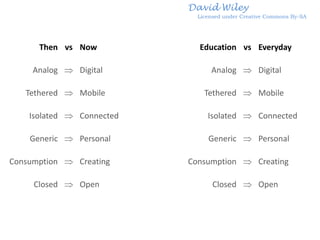
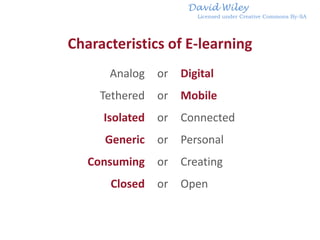
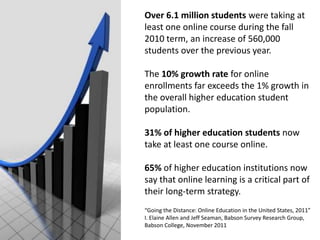
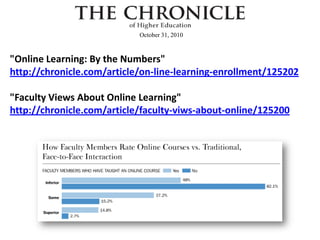
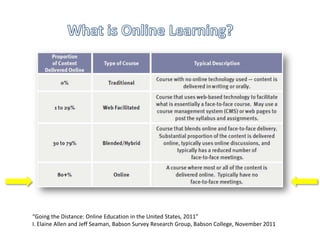
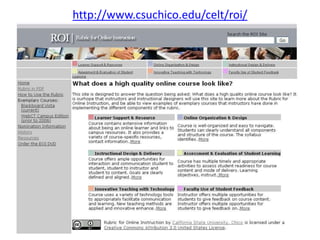
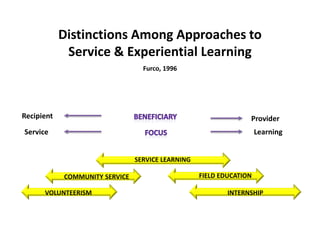
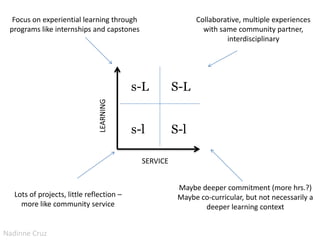
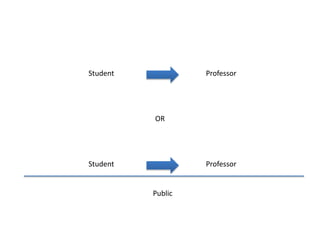
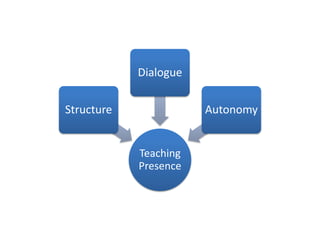
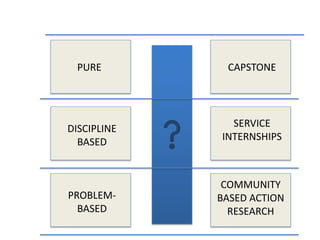
The document discusses the growth and significance of online education, highlighting a 10% increase in online enrollments with 31% of higher education students taking at least one course online. It emphasizes the effectiveness of blended learning and the importance of service learning in educational contexts, suggesting a shift from traditional service models to more collaborative and community-focused approaches. The document also outlines principles for good practice in undergraduate education and encourages innovative strategies in teaching and learning.