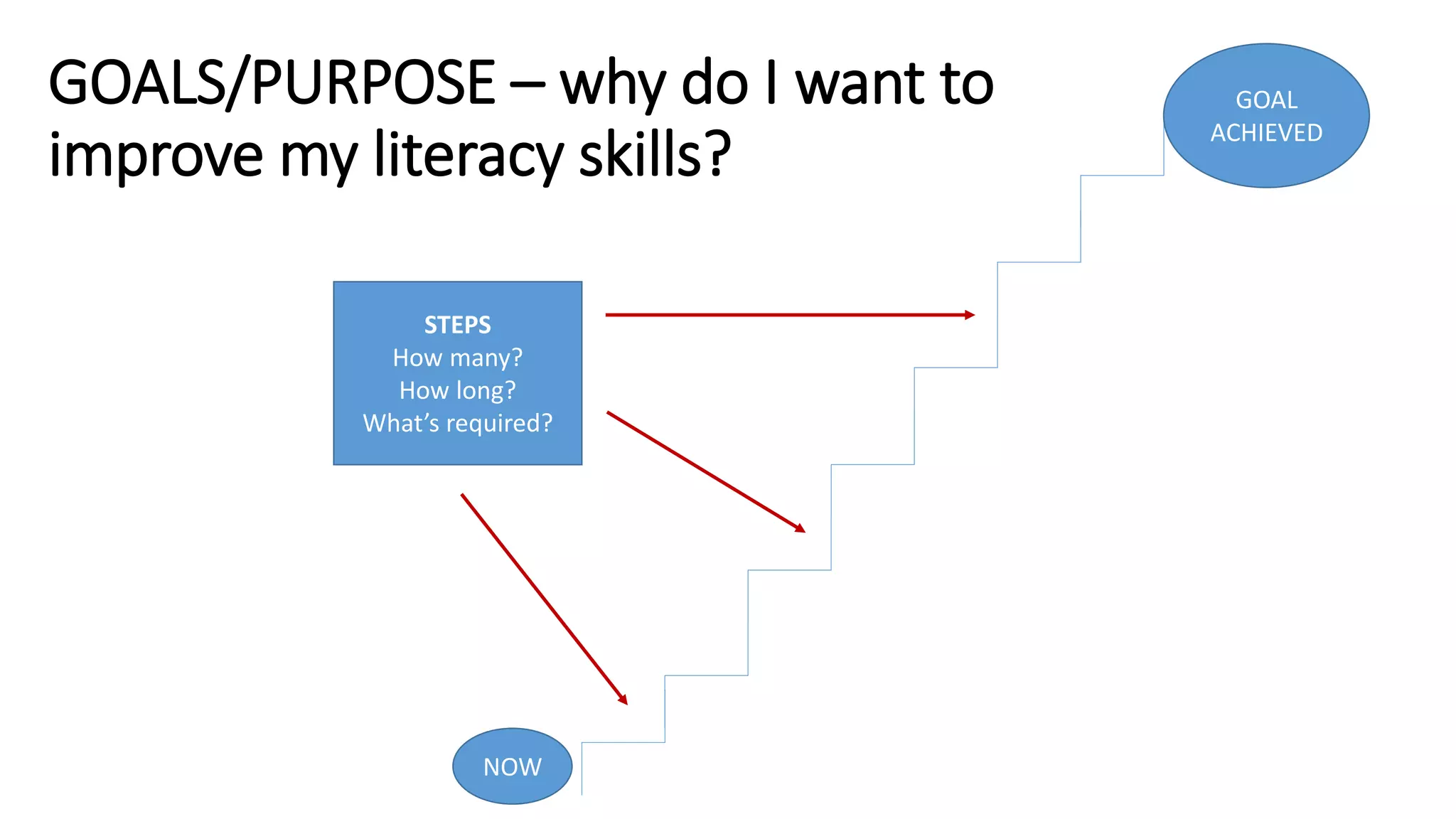
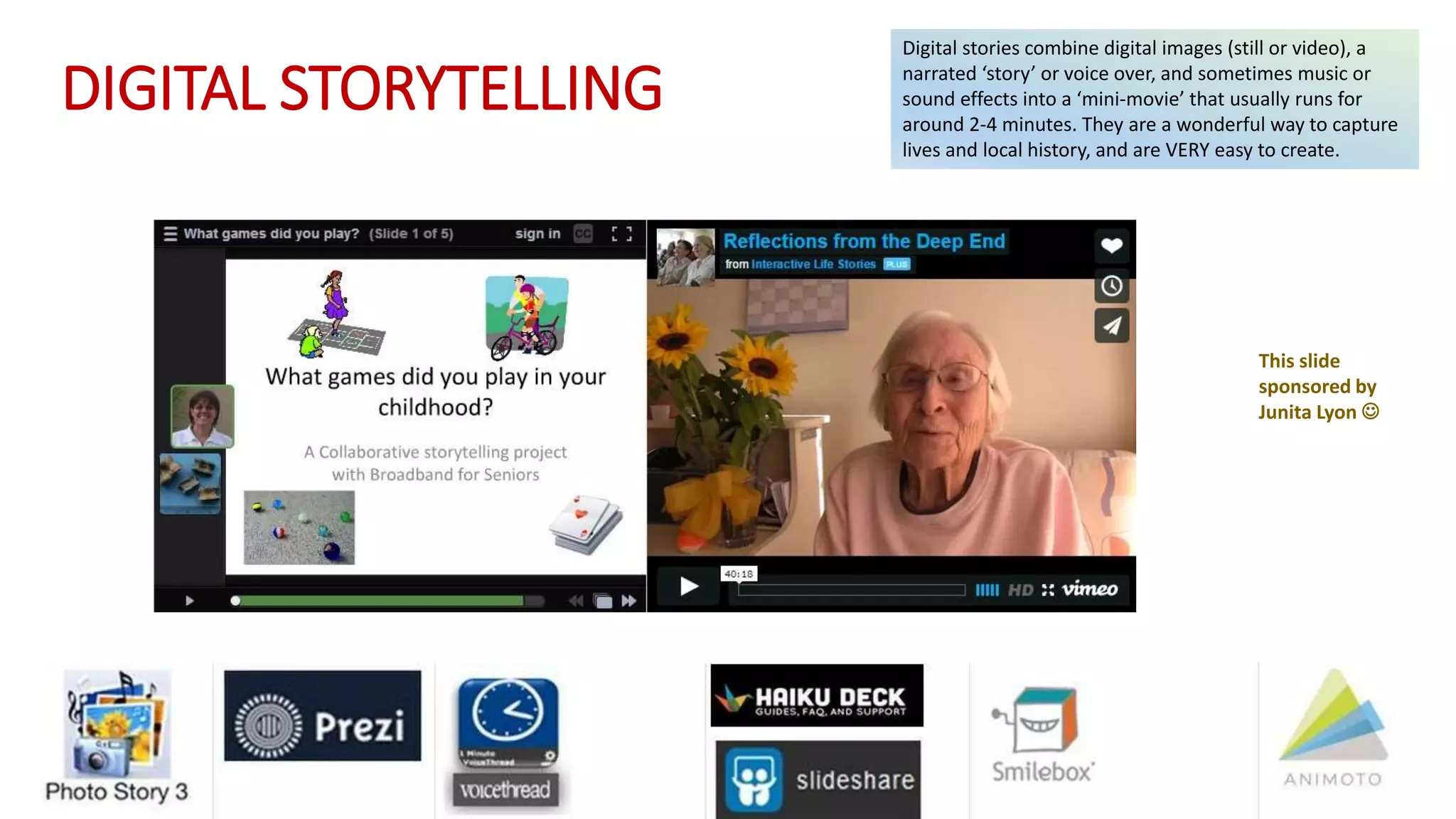
This document discusses digital delivery of literacy education for low-level literacy students. It provides background on adult literacy rates in Australia, with nearly half the adult population having problems with literacy. It then discusses various types of literacy like digital literacy and multiliteracy. It considers how to design literacy education for low-level students, emphasizing clear context and purpose, opportunity for creation and interpretation, and support. Possible activities discussed include using images from Flickr to teach tagging, digital storytelling, and apps to support learning.