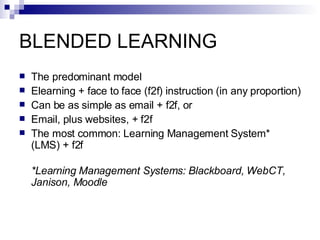
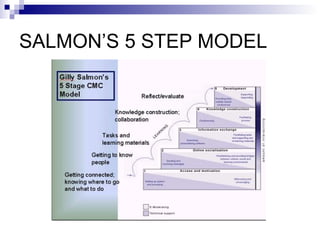
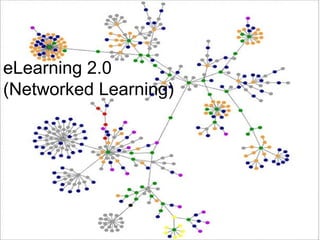
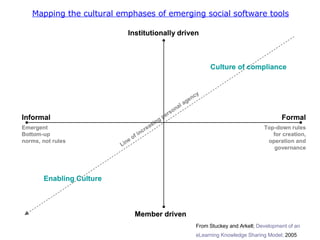
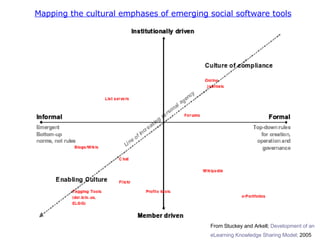
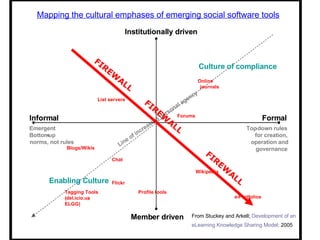
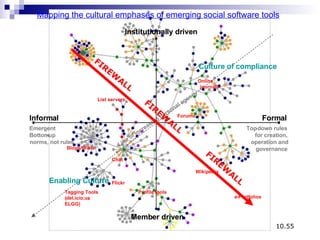
The document discusses emerging trends in eLearning, including the progression from distance learning to ubiquitous learning enabled by mobile technologies. It describes blended learning models that combine online and face-to-face instruction, and social software tools that allow user-generated content and networked learning. The document also notes tensions between traditional education systems and more student-centered approaches enabled by social software.





























![Michael Coghlan [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elearning-emerging-trends-and-issues3297/85/eLearning-emerging-trends-and-issues-40-320.jpg)
