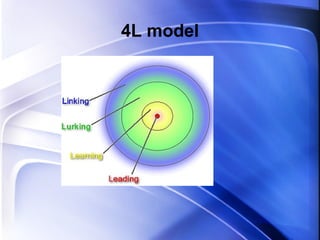
The document discusses virtual learning in schools and the use of Web 2.0 tools. It outlines key points about optimizing resources, blended learning, collaboration, and leveraging technology to transform education. It also discusses personal learning environments, learning management systems, social networking tools, and constructing models of eLearning workflows and communities of practice.
![Virtual Learning in Schools: Thriving in Web 2.0 Vincent Jansen LEARN Email: [email_address] Skype: vjansen07 http://virtualschooling.wikispaces.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nb4post3792/75/Nb4post-1-2048.jpg)