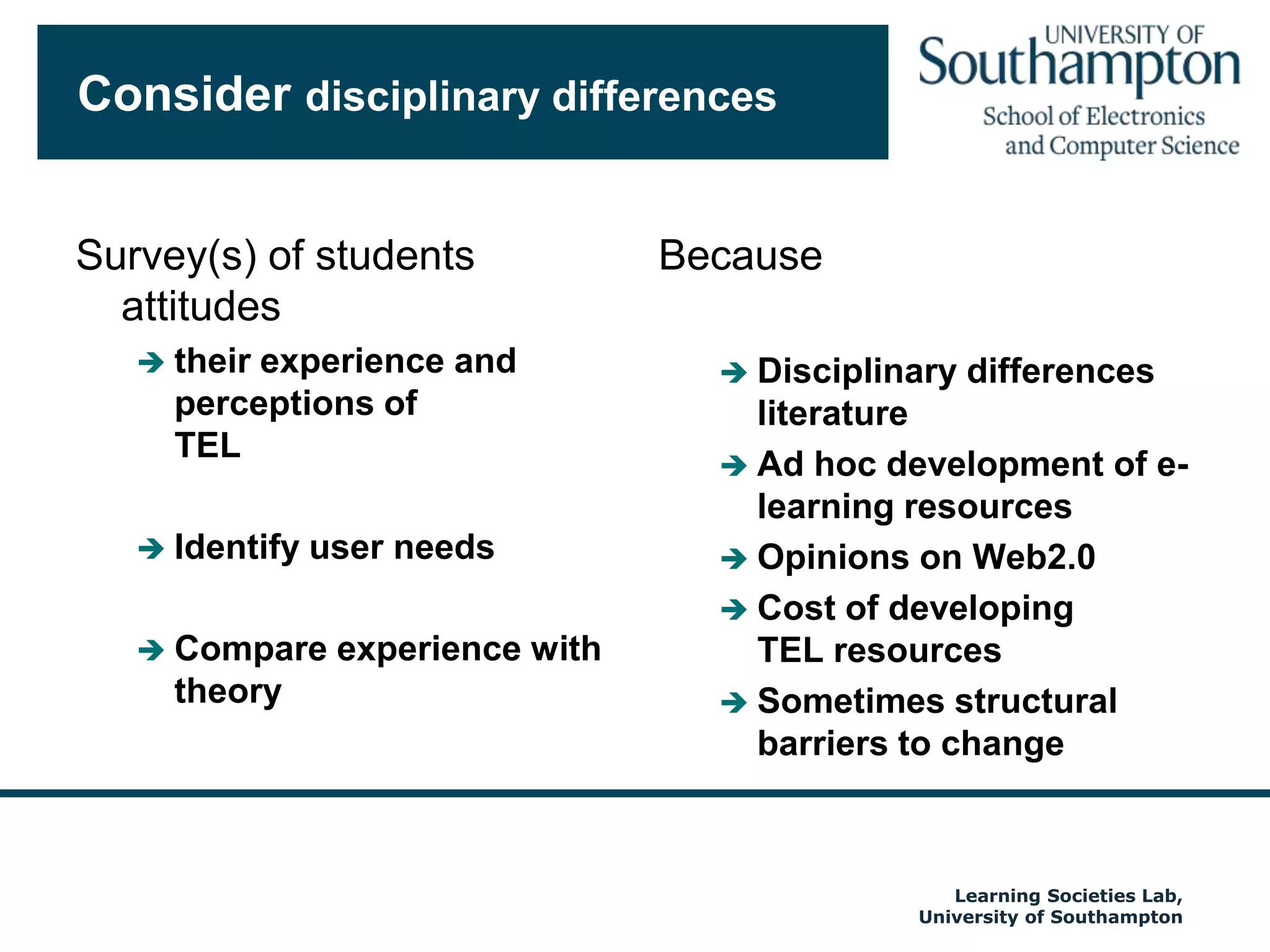
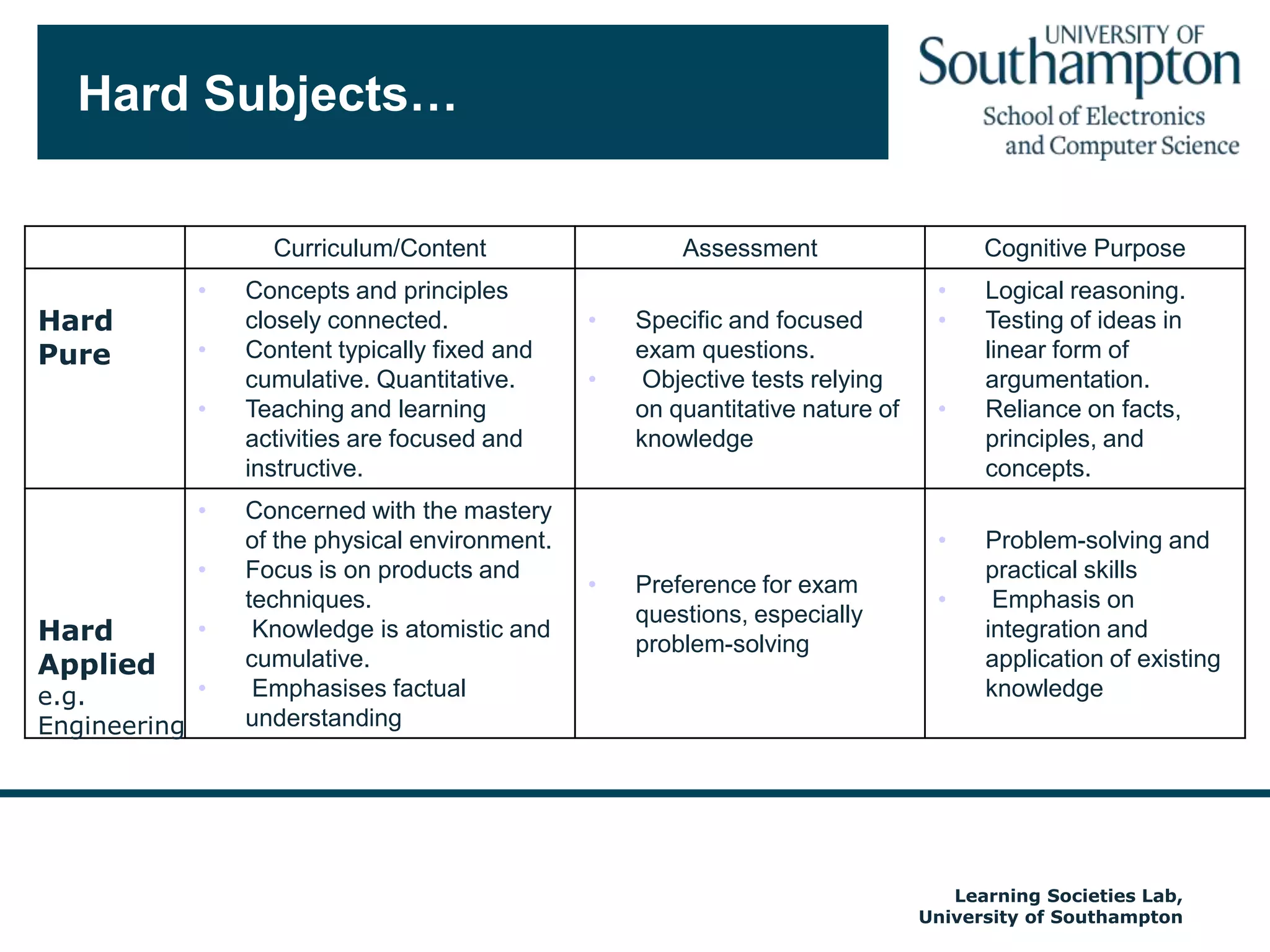
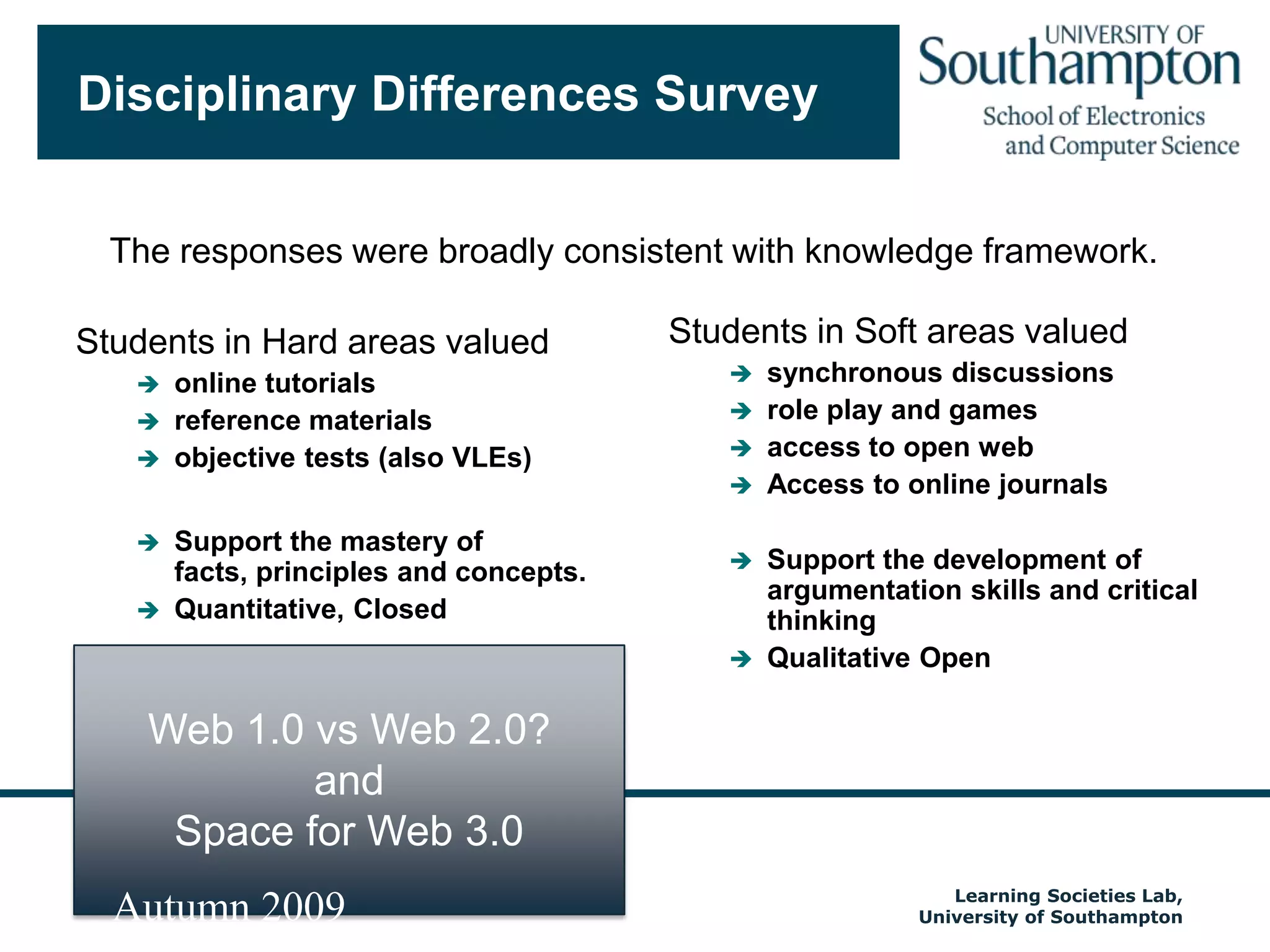
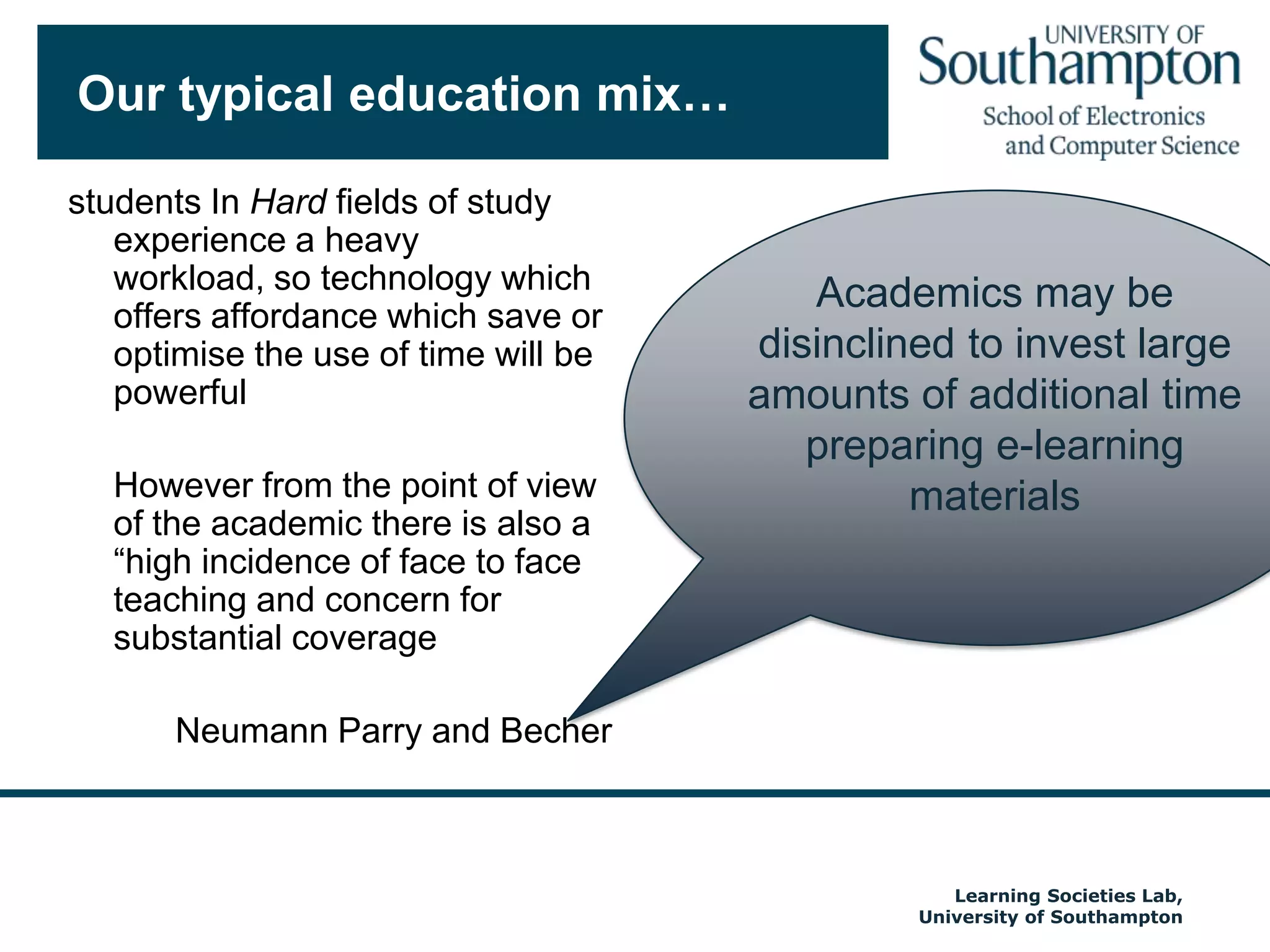
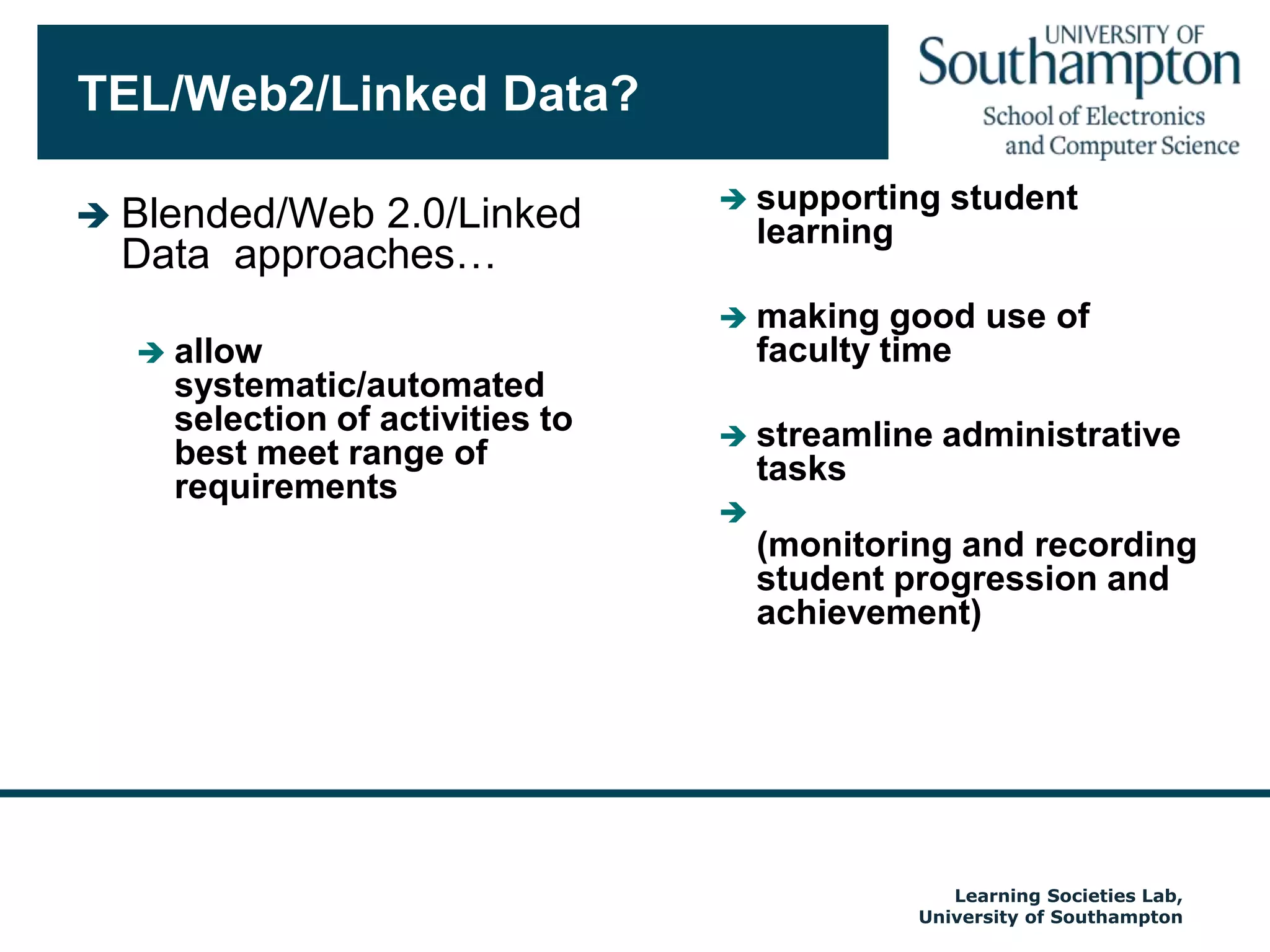
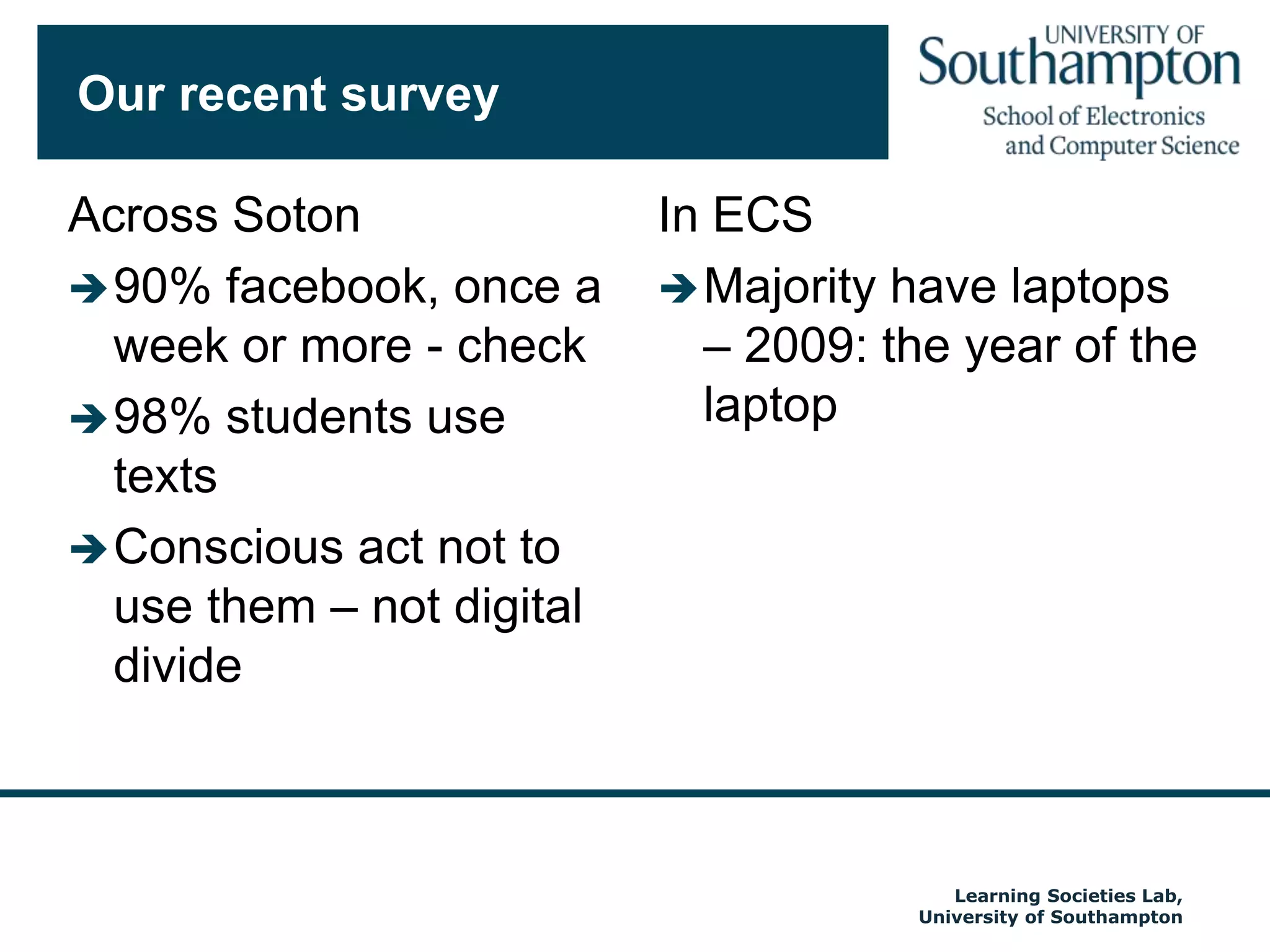
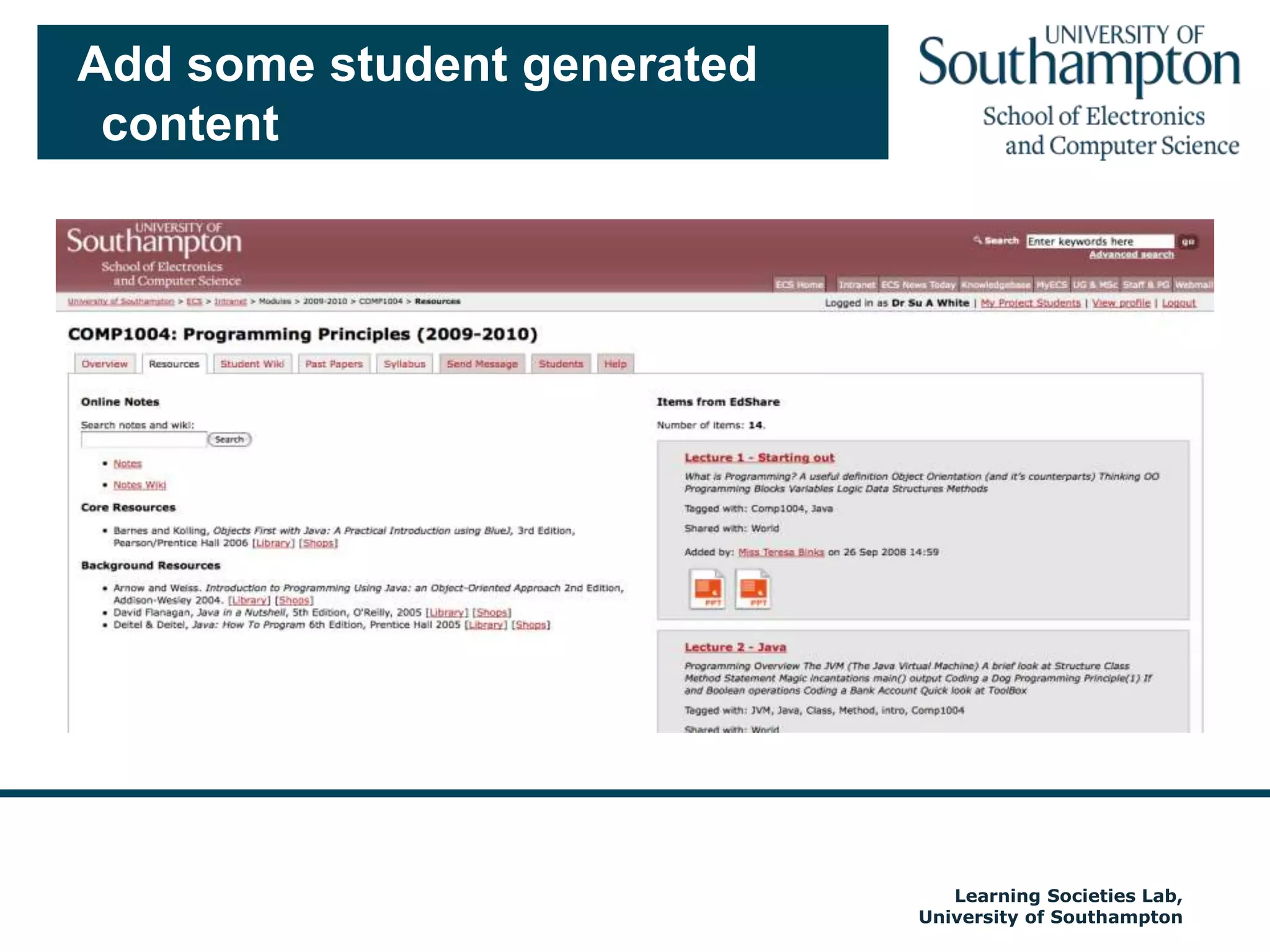
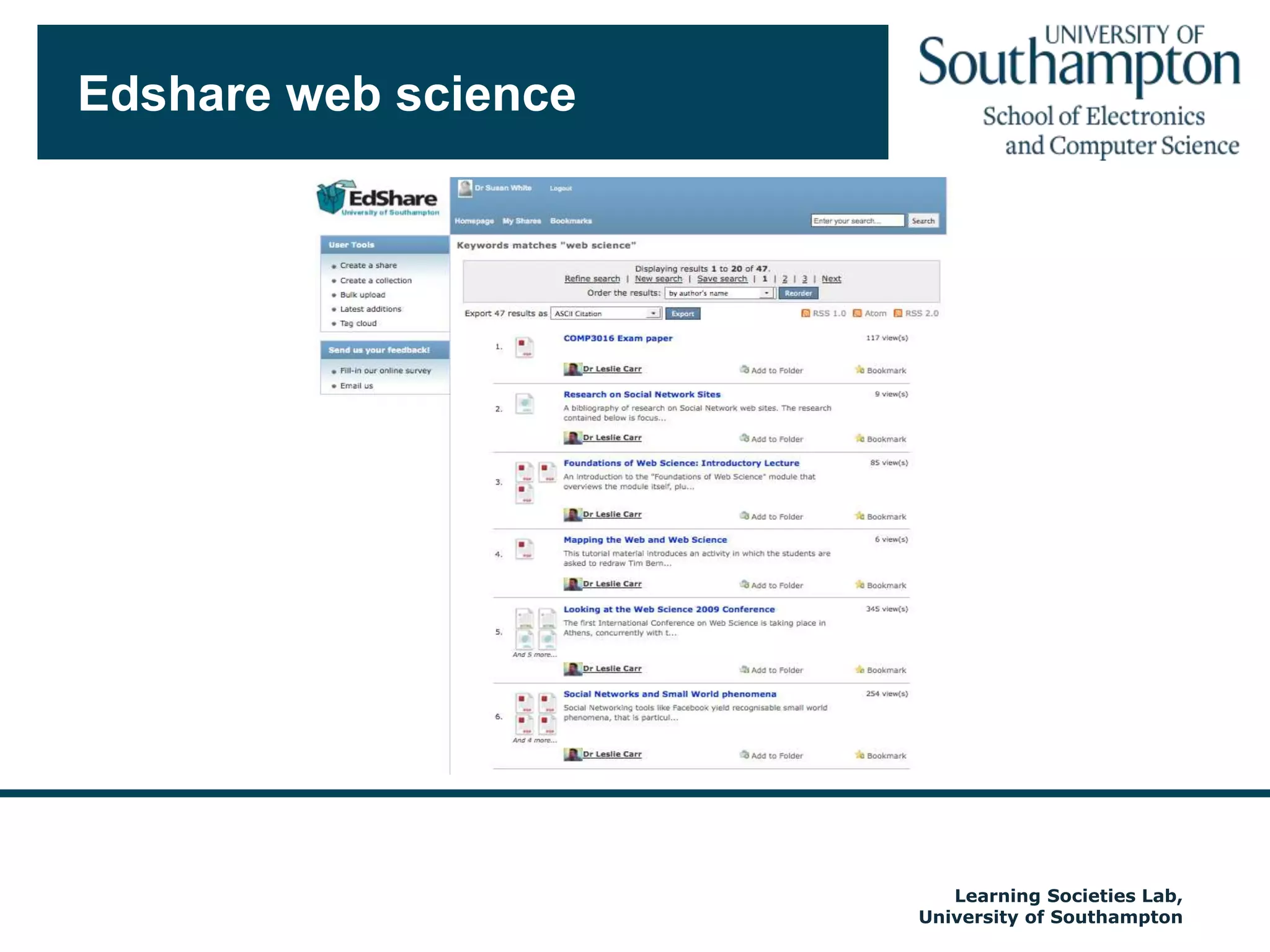
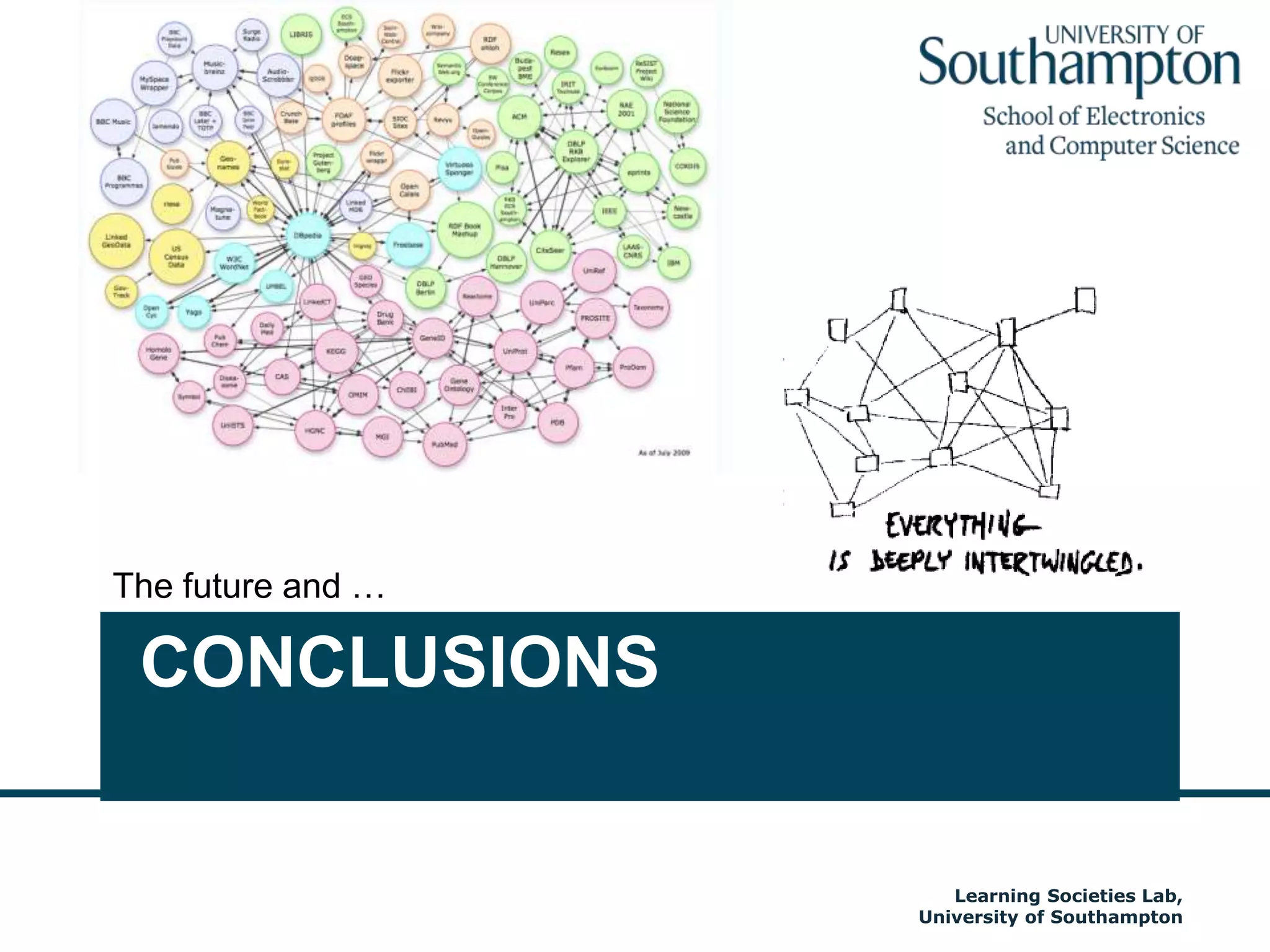
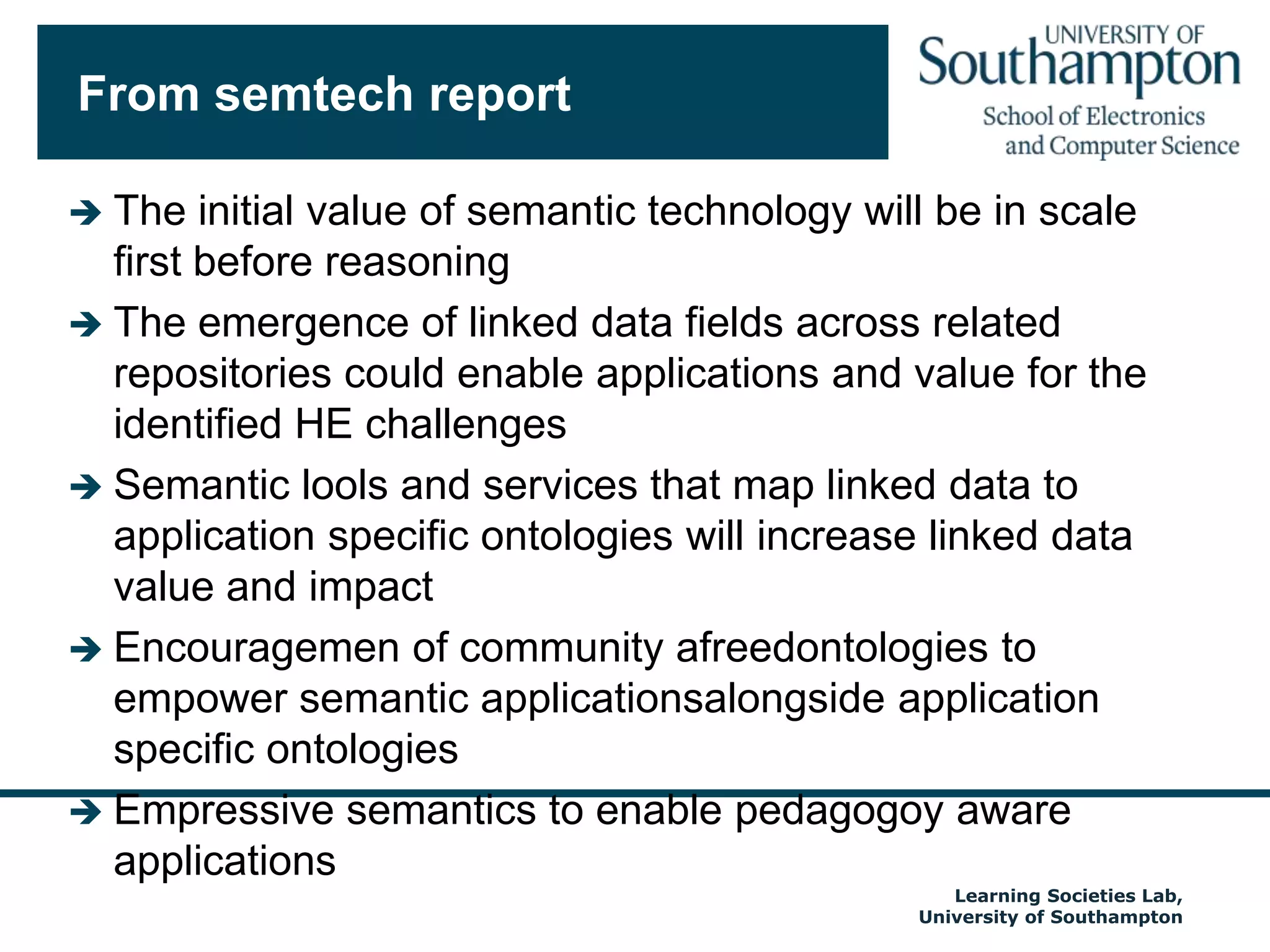
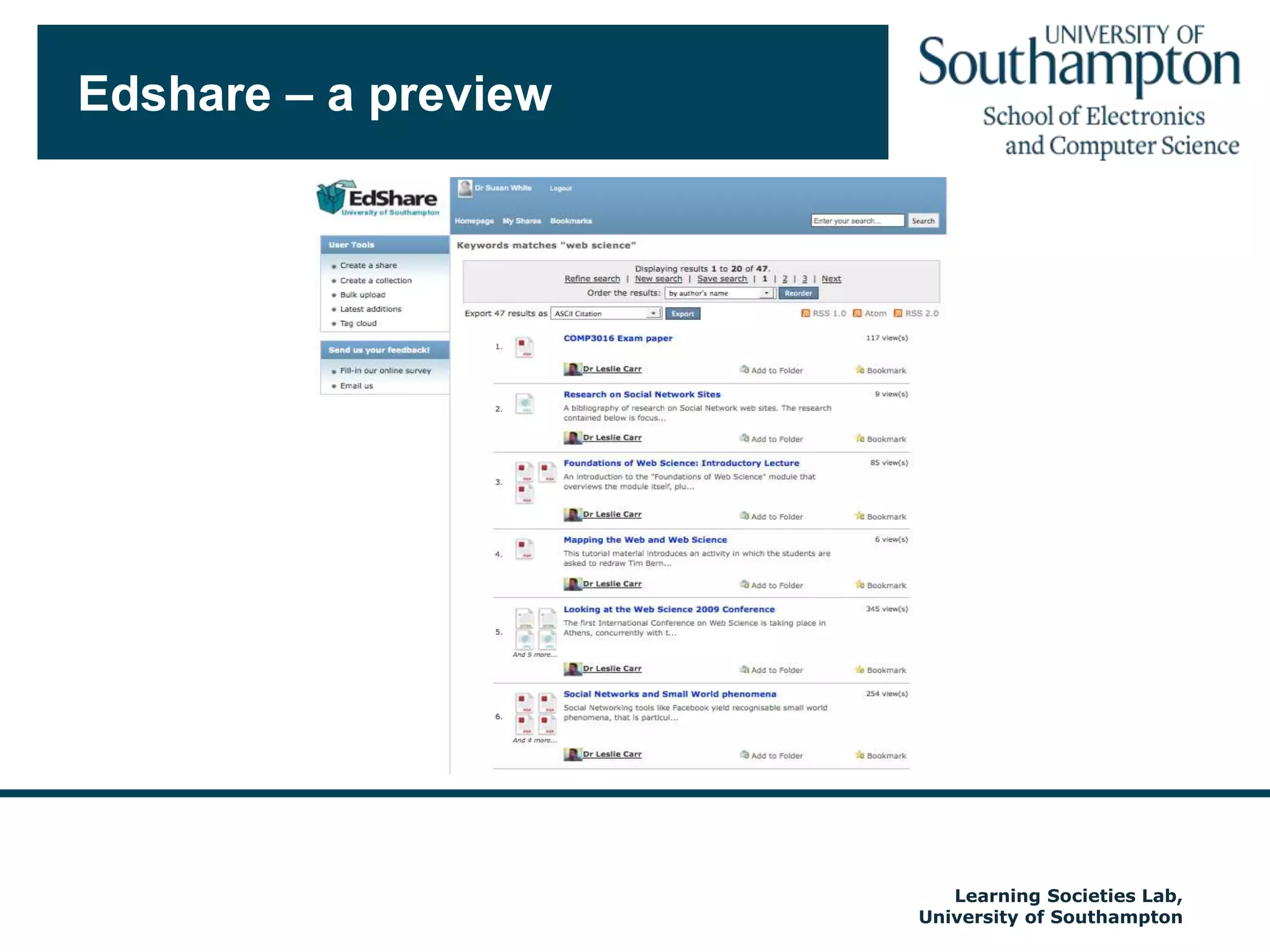
The document discusses the transformative impact of technology on education, specifically focusing on the EdShare experience in reshaping collaborative learning practices among universities. It highlights the shift from traditional teaching methods to more interactive and tech-equipped approaches, emphasizing the importance of understanding disciplinary differences and user needs in educational technology development. The conclusion emphasizes the future potential of semantic technologies and linked data to enhance learning experiences and outcomes.


![Universities and knowledge The HumboldtianIdealIn universities, learning should not be [defined] in terms of the passing on of well established knowledge, but always in terms of not yet completely solved problems.”Humboldt, 1807Thanks to Lewis EltonAutumn 2009Web 2.0affordances?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web2-0hea-icsdemontfortnov2009finalfinal-100615092022-phpapp01/75/Web2-0-hea-ics-demontfortnov2009finalfinal-5-2048.jpg)