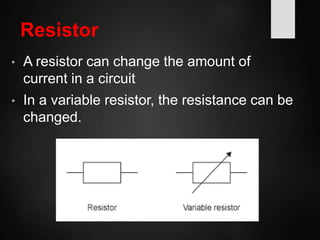
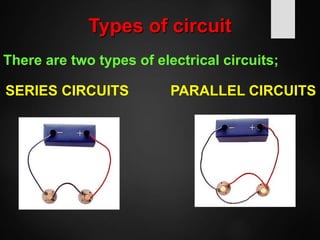
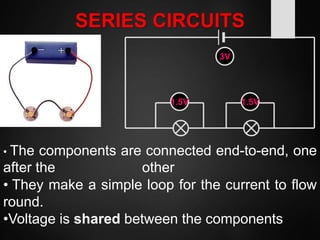
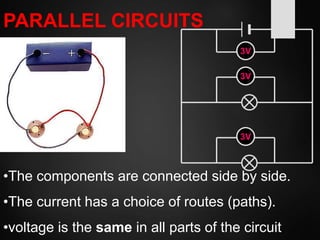
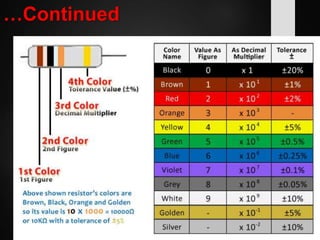
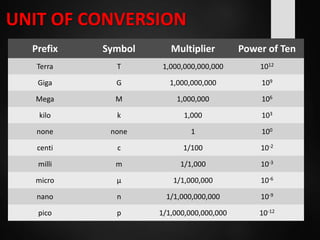
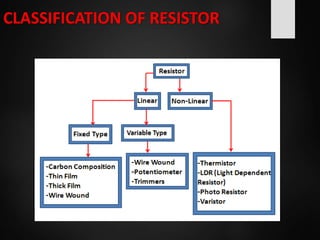
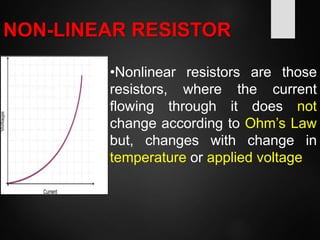
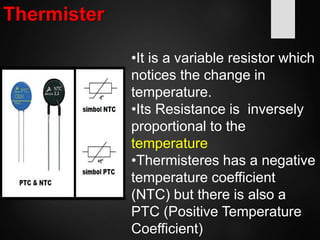
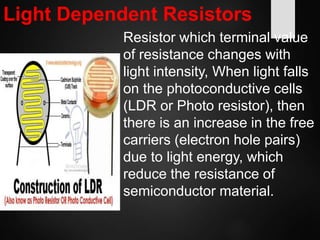
The document provides an overview of basic electrical concepts, including the principles of electricity and notable figures such as Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Edison. It explains the nature of electrical circuits, the types of circuits (series and parallel), and the concept of resistance, including Ohm's law and classifications of resistors. Additionally, it describes variable resistors and their behavior under different conditions, such as temperature and light intensity.