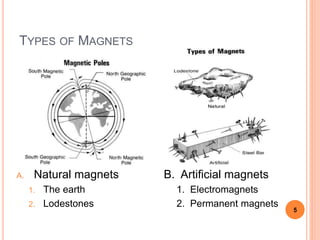
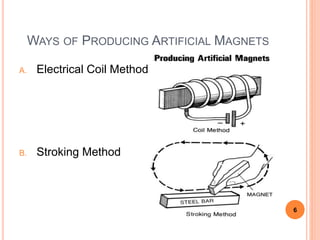
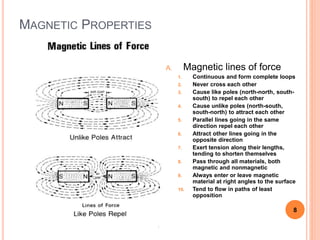
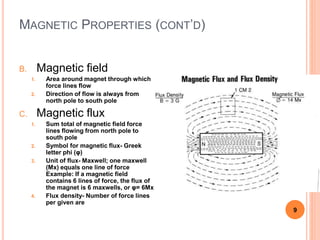
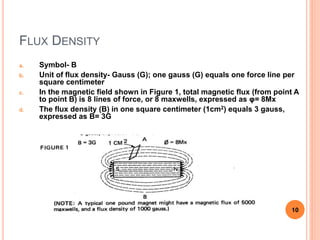
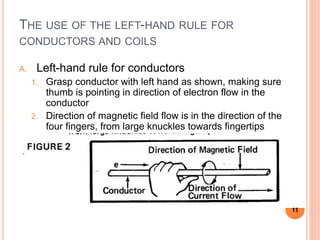
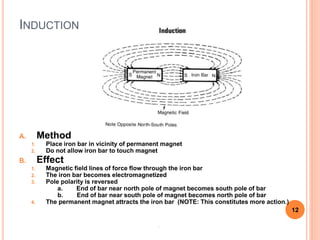
This document defines magnetic terms and properties, describes different types of magnets, and explains how artificial magnets are produced. It discusses the permeability of various materials, magnetic fields and flux, and uses of the left-hand rule. Induction is demonstrated by magnetizing an iron bar near a permanent magnet. Practical applications of induction in electronics are also outlined, including uses in transmission, transformers, motors, and memory.