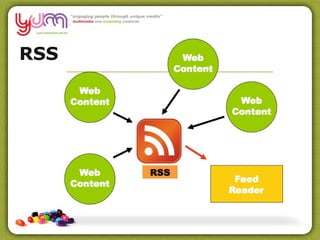
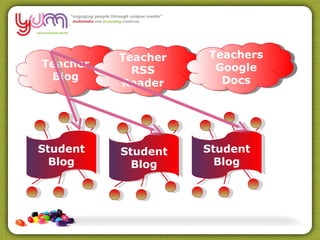
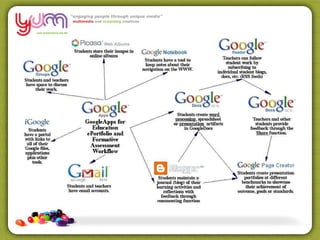
The document discusses the use of Web 2.0 tools like RSS readers, wikis, and social networks to facilitate personal learning networks (PLNs) and knowledge sharing. It notes that these tools allow learners to actively create and participate in information instead of just consuming it. The document also outlines several principles of effective knowledge sharing, including the importance of communities of practice, storytelling, and balancing online and offline interactions.






































![Support Michael Call Me – 03 5331 7625 SMS/Call – 0409 317 625 Email me – [email_address] Skype Me – swampfox_mg Twitter - @ mickgwyther](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2-100907054108-phpapp02/85/Session2-46-320.jpg)

