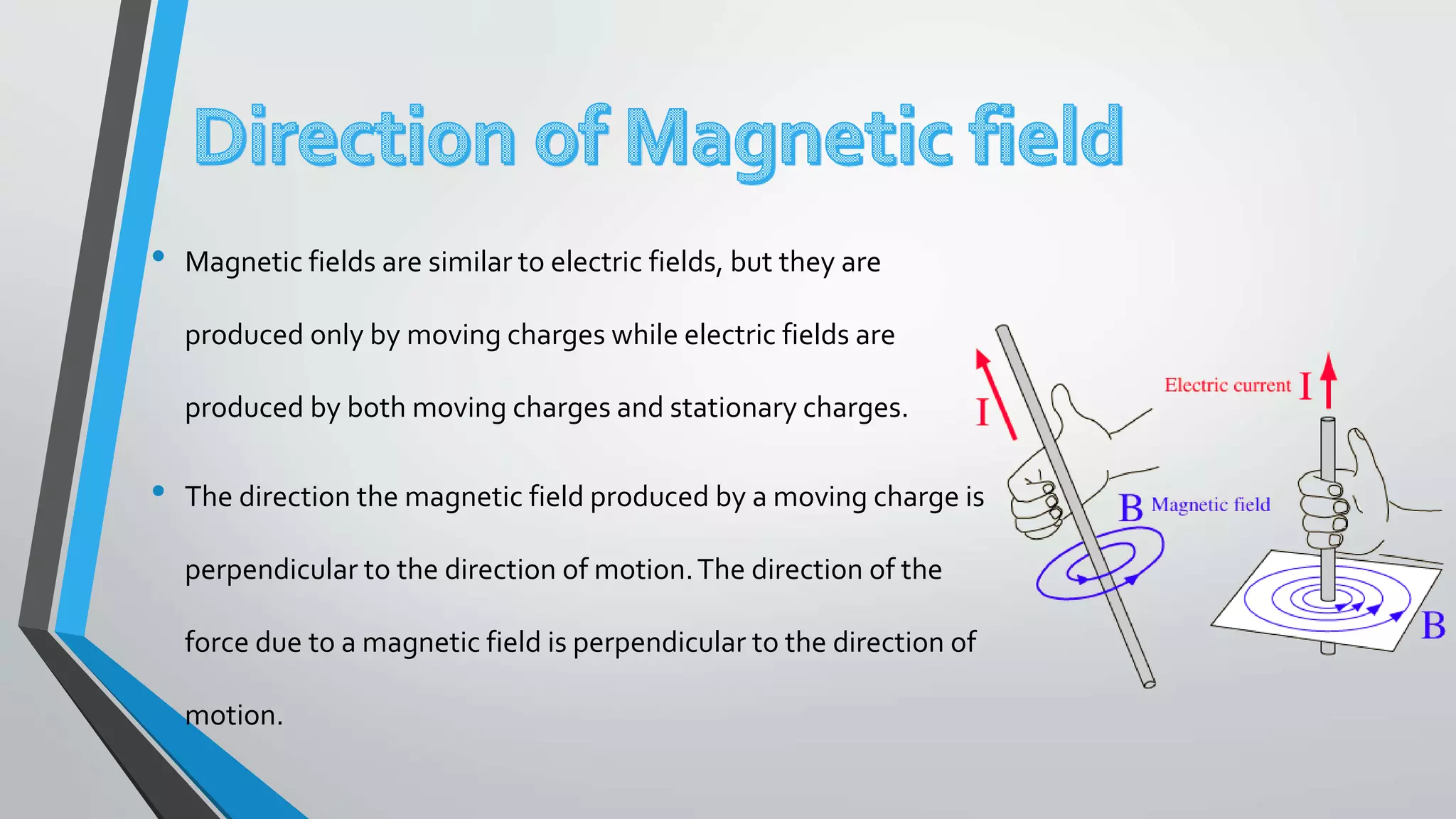
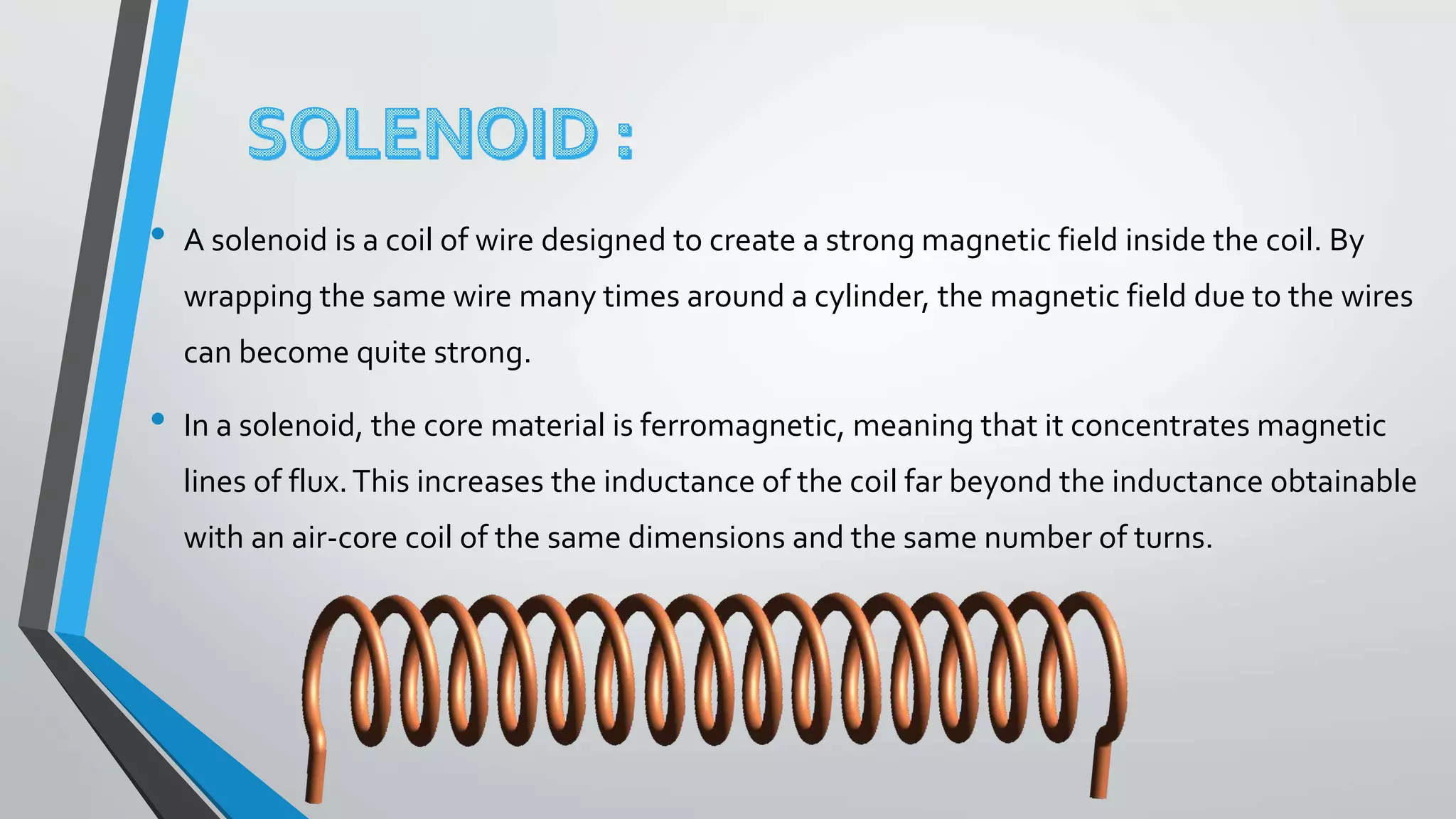
This document discusses magnetic fields produced by solenoids. It defines a solenoid as a coil of wire that produces a strong magnetic field inside its core. The magnetic field strength inside a solenoid, B, is directly proportional to the number of turns N, and the current I, as described by the equation B=μNI. It also provides an example of writing a MATLAB program to plot the magnetic field in the x-z plane for a given solenoid geometry and current.